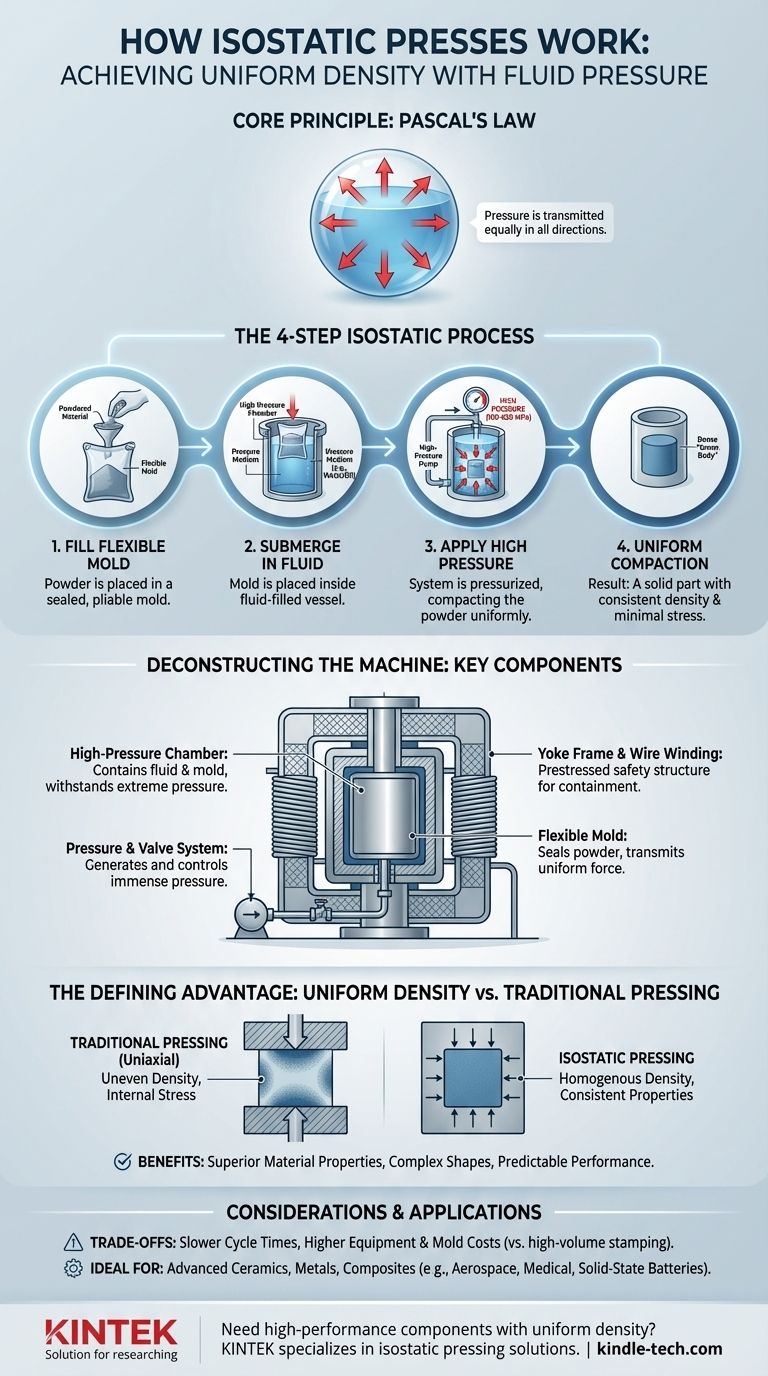
In essence, an isostatic press works by submerging a material, typically a powder, sealed in a flexible mold into a fluid-filled high-pressure chamber. A pumping system then uniformly increases the fluid's pressure, which is transmitted equally from all directions onto the material, compacting it into a solid, dense object. This method, governed by Pascal's law, ensures that pressure is applied isostatically (uniformly from all sides) to create parts with consistent density and minimal internal stress.
Isostatic pressing is a manufacturing method that excels at creating highly uniform, dense components from powdered materials. By applying pressure equally from all directions using a liquid medium, it eliminates the density variations and internal stresses common in traditional pressing, making it ideal for advanced materials and complex geometries.

The Core Principle: Pascal's Law in Action
The entire function of an isostatic press is a practical application of a fundamental principle of fluid mechanics. It leverages a liquid to transmit force in a way that rigid mechanical dies cannot.
The Process Step-by-Step
First, the powdered material (like a ceramic or metal powder) is placed into a flexible, sealed mold, often made of rubber or plastic. This sealed mold is then submerged in a liquid, such as water or oil, inside a high-pressure vessel. The system is sealed, and a high-pressure pump pressurizes the liquid, compacting the powder within the mold.
The Role of the Flexible Mold
The flexible mold is critical. It acts as a barrier to keep the powder dry and contained while being pliable enough to perfectly transmit the hydraulic pressure from the fluid to the powder. This ensures the compacting force is applied evenly to every surface of the part.
The Pressure Medium
The liquid acts as a perfect transmitter of pressure. When the pump increases the pressure on the fluid, that pressure is distributed instantly and equally to all points within the chamber, ensuring there are no pressure shadows or gradients on the part being formed.
Deconstructing the Machine: Key Components
While the principle is simple, the hardware required to contain extreme pressures is highly specialized and engineered for safety and longevity.
The High-Pressure Chamber
This is the core vessel where the mold is placed and pressurized. It is built to withstand immense forces, with pressures often ranging from 100 to 630 MPa (megapascals) in cold isostatic pressing systems.
The Yoke Frame and Wire Winding
To ensure safety, modern presses use a prestressed structure. A yoke frame contains the chamber, and both components are often wrapped with high-strength steel wire. This design puts the core components under compression, meaning they can handle extreme internal pressure without risk of catastrophic failure.
The Pressure and Valve System
A specialized superhigh pressure pump and valve system generates and controls the immense pressure. Modern designs often separate the valve body from the valve seat, a patented technology that significantly reduces failure rates and simplifies maintenance. In many systems, the only routine wearing part is a simple seal ring.
The Defining Advantage: Achieving Uniform Density
The primary reason to use an isostatic press is to achieve material properties that other methods cannot. The results are superior density, structure, and performance.
Eliminating Density Gradients
In traditional uniaxial pressing (pushing from the top and bottom), friction from the die walls causes the powder to compact unevenly. The areas nearest the punch are densest, while the center and edges are less so. Isostatic pressing eliminates this issue, creating a homogenous "green body" (un-sintered part) with uniform density throughout.
Improved Material Properties
This uniform density directly translates to superior and more predictable final properties after sintering (firing). The part will have more consistent strength, a finer microstructure, and improved overall performance, which is critical for high-performance ceramics, metals, and composites.
Versatility in Materials and Applications
This method is used for a wide range of advanced materials. It is essential in producing solid-state batteries, garnet-based solid electrolytes, and complex ceramic components for the aerospace and medical industries.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, isostatic pressing is not the solution for every manufacturing scenario. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Cycle Times
The process of filling, sealing, pressurizing, depressurizing, and unloading is inherently slower than simple mechanical stamping. It is therefore not typically suited for very high-volume, low-cost production of simple parts.
Tooling and Mold Costs
While simpler than hard tooling, the flexible molds have a finite lifespan and can be complex to design and manufacture for intricate parts. The main wearing component is the seal, but the molds themselves are a recurring operational cost.
Equipment Cost and Complexity
Isostatic presses are sophisticated, high-pressure systems. The upfront capital investment is significant, and they require a clean, controlled environment and trained personnel for safe operation and maintenance.
Is Isostatic Pressing Right for Your Application?
Choosing this technology depends entirely on your material, the geometry of your part, and your final performance requirements.
- If your primary focus is maximum density and material integrity: Isostatic pressing is the superior choice for creating mission-critical components with homogenous, predictable properties.
- If your primary focus is producing complex shapes: This method allows for the creation of parts with undercuts, internal cavities, and complex curvatures that are impossible with rigid dies.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of simple shapes: Traditional uniaxial or die compaction is almost always a faster and more cost-effective solution.
Understanding this core principle empowers you to select the right consolidation technology for your specific material and performance goals.
Summary Table:
| Key Component | Function |
|---|---|
| High-Pressure Chamber | Contains the fluid and mold, built to withstand extreme pressures (100-630 MPa). |
| Flexible Mold | Seals the powder and transmits uniform hydraulic pressure to the material. |
| Pressure System | Pump and valves that generate and control the isostatic pressure. |
| Yoke Frame & Wire Winding | Prestressed safety structure to contain the high-pressure forces. |
Need to create high-performance components with uniform density? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, including isostatic presses that deliver superior material integrity for ceramics, metals, and composites. Our expertise ensures your laboratory achieves consistent, dense parts with minimal internal stress. Contact us today to discuss how our isostatic pressing solutions can meet your advanced material needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine for Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Manual Cold Isostatic Pressing Machine CIP Pellet Press
- Warm Isostatic Press for Solid State Battery Research
- Automatic Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
People Also Ask
- What temperature is cold isostatic pressing? A Guide to Room-Temperature Powder Compaction
- Is isostatic pressing expensive? Achieve Superior Material Uniformity & Complex Shapes
- Why is cold isostatic pressing applied following steel mold dry pressing in 8YSZ? Enhance Density and Crack Prevention
- What will happen if forging is carried out at very low temperature? Discover the Power of Cold Forging
- What is uniaxial pressing and isostatic pressing? Choosing the Right Powder Compaction Method
- What is isostatic presses used for? Achieve Uniform Density and Superior Material Performance
- Why is a Cold Isostatic Press (CIP) used for copper composite powders? Enhance Sintering Efficiency and Density
- How does isostatic pressing work? Achieve Perfectly Uniform Density for Complex Parts



















