The primary methods for melting metal in a vacuum are Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) and Vacuum Arc Remelting (VAR). These processes use a vacuum chamber to remove air and other gases before and during melting, which prevents the molten metal from reacting with oxygen and nitrogen. This environment also pulls dissolved gases and impurities out of the metal itself, resulting in a cleaner, stronger, and more reliable final product.
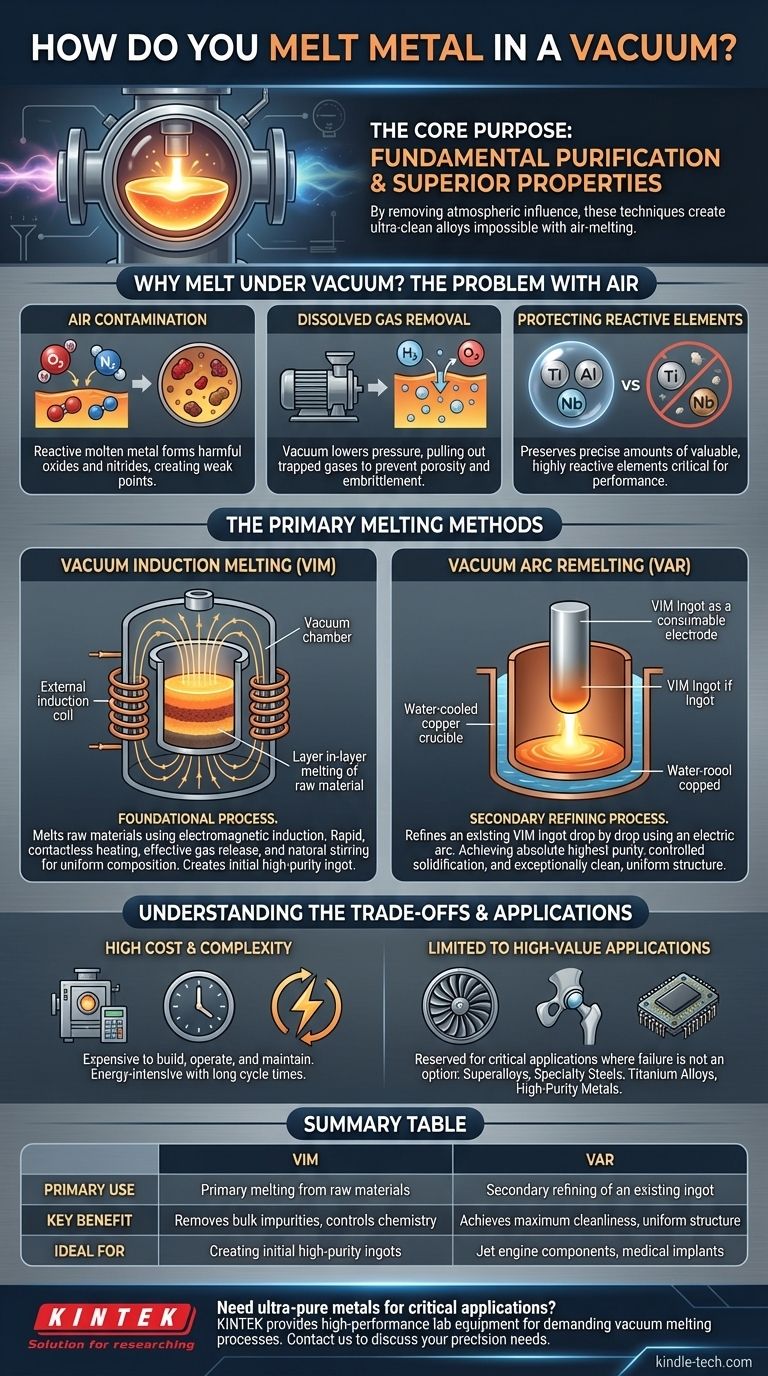
The core purpose of melting metal in a vacuum is not simply to liquefy it, but to fundamentally purify it. By removing the influence of atmospheric gases, these techniques create ultra-clean alloys with superior properties that are impossible to achieve with conventional air-melting methods.

Why Melt Metal Under Vacuum?
Before detailing the methods, it's critical to understand why this complex process is necessary. Melting metal in the open air introduces significant problems that a vacuum environment is specifically designed to solve.
The Problem with Air Contamination
When metal is molten, it is highly reactive. The oxygen and nitrogen in the air readily dissolve into the liquid metal or react with it to form non-metallic inclusions like oxides and nitrides. These impurities become trapped in the material as it solidifies, creating microscopic weak points that can lead to cracks and premature failure under stress.
Removing Dissolved Gases
Raw materials often contain dissolved gases like hydrogen and oxygen. A vacuum drastically lowers the pressure above the molten metal, creating a powerful driving force that pulls these trapped gases out of the solution. This is similar to how a bottle of soda fizzes when opened—the lower external pressure allows the dissolved CO₂ to escape. Removing these gases prevents porosity (gas bubbles) and embrittlement in the final product.
Protecting Reactive Elements
Many high-performance alloys rely on precise amounts of highly reactive elements like titanium, aluminum, and niobium. In an air-melt, these valuable elements would quickly oxidize and be lost as slag. A vacuum protects them, ensuring the final alloy has the exact chemical composition and properties it was designed for.
The Primary Melting Methods
While there are variations, the two dominant industrial processes for vacuum melting serve distinct purposes: primary melting and secondary refining.
Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM)
VIM is the foundational process used to melt raw materials and create an initial, high-purity ingot. The metal charge is placed in a crucible inside a vacuum chamber. An induction coil surrounds the crucible, and an electric current passed through it creates a powerful electromagnetic field.
This field induces eddy currents within the metal itself, causing it to heat up and melt rapidly without any direct contact from a heating element. As the reference material notes, the initial melting happens layer by layer, which is highly effective at releasing trapped gases. The electromagnetic field also naturally stirs the molten bath, promoting a uniform temperature and chemical composition.
Vacuum Arc Remelting (VAR)
VAR is a secondary refining process used to achieve the absolute highest level of purity and structural integrity. It does not start with raw materials; instead, it refines an existing ingot, often one already produced by the VIM process.
In VAR, the VIM-produced ingot is used as a large consumable electrode. This electrode is suspended inside a water-cooled copper crucible within a vacuum chamber. A high-current electric arc is struck between the bottom of the electrode and a small amount of starter material in the crucible. The intense heat of the arc melts the tip of the electrode, and the metal falls drop by drop into the crucible below, solidifying in a highly controlled, progressive manner. This second melting cycle further removes impurities and results in an exceptionally clean and uniform internal structure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Vacuum melting offers unparalleled quality, but this performance comes with significant considerations.
High Cost and Complexity
Vacuum furnaces are expensive to build, operate, and maintain. The process is energy-intensive, and cycle times are much longer than for conventional melting due to the time required to pump down the chamber to the required vacuum level.
Limited to High-Value Applications
Because of the high cost, VIM and VAR are reserved for applications where material failure is not an option. This includes superalloys for jet engine turbine blades, specialty steels for aerospace structures, titanium alloys for medical implants, and high-purity metals for the electronics industry. It is not used for common materials like structural steel or cast iron.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The choice between these processes depends entirely on the required material quality and the starting material.
- If your primary focus is creating a high-purity alloy from raw materials: VIM is the essential first step to remove bulk impurities and control the chemistry.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum cleanliness and a defect-free grain structure: VAR is the necessary secondary process used to refine a previously melted VIM ingot.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, cost-effective production for general use: Neither process is suitable; conventional air melting is the industry standard.
Ultimately, vacuum melting is a strategic tool for engineering materials where absolute purity and performance are non-negotiable.
Summary Table:
| Method | Primary Use | Key Benefit | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) | Primary melting from raw materials | Removes bulk impurities, controls chemistry | Creating initial high-purity ingots |
| Vacuum Arc Remelting (VAR) | Secondary refining of an existing ingot | Achieves maximum cleanliness, uniform structure | Jet engine components, medical implants |
Need to source or develop ultra-pure metals for your critical applications? The advanced techniques of vacuum melting are essential for achieving the material integrity required in aerospace, medical, and electronics industries. KINTEK specializes in providing the high-performance lab equipment and consumables needed for these demanding processes. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's mission for precision and reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the vacuum induction method? Master High-Purity Metal Melting for Advanced Alloys
- What is the primary function of a vacuum induction melting furnace? Melt High-Purity Metals with Precision
- What is VIM in metallurgy? A Guide to Vacuum Induction Melting for High-Performance Alloys
- What is vacuum arc melting technique? Discover the Precision of Vacuum Induction Melting
- What principle is used to generate heat in a vacuum induction melting furnace? Achieve Clean, Efficient Metal Melting



















