In essence, a sintering machine is a high-temperature furnace that transforms a compacted powder into a dense, solid object without melting it. The machine precisely controls a heating cycle that causes individual material particles to fuse, drastically reducing the gaps between them and creating a strong, coherent mass.
The fundamental principle of sintering is not melting, but solid-state diffusion. By heating a material to a temperature below its melting point, a sintering machine energizes its atoms, causing them to migrate across particle boundaries and bond together, effectively "welding" the powder into a solid part.

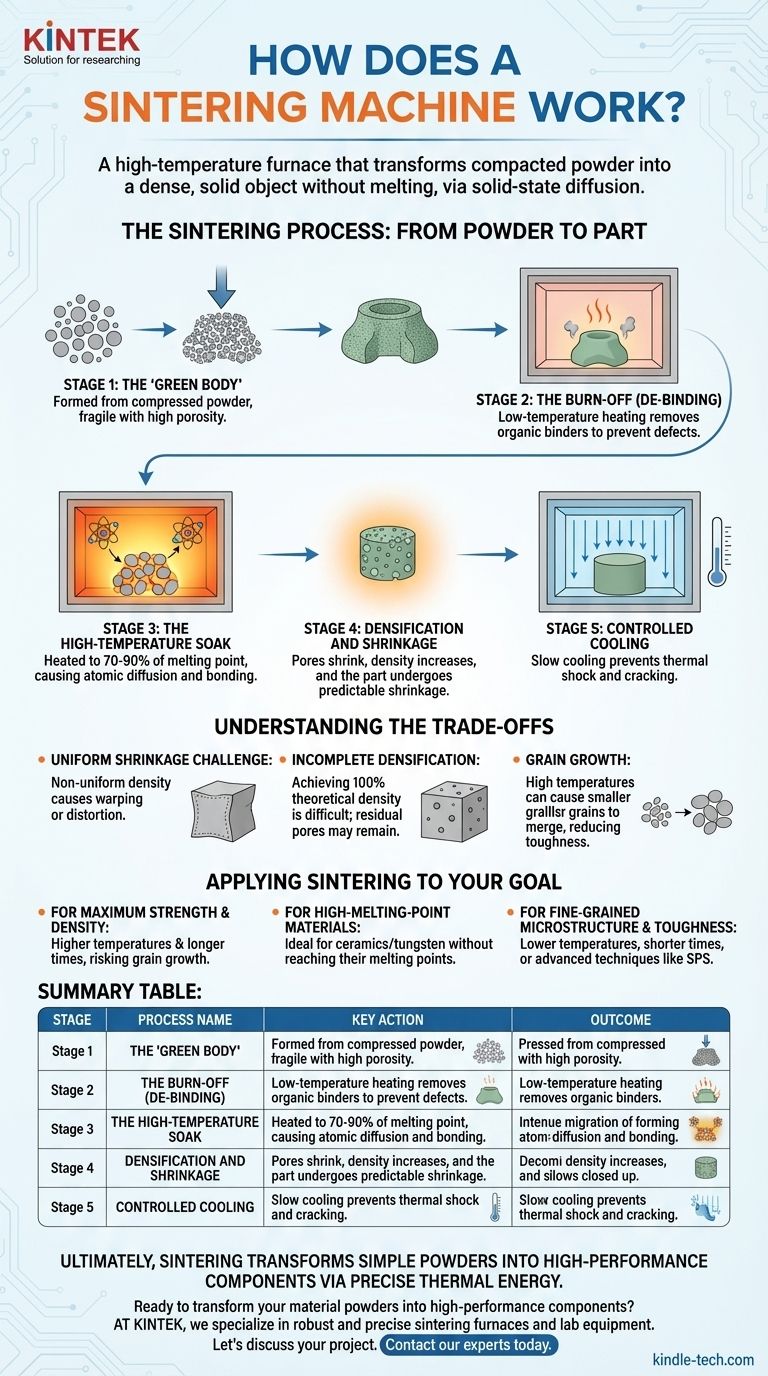
The Sintering Process: From Powder to Part
A sintering machine executes a carefully programmed thermal cycle. The process can be understood by breaking it down into its key stages, each serving a distinct purpose in the material's transformation.
Stage 1: The "Green Body"
Before entering the machine, the raw material is first pressed into a desired shape. This initial, fragile object is known as a green body or green compact. It has the shape of the final part but possesses low strength and high porosity, as the particles are only held together by mechanical friction.
Stage 2: The Burn-Off (De-binding)
The first heating phase in the sintering machine occurs at a relatively low temperature. Its primary goal is to burn off any residual organic binders or lubricants that were used to help form the green body. Removing these additives cleanly is critical to prevent defects in the final product.
Stage 3: The High-Temperature Soak
This is the core of the sintering process. The machine rapidly raises the temperature to a specific point, typically 70-90% of the material's melting point, and holds it there for a set duration.
At this high temperature, atomic diffusion becomes significant. Atoms at the contact points between powder particles become mobile and begin to migrate, forming "necks" or bridges between them. As these necks grow, they pull the particle centers closer together.
Stage 4: Densification and Shrinkage
The growth of inter-particle necks leads to two key outcomes. First, the empty spaces (pores) between particles gradually shrink and are eliminated. This process, called densification, is what gives the final part its strength and solidity.
Second, as the porosity is reduced, the entire component shrinks in size. This shrinkage is a predictable and necessary part of the process that must be accounted for during the initial design of the part.
Stage 5: Controlled Cooling
After the high-temperature soak, the machine cools the part down in a controlled manner. A slow, managed cooling rate is essential to prevent thermal shock, which could cause cracking and internal stresses, compromising the integrity of the newly formed part.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Sintering is a powerful technique, but it is not without its challenges and limitations. A successful outcome depends on precise control over the entire process.
The Challenge of Uniform Shrinkage
Achieving uniform shrinkage is difficult. Any non-uniformity in the green body's density will lead to differential shrinkage, causing the part to warp or distort. This is a primary cause of dimensional inaccuracy in sintered components.
Incomplete Densification
While sintering dramatically increases density, achieving 100% theoretical density is often impractical or impossible. Some residual porosity may remain, which can act as a stress concentration point and affect the material's ultimate mechanical properties, such as fatigue life.
Grain Growth
The same high temperatures that drive densification also cause grain growth, where smaller crystalline grains merge into larger ones. While some grain growth is inevitable, excessive growth can degrade the material's strength and toughness. There is a constant trade-off between achieving high density and maintaining a fine-grained microstructure.
Applying Sintering to Your Goal
Choosing the right sintering parameters is critical and depends entirely on the desired properties of the final component.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and density: You will need a higher sintering temperature and a longer soak time to eliminate as much porosity as possible, even at the risk of some grain growth.
- If your primary focus is working with high-melting-point materials: Sintering is the ideal choice, as it allows you to create solid parts from materials like ceramics or tungsten without having to reach their extremely high melting points.
- If your primary focus is preserving a fine-grained microstructure for toughness: You may need to use lower temperatures, shorter times, or advanced techniques like Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) to accelerate densification while inhibiting grain growth.
Ultimately, sintering enables the transformation of simple powders into high-performance, complex components through the precise application of thermal energy.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Process Name | Key Action | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Forming | Powder is pressed into a 'green body' | Creates the initial, fragile shape |
| 2 | Burn-Off (De-binding) | Low-temperature heating removes binders | Prepares the part for fusion |
| 3 | High-Temperature Soak | Heating to 70-90% of melting point | Atoms diffuse, forming bonds between particles |
| 4 | Densification | Particles fuse, pores shrink | Part gains strength and density |
| 5 | Controlled Cooling | Slow, managed cooling | Prevents cracking and internal stress |
Ready to transform your material powders into high-performance components?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing robust and precise sintering furnaces and lab equipment tailored to your research and production goals. Whether you are working with advanced metals, ceramics, or other powders, our solutions help you achieve the perfect balance of density, strength, and microstructure.
Let's discuss your project. Contact our experts today to find the ideal sintering equipment for your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
People Also Ask
- How should a sample be installed onto the sample holder? Ensure Mechanical Stability & Electrical Integrity
- How should an RVC sheet be handled and set up during an experiment? Ensure Precision and Data Integrity
- What is a hot mounting press machine? Precision Control for Metallurgy & Electronics Assembly
- What is the purpose of using epoxy resin and laboratory mounting equipment? Precision in U71Mn Weld Area Analysis
- What is the difference between hot mounting and cold mounting? Choose the Right Method for Your Sample



















