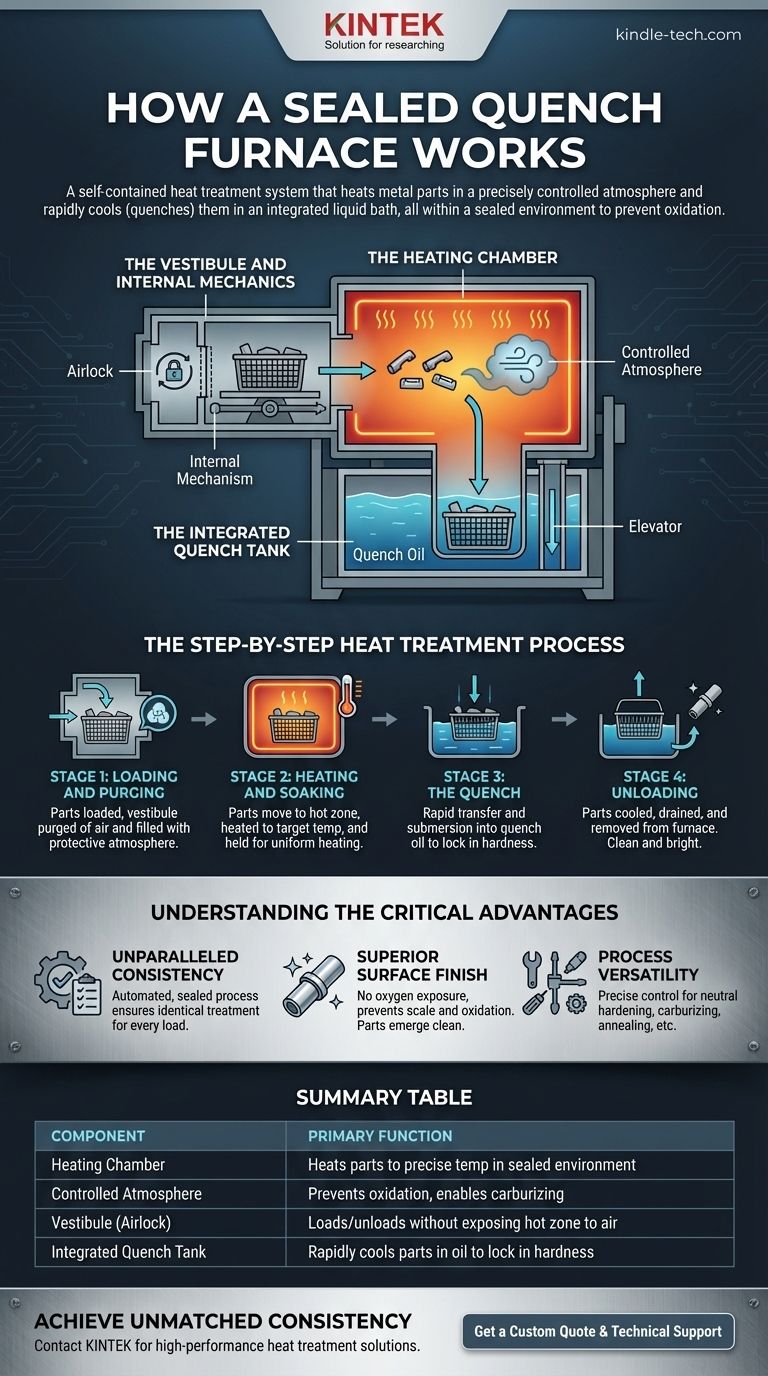
In essence, a sealed quench furnace is a self-contained heat treatment system that heats metal parts in a precisely controlled atmosphere and then rapidly cools (quenches) them in an integrated liquid bath. The entire process—from heating to quenching—occurs within a sealed environment, completely isolating the parts from external air to prevent oxidation and ensure consistent, high-quality results.
The critical insight is that a sealed quench furnace is not merely a box for heating metal. It is an integrated system designed to control the entire thermal and chemical process, delivering predictable metallurgical transformations with superior surface integrity.
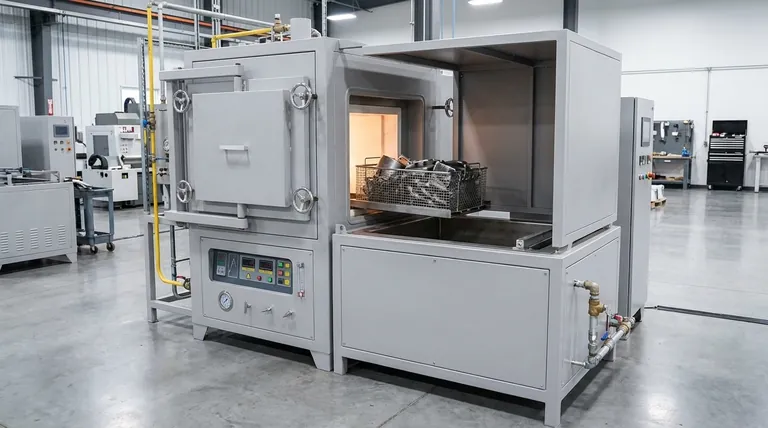

The Anatomy of a Sealed Quench Furnace
To understand how it works, you must first understand its key components. Each part serves a distinct and critical function in the overall heat treatment cycle.
The Heating Chamber
This is the core of the furnace where the parts are brought to a specific temperature. The chamber is heavily insulated and lined with refractory material to withstand extreme heat.
Heating is typically accomplished through electric resistance elements or gas-fired radiant tubes. While less common for this specific furnace type, induction heating—which uses an electromagnetic field to generate heat directly within the metal part—is another method used in heat treatment.
The Controlled Atmosphere
The "sealed" aspect is arguably the most important feature. The heating chamber is filled with a specific mixture of gases, known as a controlled atmosphere.
This atmosphere prevents oxidation and scaling (surface rust and discoloration) that would occur if the hot metal were exposed to oxygen. It can also be used for case-hardening processes like carburizing, where carbon is intentionally diffused into the surface of the steel.
The Vestibule and Internal Mechanics
The vestibule acts as an airlock between the outside world and the furnace's interior. Parts are loaded into this antechamber first.
Once the outer door is closed, the vestibule is purged of air and filled with the same protective atmosphere as the heating chamber. An internal mechanism then automatically transfers the parts from the vestibule into the heating chamber, and later, from the heating chamber to the quench tank.
The Integrated Quench Tank
Located directly below the heating chamber and vestibule is a tank filled with a quenching medium, most commonly oil. After the parts have been heated for the required amount of time, they are rapidly moved and submerged into this liquid.
This immediate, drastic cooling is the quench, which locks in the desired grain structure and hardness of the metal. Because it's integrated, the transfer from heat to quench is extremely fast and occurs without ever exposing the part to oxygen.
The Step-by-Step Heat Treatment Process
The operation follows a precise, automated sequence that ensures repeatability from one batch to the next.
Stage 1: Loading and Purging
A basket of parts is loaded into the vestibule. The outer door seals, and the chamber is purged of oxygen and filled with the protective atmosphere gas.
Stage 2: Heating and Soaking
An inner door opens, and the parts are mechanically moved into the hot zone. The furnace heats the parts to the target temperature (e.g., 1550°F / 845°C for steel hardening) and holds them at that temperature—a process called soaking—to ensure the entire part is evenly heated.
Stage 3: The Quench
After soaking, the parts are rapidly transferred from the hot zone, through the vestibule, and dropped onto an elevator that lowers them into the quench tank below. This rapid cooling transforms the metal's microstructure, creating hardness.
Stage 4: Unloading
The parts remain in the quench oil long enough to cool completely. The elevator then raises them out of the oil, allowing them to drain before being removed from the furnace for subsequent steps like tempering.
Understanding the Critical Advantages
The design of a sealed quench furnace directly addresses common challenges in heat treatment, offering significant benefits over more basic furnace types.
Unparalleled Consistency
Because the entire cycle is automated and sealed from external variables, every part in every load receives an identical treatment. This high degree of process control is essential for modern manufacturing.
Superior Surface Finish
By eliminating exposure to oxygen, the furnace prevents the formation of scale. Parts emerge from the furnace clean and bright, minimizing the need for costly and time-consuming post-processing like sandblasting.
Process Versatility
The ability to precisely control both temperature and atmosphere composition makes these furnaces extremely versatile. They are the industry standard for critical processes like neutral hardening, carburizing, carbonitriding, and annealing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right heat treatment process depends entirely on your final objective for the component.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production with repeatable hardness: The automated and consistent nature of a sealed quench furnace is the industry standard.
- If your primary focus is superior surface integrity and finish: The sealed, controlled atmosphere is non-negotiable for preventing oxidation and scale.
- If your primary focus is specialized surface hardening: This furnace is the definitive choice for processes like carburizing that require precise atmospheric control.
Ultimately, the sealed quench furnace provides an unmatched level of control over the metallurgical transformation of metal components.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Function |
|---|---|
| Heating Chamber | Heats parts to precise temperature in a sealed, insulated environment. |
| Controlled Atmosphere | Prevents oxidation and enables processes like carburizing. |
| Vestibule (Airlock) | Allows parts to be loaded/unloaded without exposing the hot zone to air. |
| Integrated Quench Tank | Rapidly cools parts in oil to lock in hardness and microstructure. |
Achieve Unmatched Consistency in Your Heat Treatment Processes
Does your production demand repeatable hardness and superior surface finishes without scale? The controlled, automated process of a sealed quench furnace is the industry standard for a reason.
At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance lab and production equipment. Our expertise can help you integrate the right heat treatment solution for your specific metals and goals, whether it's neutral hardening, carburizing, or annealing.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your quality and efficiency.
Get a Custom Quote & Technical Support
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why nitrogen is used in furnace? A Cost-Effective Shield for High-Temperature Processes
- Can nitrogen gas be heated? Leverage Inert Heat for Precision and Safety
- What is meant by inert atmosphere? A Guide to Preventing Oxidation & Ensuring Safety
- What gases are used in inert atmospheres? Choose the Right Gas for Non-Reactive Environments
- What provides an inert atmosphere? Achieve Safety and Purity with Nitrogen, Argon, or CO2



















