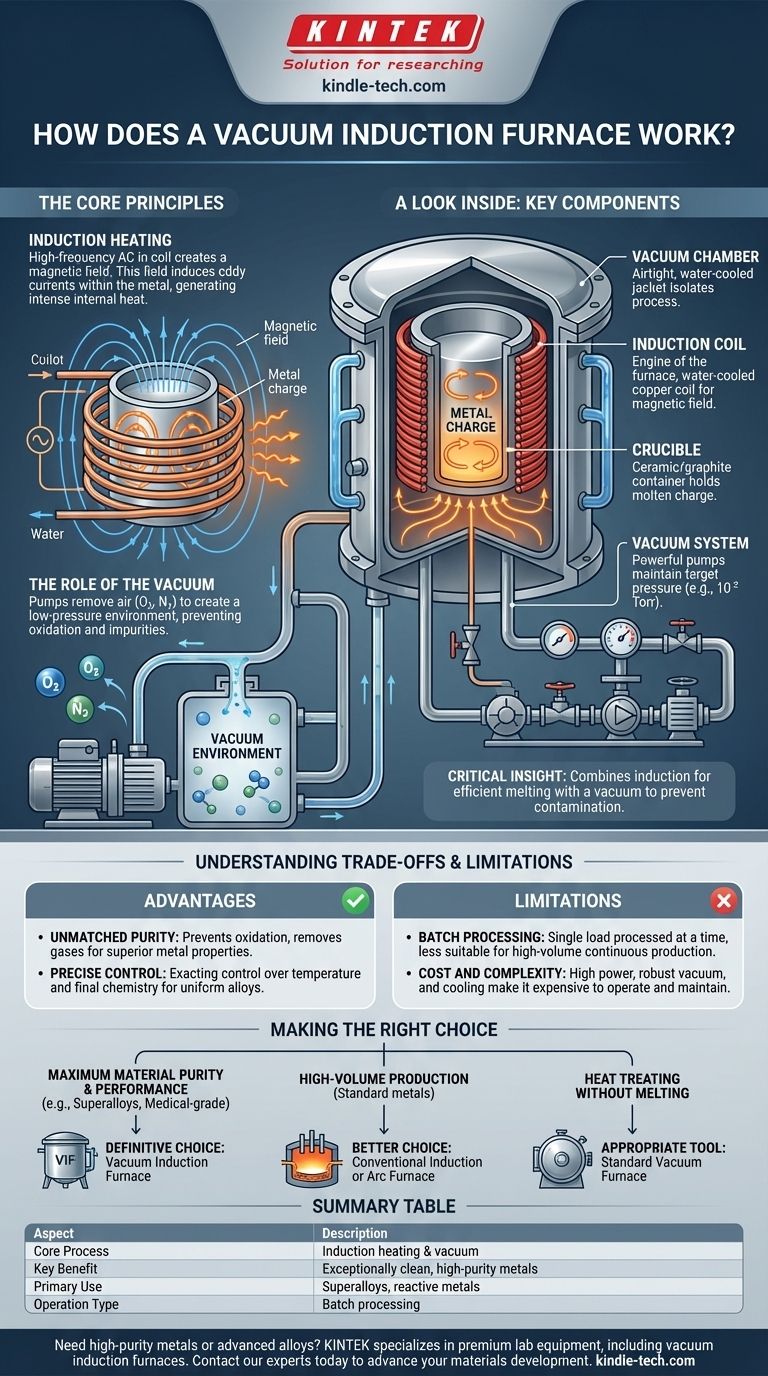
At its core, a vacuum induction furnace is a highly controlled environment that melts metal using electromagnetic fields inside a vacuum. It works by passing a powerful alternating current through a copper coil, which generates a magnetic field. This field induces electrical "eddy" currents within the metal charge itself, causing it to heat rapidly and melt without any direct contact or open flame.
The critical insight is that this technology combines two powerful principles: induction heating for clean, efficient melting and a vacuum environment to prevent contamination. This unique combination is what makes it indispensable for producing the highest purity metals and advanced alloys.
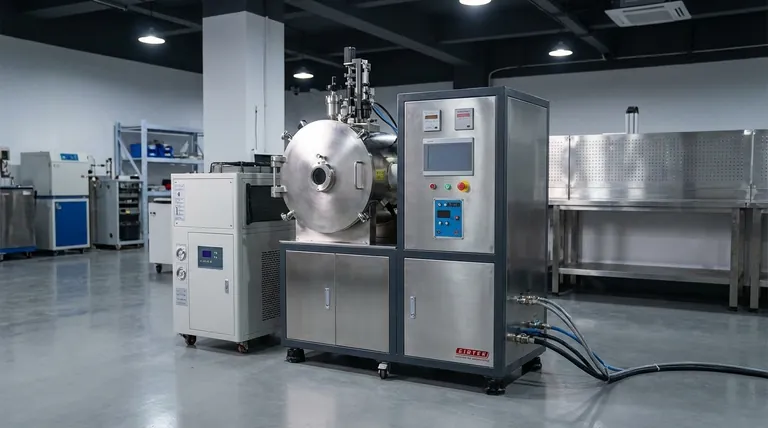

The Core Principles: Induction and Vacuum
A vacuum induction furnace (VIF) doesn't just melt metal; it refines it. Understanding the two fundamental processes at play—induction and vacuum—is key to grasping its value.
How Induction Heating Works
An induction power unit sends a high-frequency alternating current through a hollow, water-cooled copper coil. This coil surrounds a crucible containing the solid metal charge.
The alternating current in the coil creates a powerful and rapidly changing magnetic field. This field passes through the metal charge, inducing its own electrical currents within the metal, known as eddy currents.
It is the resistance of the metal to the flow of these eddy currents that generates intense, localized heat. The heat is created directly inside the metal, not in the furnace walls, leading to extremely fast and efficient melting.
The Role of the Vacuum
Before heating begins, a vacuum system pumps nearly all the air out of the sealed furnace chamber, creating a low-pressure environment.
This step is crucial because it removes gases like oxygen and nitrogen. At high temperatures, these gases would aggressively react with the molten metal, causing oxidation and forming impurities that degrade the material's final properties.
By melting in a vacuum, the furnace ensures the resulting metal or alloy is exceptionally clean, pure, and free from gas-related defects.
A Look Inside the Furnace: Key Components
The furnace is an integrated system where each part serves a specific function to achieve a pure, controlled melt.
The Vacuum Chamber
This is the airtight outer shell, typically a water-cooled steel jacket. Its entire purpose is to contain the vacuum and isolate the melting process from the outside atmosphere.
The Induction Coil
This component is the engine of the furnace. It's a precisely wound copper coil that carries the alternating current to generate the magnetic field. It is also water-cooled to handle the immense electrical energy flowing through it.
The Crucible
Housed inside the induction coil, the crucible is the ceramic or graphite container that holds the metal to be melted. It must be able to withstand extreme temperatures while remaining non-reactive with the molten charge.
The Vacuum System
This system consists of powerful pumps, valves, and gauges. It is responsible for evacuating the chamber to the target pressure (often in the 10⁻² Torr range) and maintaining that vacuum throughout the melting cycle.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, vacuum induction technology is not a universal solution. Its benefits come with specific operational realities.
Advantage: Unmatched Purity
The primary reason to use a VIF is to achieve the highest possible material purity. By preventing oxidation and allowing for the removal of dissolved gases, it produces metals and alloys with superior mechanical properties, crucial for demanding applications.
Advantage: Precise Control
The process offers exacting control over both temperature and final chemistry. Alloying elements can be added to the molten bath under vacuum to create alloys with an extremely precise and uniform composition.
Limitation: Batch Processing
A VIF operates as a batch furnace. A single load of material is processed, cooled, and unloaded before the next can begin. This makes it less suitable for high-volume, continuous production compared to other furnace types.
Limitation: Cost and Complexity
The combination of high-power electrical systems, robust vacuum technology, and water-cooling circuits makes VIF systems more complex and expensive to operate and maintain than standard atmospheric furnaces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct melting technology depends entirely on the requirements of your final product.
- If your primary focus is maximum material purity and performance: The vacuum induction furnace is the definitive choice for producing high-performance superalloys, reactive metals, and medical-grade materials.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of standard metals: A conventional induction or arc furnace operating in the open atmosphere is often more efficient and cost-effective.
- If your primary focus is simply heat treating parts without melting: A standard vacuum furnace (which heats with resistive elements, not induction) is the appropriate tool for the job.
Ultimately, a vacuum induction furnace is a specialized instrument for when the absolute quality and chemical integrity of the material cannot be compromised.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Process | Induction heating combined with a vacuum environment. |
| Key Benefit | Produces exceptionally clean, high-purity metals and alloys. |
| Primary Use | Melting superalloys, reactive metals, and medical-grade materials. |
| Operation Type | Batch processing. |
Need to produce high-purity metals or advanced alloys? KINTEK specializes in premium lab equipment, including vacuum induction furnaces, to meet the demanding needs of research and high-tech manufacturing laboratories. Our systems are engineered for superior performance, precise control, and exceptional material integrity. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can advance your materials development.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the principle of vacuum induction melting? Achieve Ultra-High Purity Metals
- What is vacuum arc melting technique? Discover the Precision of Vacuum Induction Melting
- What are the advantages of induction melting? Achieve Faster, Cleaner, and More Controlled Metal Melting
- What is VIM in metallurgy? A Guide to Vacuum Induction Melting for High-Performance Alloys
- What types of metals are typically processed in a vacuum induction melting furnace? High-Purity Alloys for Critical Applications



















