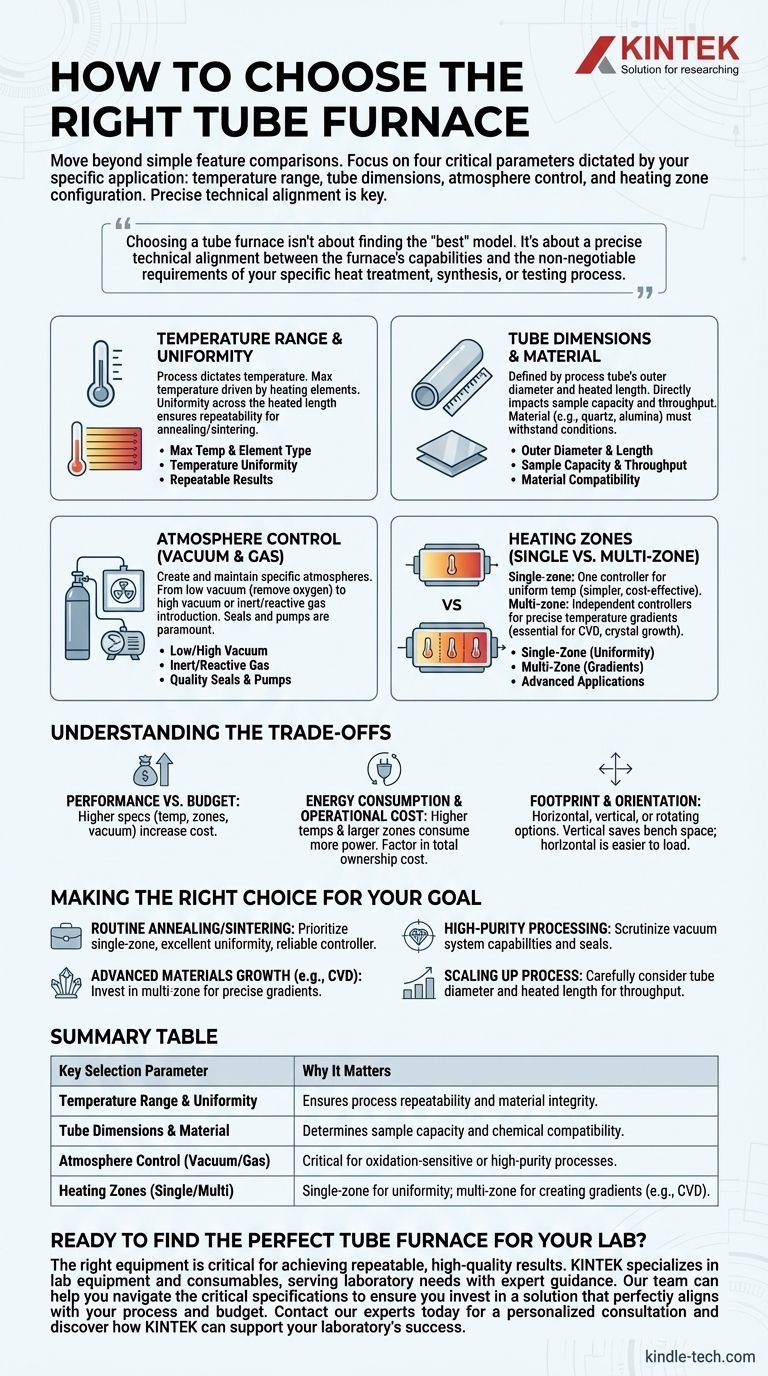
To choose the right tube furnace, you must move beyond a simple feature comparison and instead focus on four critical parameters dictated by your specific application: the required temperature range, the necessary tube dimensions, the level of atmosphere control (vacuum or gas), and the heating zone configuration (single or multi-zone). Matching these specifications to your scientific or industrial process is the most important step in making a sound investment.
Choosing a tube furnace isn't about finding the "best" model on the market. It's about a precise technical alignment between the furnace's capabilities and the non-negotiable requirements of your specific heat treatment, synthesis, or testing process.
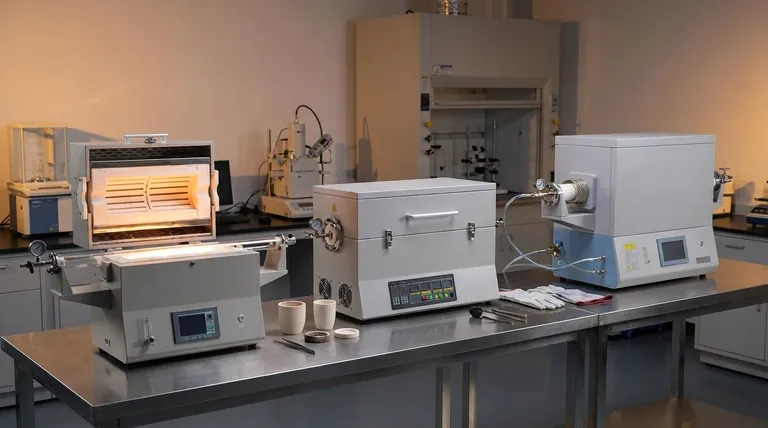

Deconstructing the Core Specifications
The function of a tube furnace is straightforward: to provide a controlled, high-temperature environment for processing samples within a tube. However, the details of how it achieves this are what separate one furnace from another.
Temperature Range and Uniformity
Your process dictates your required temperature. A furnace's maximum operating temperature is a primary specification, driven by the type of heating elements used.
Equally important is temperature uniformity, which is the consistency of temperature across the heated length of the tube. A uniform hot zone ensures that your entire sample experiences the same thermal conditions, critical for repeatable results in annealing and sintering.
Tube Dimensions and Material
Tube furnaces are defined by the dimensions of the process tube they can accommodate, typically specified by outer diameter and heated length.
These dimensions directly impact your sample capacity and throughput. A larger diameter allows for bigger samples or batches, while a longer heated zone can increase processing volume. The tube material itself (e.g., quartz, alumina, silicon carbide) is also a critical choice, as it must withstand your target temperature and chemical atmosphere without reacting.
Atmosphere Control (Vacuum and Gas)
Many modern processes cannot be performed in ambient air. Your furnace must be able to create and maintain the specific atmosphere your process requires.
This can range from a low vacuum to remove oxygen, to a high vacuum for high-purity applications, or the introduction of a specific inert or reactive gas. The quality of the seals and the capability of the vacuum pump and gas delivery system are paramount here.
Heating Zones (Single vs. Multi-Zone)
A single-zone furnace has one controller and aims to create one uniform temperature zone. It is simpler and more cost-effective for processes like basic heat treatment.
A multi-zone furnace (typically three zones) has independent controllers for different sections of the heating element. This allows you to create a precise temperature gradient across the tube, which is essential for advanced applications like chemical vapor deposition (CVD) and crystal growth.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a tube furnace involves balancing capabilities with practical constraints. Being aware of these trade-offs is key to making an objective decision.
Performance vs. Budget
Higher performance specifications invariably increase cost. A furnace with a maximum temperature of 1700°C will be significantly more expensive than one rated for 1200°C. Similarly, multi-zone control, high-vacuum compatibility, and advanced programming features all add to the initial investment.
Energy Consumption and Operational Cost
While many tube furnaces are designed for thermal efficiency, higher temperatures and larger hot zones consume more power. When calculating the total cost of ownership, factor in the ongoing energy costs, especially for continuous or long-duration processes.
Footprint and Orientation
Tube furnaces are available in horizontal, vertical, or rotating configurations. A vertical furnace can save bench space and may be ideal for certain crystal growth or drop-down sample processes. A horizontal furnace is the most common and is generally easier to load. The physical space and workflow of your lab will influence this choice.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Base your final decision on a clear-eyed assessment of your primary application. Do not over-specify for capabilities you will never use, but do not compromise on features that are critical for your results.
- If your primary focus is routine annealing or sintering: Prioritize a single-zone furnace with excellent temperature uniformity and a reliable controller.
- If your primary focus is advanced materials growth (e.g., CVD): Invest in a multi-zone furnace to achieve the precise temperature gradients your process requires.
- If your primary focus is high-purity processing: Scrutinize the vacuum system's capabilities, leak rate, and the quality of the end seals.
- If your primary focus is scaling up a process: Carefully consider the tube diameter and heated length to ensure the furnace meets your throughput requirements.
Ultimately, a methodical evaluation of your process needs is the only reliable path to selecting the correct furnace.
Summary Table:
| Key Selection Parameter | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| Temperature Range & Uniformity | Ensures process repeatability and material integrity. |
| Tube Dimensions & Material | Determines sample capacity and chemical compatibility. |
| Atmosphere Control (Vacuum/Gas) | Critical for oxidation-sensitive or high-purity processes. |
| Heating Zones (Single/Multi) | Single-zone for uniformity; multi-zone for creating gradients (e.g., CVD). |
Ready to find the perfect tube furnace for your lab?
The right equipment is critical for achieving repeatable, high-quality results in heat treatment, synthesis, and materials testing. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs with expert guidance.
Our team can help you navigate the critical specifications—temperature, tube size, atmosphere control, and heating zones—to ensure you invest in a solution that perfectly aligns with your process and budget.
Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory's success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What specific capabilities must laboratory tube furnaces or muffle furnaces possess? Precision for 300 K to 600 K Heat
- What is the role of vacuum annealing in a tube furnace for Cr-Al-C coatings? Optimize Phase Transformation Safely
- What is the temperature of rapid thermal annealing? Mastering High-Temp, Short-Duration Processing
- What protections do high vacuum tube furnaces offer for DMR? Ensure Precise Atmosphere Control & Catalyst Purity
- What are the advantages of using U-shaped quartz reactors? Boost Accuracy in CO2 Hydrogenation & Kinetic Studies
- Why is a quartz glass tube selected for plastic pyrolysis corrosion experiments? Ensure Pure, Unbiased Results
- Does pyrolysis produce biogas? Discover the Syngas Difference for Your Lab
- What is the purpose of treating metal precursors in a high-temperature tube furnace under a hydrogen atmosphere?



















