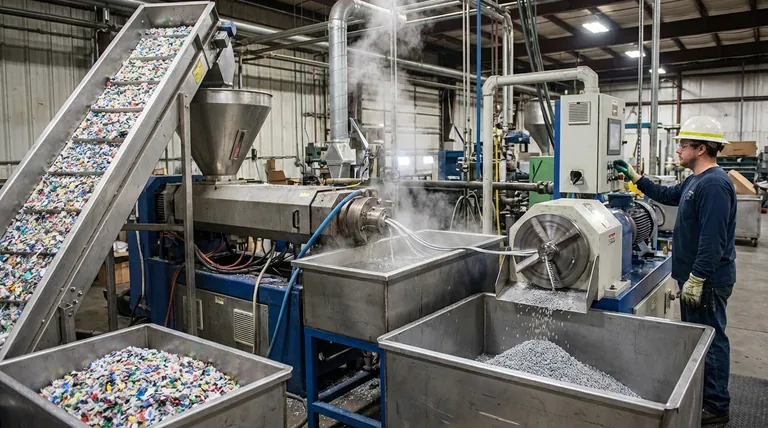
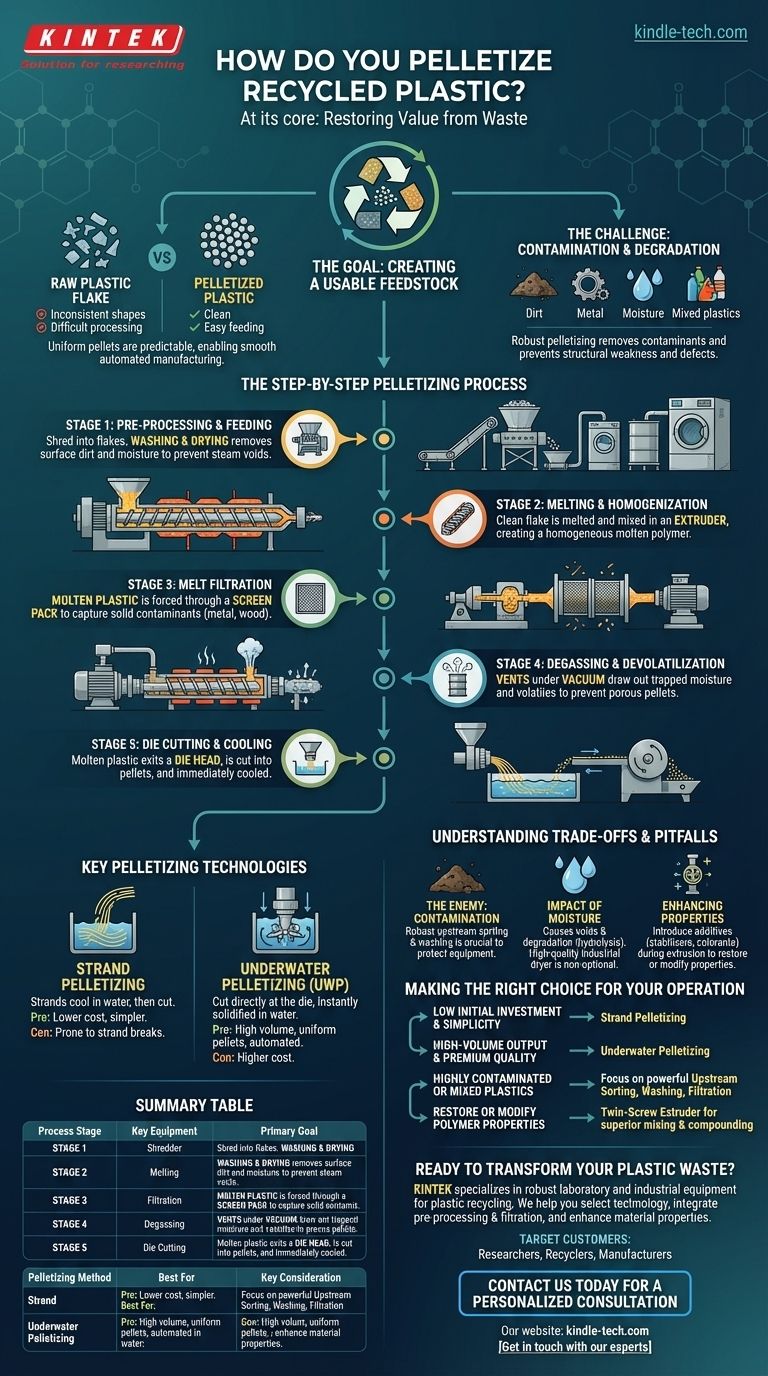
At its core, pelletizing recycled plastic is a process of re-melting, filtering, and reforming plastic waste into uniform granules, or pellets. This is accomplished using a machine called an extruder, which melts the plastic, forces it through a filtration system to remove contaminants, and then pushes the purified molten plastic through a die. A cutting system then chops the emerging plastic strands into small, consistent pellets ready for reuse in manufacturing.
The fundamental goal of pelletizing is not just to chop up plastic, but to restore value by creating a clean, consistent, and predictable raw material from a highly variable and often contaminated waste stream. Success hinges on purification and homogenization.

Why Pelletizing is a Critical Recycling Step
The Goal: Creating a Usable Feedstock
Manufacturers need raw materials that are predictable and easy to process. Raw, shredded plastic flake is often inconsistent in size, shape, and purity, making it difficult to feed into manufacturing equipment like injection molders.
Pellets, by contrast, are uniform. Their consistent size and density allow for predictable melting behavior and smooth, automated feeding, making them a direct substitute for virgin plastic resins.
The Challenge: Contamination and Degradation
Recycled plastic is never perfectly clean. It contains non-plastic contaminants like paper, metal, and dirt, as well as moisture and different types of incompatible plastics.
Without a robust pelletizing process, these contaminants would end up in the final product, causing structural weaknesses, cosmetic defects, and equipment damage. The heat required for processing can also further degrade the plastic if not managed correctly.
The Step-by-Step Pelletizing Process
Stage 1: Pre-Processing and Feeding
Before plastic even enters the pelletizer, it must be prepared. This usually involves shredding it into smaller, manageable flakes.
Following shredding, a crucial washing and drying phase removes surface dirt, labels, and residual liquids. Inadequate drying is a primary cause of poor pellet quality, as trapped moisture will turn to steam and create voids in the final product.
Stage 2: Melting and Homogenization
The clean, dry flake is fed into an extruder. Inside the extruder, a rotating screw conveys the plastic through a series of heated zones.
This process melts the plastic and uses the screw's shearing action to mix it thoroughly, creating a homogenous molten polymer. This ensures that any variations in the source material are blended together for a more consistent output.
Stage 3: Melt Filtration
This is arguably the most critical stage for recycled materials. The molten plastic is forced through a fine screen pack or filter.
This melt filtration step physically captures solid contaminants that were not removed during washing, such as bits of metal, wood, or unmelted materials. Advanced systems use continuous screen changers that allow for filter replacement without shutting down the entire line.
Stage 4: Degassing and Devolatilization
Many plastics, especially those that were not perfectly dried, will release trapped moisture and other volatile compounds when melted.
The extruder is typically equipped with vents (often under vacuum) to draw out these gases. This degassing step is essential for preventing porous, foamy pellets and improving the overall density and structural integrity of the plastic.
Stage 5: Die Cutting and Cooling
After being filtered and degassed, the clean molten plastic is pushed through a die head, forming continuous strands. A cutting system then chops these strands into pellets.
The pellets are immediately cooled, typically with water or air, which solidifies them into their final form. The two primary methods for this are strand pelletizing and underwater pelletizing.
Key Pelletizing Technologies
Strand Pelletizing
In this method, the plastic strands exit the die and are pulled through a water bath to cool, much like spaghetti. A rotating cutter at the end of the line then chops the solidified strands into pellets.
This system is mechanically simpler and generally has a lower initial investment cost. However, it can be prone to strand breaks, which require operator intervention and can lead to downtime.
Underwater Pelletizing (UWP)
Here, the die head is in direct contact with a flow of water. As the molten plastic exits the die, a set of rotating blades immediately cuts it into pellets, which are instantly solidified and conveyed away by the water.
UWP systems are highly automated, produce more uniform spherical pellets, and eliminate the issue of strand breakage. They are the standard for high-volume, high-quality operations but come with a higher capital cost and complexity.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
The Enemy: Contamination
Even small amounts of contamination can ruin a batch of pellets or, worse, damage expensive equipment like the extruder screw or die. Investing in robust up-front sorting and washing is always more cost-effective than dealing with contamination downstream.
The Impact of Moisture
Moisture is a persistent challenge. In addition to causing voids in pellets, it can cause hydrolytic degradation in certain polymers like PET, permanently breaking down the plastic's molecular chains and reducing its strength. A high-quality industrial dryer is not an optional expense.
Enhancing Properties with Additives
The recycling process can degrade a plastic's original properties. Pelletizing provides the perfect opportunity to introduce additives directly into the extruder. These can include stabilizers to protect against further heat degradation, impact modifiers to increase toughness, or colorants.
Making the Right Choice for Your Operation
- If your primary focus is low initial investment and operational simplicity: Strand pelletizing is often the most cost-effective entry point for smaller-scale or less demanding applications.
- If your primary focus is high-volume output and premium pellet quality: An automated underwater pelletizing system will deliver superior consistency, higher uptime, and lower long-term labor costs.
- If you are processing highly contaminated or mixed plastics: Your success depends less on the cutting method and more on investing in powerful upstream sorting, washing, and melt filtration technologies.
- If you need to restore or modify polymer properties: A twin-screw extruder offers superior mixing capabilities, making it ideal for compounding with additives compared to a standard single-screw extruder.
Ultimately, successful plastic pelletizing transforms a problematic waste stream into a valuable and reliable industrial resource.
Summary Table:
| Process Stage | Key Equipment | Primary Goal |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-Processing | Shredder, Washer, Dryer | Clean and dry plastic flakes |
| Melting & Homogenization | Extruder (Single/Twin-Screw) | Create uniform molten plastic |
| Melt Filtration | Screen Changer/Filter | Remove contaminants |
| Degassing | Vented Extruder (Vacuum) | Remove moisture and volatiles |
| Pelletizing & Cooling | Die, Cutter, Water/Air Cooler | Form uniform, solid pellets |
| Pelletizing Method | Best For | Key Consideration |
| Strand Pelletizing | Lower volume, cost-sensitive operations | Prone to strand breaks, simpler mechanics |
| Underwater Pelletizing (UWP) | High-volume, high-quality output | Higher cost, superior pellet uniformity |
Ready to Transform Your Plastic Waste into a Valuable Resource?
KINTEK specializes in providing robust laboratory and industrial equipment for plastic recycling and pelletizing processes. Whether you are scaling up your operation or optimizing pellet quality, our expertise in extruders, filtration systems, and pelletizing technology can help you achieve consistent, high-value results.
We help you:
- Select the right pelletizing technology (Strand or Underwater) for your volume and quality requirements.
- Integrate efficient pre-processing (washing, drying) and melt filtration systems to maximize purity.
- Enhance material properties with compounding and additive integration solutions.
Target Customers: Laboratory researchers, plastic recyclers, and manufacturers seeking to improve the efficiency and quality of their recycled plastic pellets.
Contact us today to discuss your specific needs and discover how KINTEK's solutions can turn your plastic waste into a reliable, profitable raw material.
Get in touch with our experts for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Open Type Two Roll Mixing Mill Machine for Rubber Crusher
- Single Punch Tablet Press Machine and Mass Production Rotary Tablet Punching Machine for TDP
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
People Also Ask
- What is a two-roll differential speed mill? Achieve Superior Polymer Mixing & Dispersion
- What are the advantages of a two roll mill? Achieve Superior Polymer Mixing & Quality Control
- What is the difference between Banbury and internal mixer? Understanding Rotor Design for Better Mixing
- What is a two-high roll mill? Master Precise Material Compounding and Testing
- What is the use of two roll mill? Essential for Polymer Mixing, R&D, and Quality Control



















