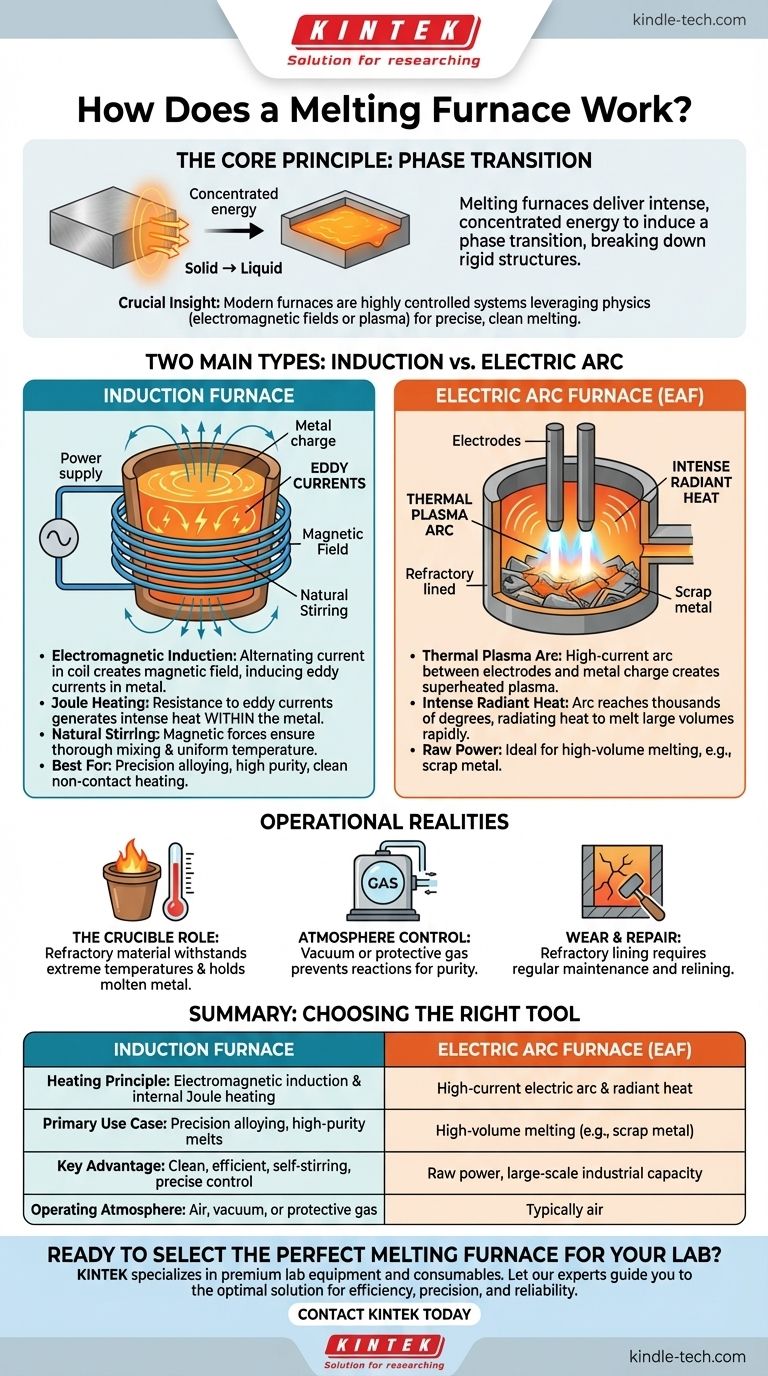
At its core, a melting furnace works by delivering intense, concentrated energy to a solid material until it undergoes a phase transition into a liquid state. While methods vary, the most common industrial furnaces use principles like electromagnetic induction or high-energy electric arcs to generate heat directly within the material, rather than simply applying it from an external flame.
The crucial insight is that modern melting furnaces are not just simple ovens. They are highly controlled systems that leverage fundamental physics—either electromagnetic fields or plasma arcs—to efficiently generate extreme heat inside the target material for precise and clean melting.

The Primary Goal: Inducing a Phase Transition
Every melting furnace, regardless of its design, is built to accomplish one primary task: to heat a material to its specific melting point.
### From Solid to Liquid
This process physically breaks down the rigid structure of a solid, allowing it to flow as a liquid. This liquid state is essential for processes like casting, alloying, and refining metals.
### Control is Paramount
Different materials have vastly different melting points. A successful furnace allows for precise temperature control to melt the target material without damaging the equipment or wasting energy.
How an Induction Furnace Generates Heat
Induction furnaces are a common and highly efficient type, known for their clean operation. They don't burn fuel; instead, they use electromagnetism to heat the metal from the inside out.
### The Core Components
An induction furnace consists of three main parts: a power supply that provides a high-frequency alternating current, a coil (the induction ring), and a crucible made of refractory material to hold the metal charge.
### The Principle: Electromagnetic Induction
An alternating current is sent through the copper coil, creating a rapidly reversing magnetic field. When conductive material like metal is placed inside this coil, the magnetic field induces powerful electrical currents, known as eddy currents, within the metal itself.
### The Mechanism: Joule Heating
These eddy currents flow against the metal's natural electrical resistance. This resistance converts the electrical energy directly into intense heat—a phenomenon called Joule heating. The heat is generated within the metal, making the process exceptionally fast and efficient.
### An Added Benefit: Natural Stirring
The same magnetic forces that create the eddy currents also cause the molten metal to stir. This self-stirring action ensures that alloys mix thoroughly and the temperature remains uniform throughout the liquid batch.
How an Electric Arc Furnace Uses Plasma
The electric arc furnace (EAF) represents a different approach, one that relies on raw power to generate immense heat.
### The Core Components
The primary component is a high-power source, similar to a massive electric welder, and large electrodes. The furnace itself is a refractory-lined vessel that contains the material to be melted.
### The Principle: A Self-Sustaining Arc
The furnace works by striking a high-current, low-voltage arc between the electrodes and the metal charge. This arc is a thermal plasma—a channel of superheated, ionized gas with an extremely high temperature.
### The Mechanism: Intense Radiant Heat
The arc itself reaches temperatures of thousands of degrees. This intense heat radiates to the material in the furnace, rapidly melting it. The process is powerful enough to melt large volumes of scrap metal and other materials.
Understanding the Operational Realities
Operating a melting furnace involves more than just turning it on. The extreme environment requires specialized components and careful maintenance.
### The Critical Role of the Crucible
The crucible is the container that holds the molten metal. It must be made from refractory materials, like quartz sand, that can withstand extreme temperatures without melting, cracking, or reacting with the liquid metal.
### The Need for Atmosphere Control
Some advanced processes require melting under specific conditions. A vacuum induction furnace, for example, operates under a vacuum or a protective atmosphere to prevent the molten metal from reacting with oxygen or other gases.
### Inevitable Wear and Repair
The harsh conditions cause uniform erosion and cracks in the furnace's refractory lining. Maintenance involves scraping away damaged areas and relining the furnace, often with a specialized quartz sand mixture that is compacted and heated to form a new, durable surface.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
- If your primary focus is alloy precision and purity: An induction furnace is the superior choice due to its clean, non-contact heating and self-stirring properties.
- If your primary focus is high-volume melting of raw materials like scrap: An electric arc furnace provides the raw power and scale necessary for large industrial foundry operations.
Understanding the underlying mechanism of each furnace is the key to selecting the right tool for the job.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Induction Furnace | Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Principle | Electromagnetic induction & internal Joule heating | High-current electric arc & radiant heat |
| Primary Use Case | Precision alloying, high-purity melts | High-volume melting (e.g., scrap metal) |
| Key Advantage | Clean, efficient, self-stirring, precise temperature control | Raw power, large-scale industrial capacity |
| Operating Atmosphere | Air, vacuum, or protective gas | Typically air |
Ready to Select the Perfect Melting Furnace for Your Lab?
Understanding the core technology is the first step. The next is choosing the right equipment to achieve your specific goals in metal processing, alloy development, or material research.
KINTEK specializes in premium lab equipment and consumables, serving the precise needs of laboratories. We can help you navigate the choice between induction furnaces for unparalleled purity and control, or arc furnaces for high-volume throughput.
Let our experts guide you to the optimal solution for efficiency, precision, and reliability. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your application and receive a personalized recommendation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is vacuum arc melting technique? Discover the Precision of Vacuum Induction Melting
- How does induction work in a vacuum? Achieve Ultra-Pure Metal Melting with VIM
- What is the difference between induction melting and vacuum induction melting? Choosing the Right Process for Purity
- What principle is used to generate heat in a vacuum induction melting furnace? Achieve Clean, Efficient Metal Melting
- What is VIM in metallurgy? A Guide to Vacuum Induction Melting for High-Performance Alloys



















