At its core, a PVD chamber is a high-vacuum environment where a solid material is vaporized, transported, and then condensed atom-by-atom onto a component's surface to form a high-performance thin film. The entire process hinges on creating a nearly perfect vacuum, which allows for the precise, line-of-sight travel of vapor particles from a source material (the "target") to the part being coated (the "substrate"). This process can be broken down into three or four key stages: Vaporization, Transportation, an optional Reaction, and finally, Deposition.
The fundamental purpose of a PV D chamber is not just to hold the parts, but to create an extremely pure, controlled environment. The high vacuum is the single most critical factor, as it eliminates atmospheric contaminants and allows vaporized atoms to travel unimpeded from the source to the substrate, ensuring a dense and pure coating.
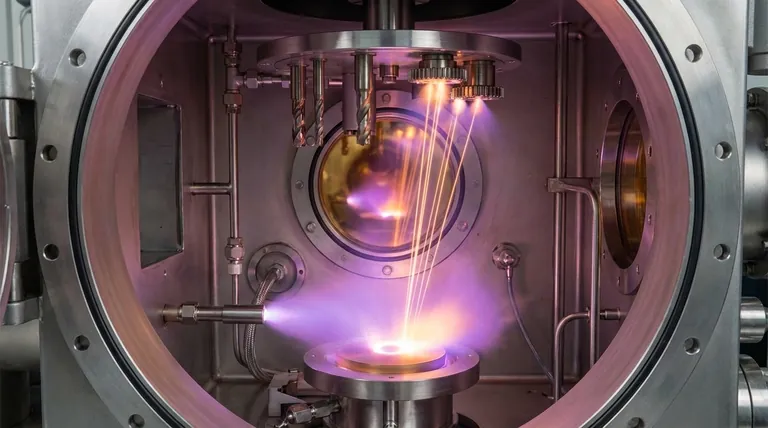
The Core Principle: Creating a Contaminant-Free Pathway
To understand how a PVD chamber works, you must first understand why it is a vacuum chamber. The entire process relies on creating an atomically clean environment.
The Role of the Vacuum
The chamber is sealed and powerful pumps remove nearly all the air, reducing the internal pressure to a fraction of a billionth of normal atmospheric pressure. This process removes gases like oxygen, nitrogen, and water vapor that would otherwise interfere with the coating.
Preventing Unwanted Reactions
If left in the chamber, atmospheric gases would immediately react with the hot, energized metal vapor. This would create oxides and other compounds, contaminating the final film and drastically altering its properties, such as color, hardness, and adhesion.
Ensuring a Straight-Line Path
In a vacuum, the vaporized coating atoms can travel in a straight line from the source to the substrate. Without a vacuum, these atoms would constantly collide with air molecules, scattering them randomly throughout the chamber and preventing the formation of a uniform, dense film.
The Four Stages of the PVD Process
While technologies vary, the process within the chamber follows a clear sequence.
Stage 1: Vaporization (Generating the Coating Material)
First, a solid source material, known as the target, must be converted into a vapor. This is typically achieved in one of two ways:
- Sputtering: The chamber is backfilled with a small amount of an inert gas, usually Argon. A high voltage is applied, creating a plasma. The positively charged Argon ions are accelerated into the negatively charged target, striking it with enough force to dislodge, or "sputter," atoms of the target material.
- Thermal Evaporation: The source material is heated in a crucible using electrical resistance or an electron beam until it boils and evaporates.
Stage 2: Transportation (Moving from Source to Substrate)
The vaporized atoms or molecules travel through the high-vacuum space inside the chamber. Because there are virtually no other gas molecules to interfere, they move in a direct, line-of-sight path from the target to the substrate.
Stage 3: Reaction (An Optional, Powerful Step)
For certain coatings, this is the most important stage. A precisely controlled amount of a reactive gas (like nitrogen, oxygen, or a carbon-based gas) is introduced into the chamber. This gas reacts with the metal vapor to form a ceramic compound, creating coatings like Titanium Nitride (TiN) or Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC). This reaction can happen mid-flight or on the surface of the substrate itself.
Stage 4: Deposition (Building the Film Atom by Atom)
When the vapor atoms reach the surface of the comparatively cooler substrate, they condense. This condensation builds up, layer by layer, to form a thin, dense, and highly adhered film. The orientation of the parts within the chamber is critical to ensure uniform exposure to this vapor stream.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
The PVD process is not a single setting but a balance of competing variables that must be managed to achieve the desired result.
Vacuum Level vs. Throughput
Achieving a higher vacuum results in a purer coating because it removes more potential contaminants. However, pumping down to extremely low pressures takes significantly more time, which reduces the number of cycles a machine can run in a day (throughput).
Deposition Rate vs. Film Quality
It is often possible to increase the power to the target to generate vapor and deposit the film more quickly. However, depositing too fast can sometimes result in a coating with higher internal stress or a less-ordered atomic structure, which can impact its performance and adhesion.
Temperature vs. Substrate Material
While PVD is a "low temperature" process compared to methods like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), heat is still a factor. Higher substrate temperatures can improve film adhesion and density, but they may be unsuitable for temperature-sensitive materials like plastics or certain aluminum alloys.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the chamber's function allows you to tailor the process to your specific outcome.
- If your primary focus is a pure, decorative metallic coating (e.g., chrome): The key is achieving the highest possible vacuum to eliminate oxygen and water vapor, which would tarnish the finish.
- If your primary focus is a hard, wear-resistant ceramic coating (e.g., TiN): The critical step is the precise control and uniform introduction of the reactive nitrogen gas.
- If your primary focus is uniform coverage on a complex 3D part: The design of the racking and rotation of parts inside the chamber is just as important as the deposition parameters themselves.
By mastering the principles of this vacuum-based environment, you move from simply using a process to engineering a specific material outcome.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Process | Key Action |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Vaporization | Generating the Coating Material | Target material is vaporized via sputtering or thermal evaporation. |
| 2. Transportation | Moving from Source to Substrate | Vaporized atoms travel unimpeded in a straight line through the vacuum. |
| 3. Reaction (Optional) | Forming Ceramic Compounds | Reactive gas (e.g., Nitrogen) is introduced to create coatings like TiN. |
| 4. Deposition | Building the Film | Atoms condense on the substrate surface, forming a dense, adhered thin film. |
Ready to Engineer Superior Thin Films with Precision PVD?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for materials science and surface engineering. Whether you are developing wear-resistant coatings, decorative finishes, or functional thin films, our expertise and solutions can help you optimize your PVD process for superior results.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific coating challenges and goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Oxygen-Free Copper Crucible and Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between PECVD and CVD? Unlock the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- What is PECVD used for? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Performance Thin Films
- What is plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Films
- What materials are deposited in PECVD? Discover the Versatile Thin-Film Materials for Your Application
- What is meant by vapor deposition? A Guide to Atomic-Level Coating Technology



















