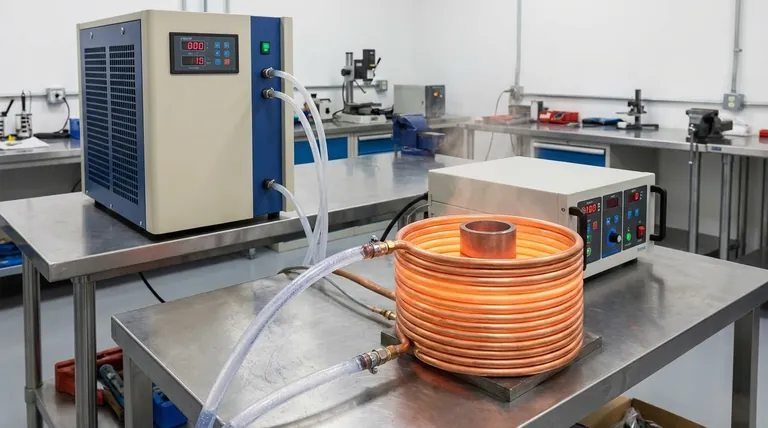
At its core, an induction coil is cooled by circulating a fluid, most commonly water, directly through the hollow copper tubing from which the coil is constructed. For lower-power applications, forced air may be sufficient, but direct fluid cooling is the industry standard for managing the intense heat generated during operation.
The method used to cool an induction coil is not merely a maintenance task; it is a fundamental design choice that dictates the system's efficiency, reliability, and operational lifespan. Improper cooling is the single most common cause of coil failure and inconsistent heating performance.

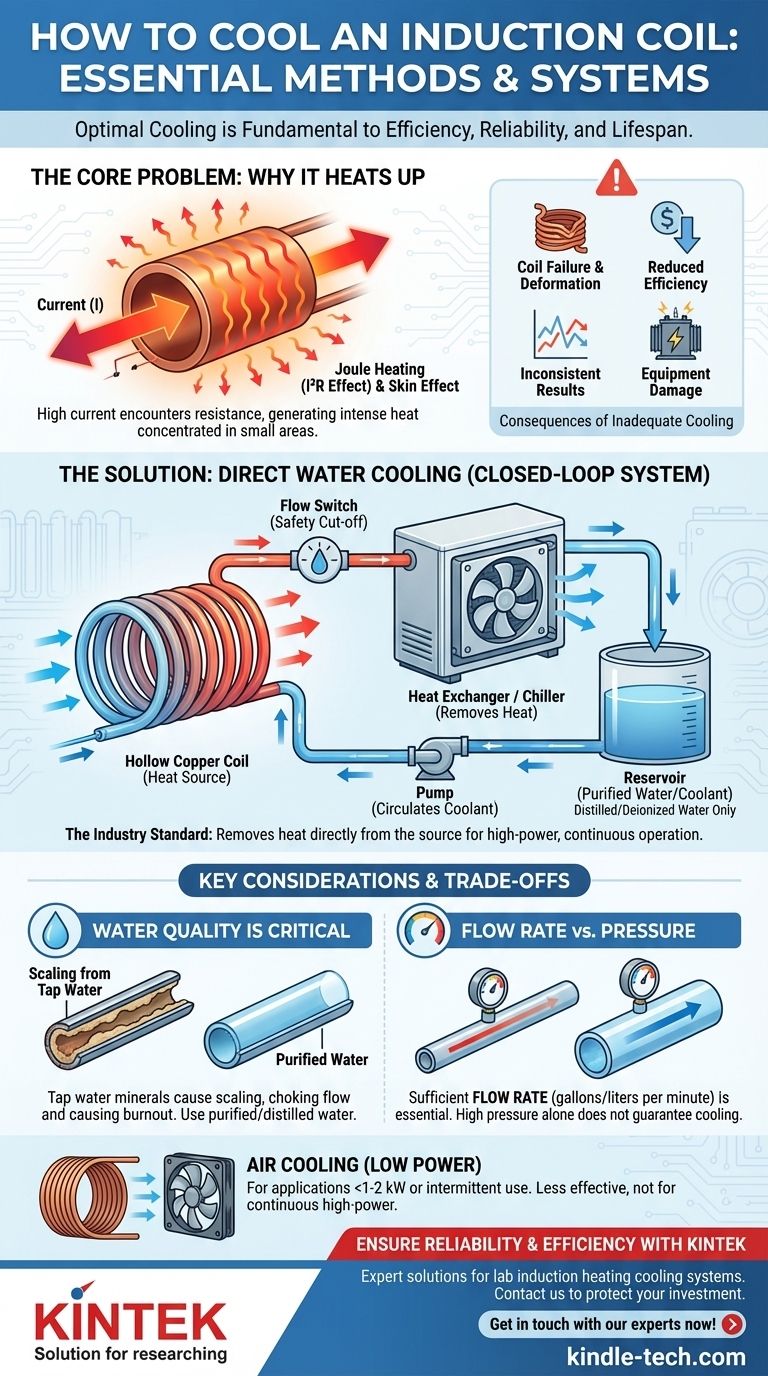
Why Cooling is Non-Negotiable
To select the right cooling method, you must first understand why a coil, which is designed to heat another object, gets hot itself. The heat is a byproduct of the very physics that make induction work.
The Source of the Heat
The primary source of heat in the coil is electrical resistance. Even though copper is an excellent conductor, it isn't perfect. The massive electrical currents—often hundreds or thousands of amperes—flowing through the coil encounter this slight resistance.
This generates significant heat due to the I²R effect, also known as Joule heating. The skin effect and proximity effect, which are fundamental to induction, further concentrate this current into smaller areas of the copper, intensifying the heating.
Consequences of Inadequate Cooling
Failing to remove this heat effectively leads to a cascade of problems, ranging from reduced performance to catastrophic failure.
-
Coil Failure: As copper heats up, it anneals and softens. This can cause the coil to deform under magnetic forces or simply melt, resulting in a short circuit or an open circuit.
-
Reduced Efficiency: The electrical resistance of copper increases with temperature. A hotter coil means more of your expensive electricity is wasted heating the coil itself, rather than being transferred to your workpiece.
-
Inconsistent Results: A change in coil temperature alters its electrical properties. This can shift the system's resonant frequency and affect the power draw, leading to inconsistent heating cycles and poor quality control.
-
Equipment Damage: An overheating coil can damage its own insulation, support structures, and the transformer or output connections of the induction power supply.
Primary Cooling Methods
The choice of cooling method is directly tied to the power density and duty cycle of your application.
Direct Water Cooling (The Industry Standard)
For any serious industrial or high-power application, direct water cooling is the only viable method. The coil is fabricated from hollow copper tubing, and a coolant is actively pumped through it.
This technique is extremely effective because it removes heat from the inside out, directly at the source. It keeps the copper well below its annealing temperature, ensuring structural integrity and stable electrical performance.
Coolant System Design
The system that supplies the water is just as important as the coil itself.
-
Open-Loop Systems: These use a continuous supply of fresh water from a tap or well, which is then discarded. While simple and cheap initially, they are highly discouraged for professional use due to the risk of mineral deposits (scaling) and corrosion.
-
Closed-Loop Systems: This is the professional standard. A dedicated reservoir of clean coolant is circulated through the coil and then cooled via a heat exchanger or a refrigerated chiller. This provides precise temperature control and allows the use of purified water.
-
Coolant Fluid: In a closed-loop system, you can use distilled or deionized water to prevent mineral buildup. Additives like propylene glycol can be mixed in for freeze protection and biocides to prevent algae growth.
Air Cooling (For Low-Power Applications)
For very low-power systems (typically under 1-2 kW) or applications with a very low duty cycle, forced air from fans may be sufficient. The coil is built from solid copper wire or tubing, and air is blown across its surface.
This method is far less effective than liquid cooling and is not suitable for situations requiring high power density or continuous operation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
A reliable cooling system requires careful attention to detail. Ignoring these factors is a common and costly mistake.
Water Quality is Critical
Using untreated tap water in an induction coil is a recipe for failure. Dissolved minerals, like calcium and magnesium, will precipitate out of the water as it's heated, forming a hard, insulating layer of scale on the inside of the coil.
This scale chokes coolant flow and prevents heat transfer, creating hotspots that lead to a rapid burn-out. A closed-loop system using purified water completely avoids this problem.
Flow Rate vs. Pressure
High pressure does not guarantee proper cooling; flow rate does. You must have a sufficient volume of water (measured in gallons or liters per minute) moving through the coil to carry the heat away.
A partially blocked coil can show high pressure at the inlet but have a dangerously low flow rate. For this reason, all professional induction systems should include a flow switch that shuts down the power supply if the coolant flow drops below a safe minimum.
Cost vs. Reliability
An open-loop system is cheap to set up but exposes your expensive power supply and coil to constant risk from contamination and scaling. The maintenance and downtime costs will quickly surpass any initial savings.
A closed-loop chiller system has a higher upfront cost but protects your entire investment. It provides the stability, reliability, and process control required for any serious manufacturing or research environment.
Selecting the Right Cooling Strategy
Your choice should be guided by the demands of your application and your tolerance for risk.
-
If your primary focus is hobbyist work or intermittent lab experiments: Air cooling might be acceptable for very low power, but a simple pump and a radiator with treated water is a far more robust starting point.
-
If your primary focus is industrial production or high-power research: A closed-loop, temperature-controlled chiller system using purified water is the only professional choice to ensure reliability, efficiency, and process consistency.
-
If you are experiencing frequent coil failures: Immediately investigate your cooling system for signs of scaling, low flow rate, or incorrect coolant temperature before running the system again.
Ultimately, viewing your cooling system as an integral part of the induction machine, rather than an accessory, is the key to building a powerful and reliable process.
Summary Table:
| Cooling Method | Best For | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Direct Water Cooling | Industrial production, high-power applications | Requires purified water, closed-loop system, and adequate flow rate |
| Air Cooling | Low-power (<1-2 kW), intermittent use | Limited effectiveness; not suitable for continuous operation |
Ensure your induction heating process is reliable and efficient. Inadequate cooling is the leading cause of coil failure and inconsistent results. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs with robust solutions for induction heating systems. Our experts can help you select or design the right cooling system—whether a simple closed-loop setup or a full chiller system—to protect your investment and guarantee performance. Contact us today to discuss your application and get a solution tailored to your lab's requirements.
Get in touch with our experts now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 100L Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Circulator for Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction Bath Water Bath Cooling
- 80L Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Circulator for Water Bath Cooling and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction Bath
- 5L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
- 20L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
- 50L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a Vacuum Induction Furnace in RAFM steel? Ensure High Purity for Reactive Elements Y & Ti
- What are the basics of induction melting? A Guide to Fast, Clean Metal Processing
- Which metals can be heated using induction? Discover the best metals for efficient induction heating.
- What is the structural composition of an induction furnace body? Expert Guide to Its 4-Layer Design
- Where is induction furnace used? Unlock Precision Heating for Metals & Alloys
- How does magnetic field heat metal? Achieve Precise Thermal Control with Induction Heating
- What are the benefits of using an induction heating source for the direct conversion of methane into hydrogen?
- What is the highest temperature for an induction furnace? Unlocking 2000°C for High-Purity Melting



















