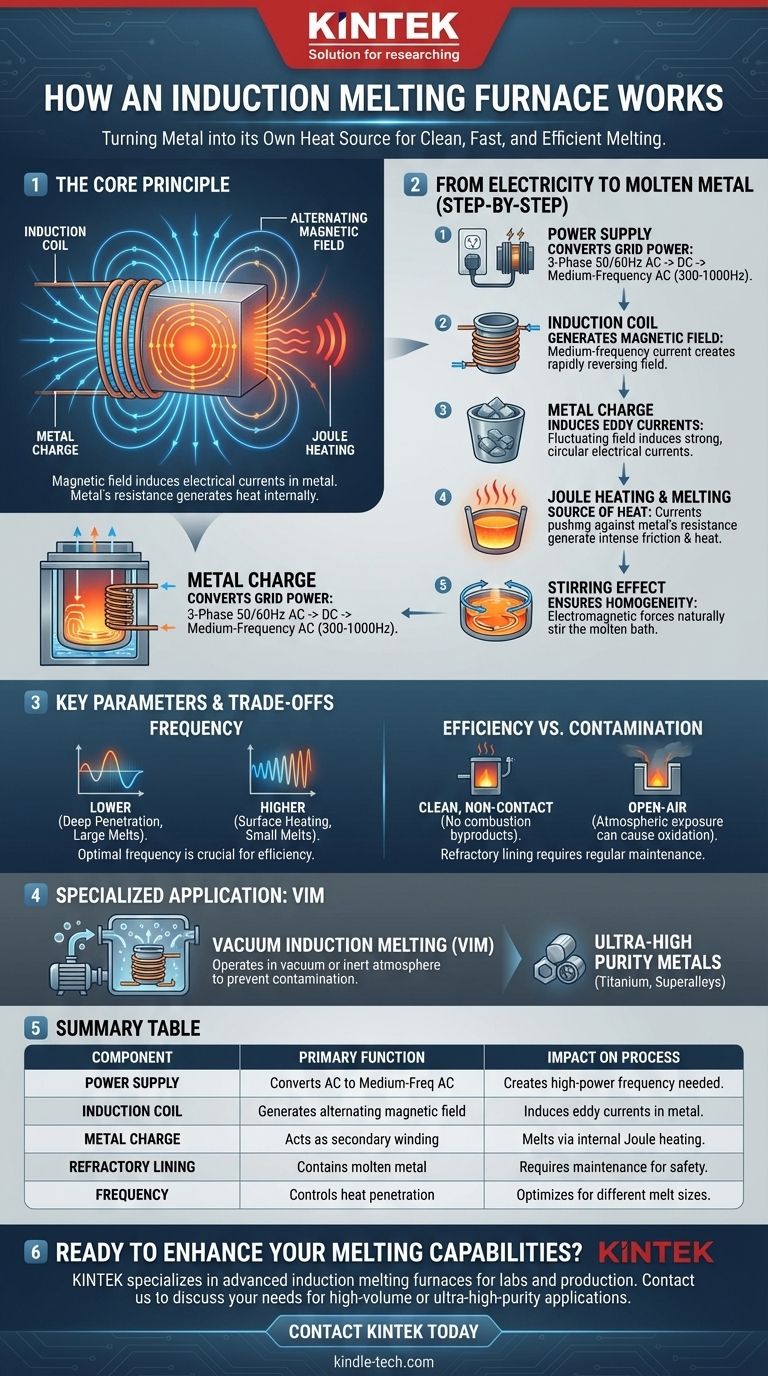
At its core, an induction melting furnace works by turning the metal itself into a heat source. It uses a powerful, alternating magnetic field to induce strong electrical currents directly within the metal charge. The metal’s natural resistance to these "eddy currents" generates intense heat through a process called Joule heating, melting the material from the inside out without any direct contact from an external flame or heating element.
The fundamental advantage of induction melting is its direct, non-contact method of heating. By generating heat within the metal, the process is remarkably clean, fast, and efficient compared to traditional methods that heat from the outside.
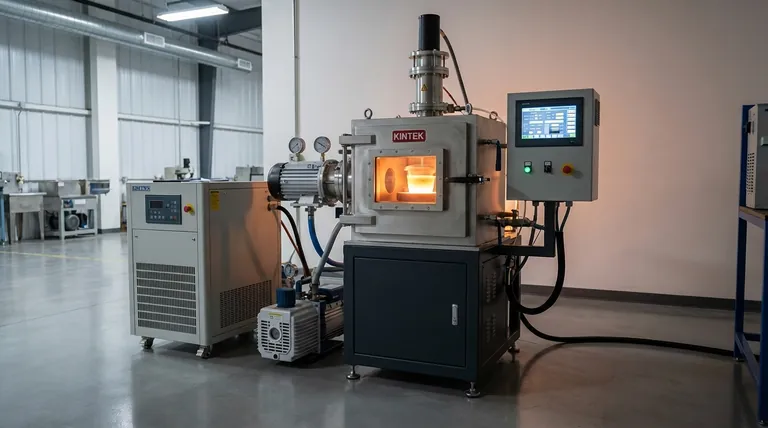

The Core Principle: From Electricity to Molten Metal
The entire process is a masterful conversion of energy, transforming standard grid electricity into the thermal energy needed to melt even the most robust metals. This happens in a precise, multi-stage sequence.
The Power Supply: Converting Grid Power
The process begins at the power supply unit. This device takes standard three-phase, low-frequency (50/60 Hz) alternating current (AC) from the electrical grid and converts it.
First, it rectifies the AC into direct current (DC). Then, an inverter converts the DC back into a single-phase, medium-frequency AC, typically between 300 Hz and 1000 Hz. This controlled, high-power frequency is the engine of the entire system.
The Induction Coil: Generating the Magnetic Field
This medium-frequency current is sent to a large, water-cooled copper coil that encircles the crucible holding the metal. As the current flows through the coil, it generates a powerful and rapidly reversing magnetic field that passes through the crucible and into the metal charge.
The Metal Charge: Inducing Eddy Currents
Based on the principle of electromagnetic induction, this fluctuating magnetic field induces strong, circular electrical currents within the conductive metal. These are known as eddy currents.
Essentially, the induction coil acts as the primary winding of a transformer, and the metal charge acts as a short-circuited secondary winding.
Joule Heating: The Source of Heat
The induced eddy currents are not flowing through a perfect conductor. The metal has its own inherent electrical resistance. As the eddy currents push against this resistance, they generate tremendous friction and heat.
This phenomenon, known as Joule heating, is what melts the metal. Since the heat is generated internally, the process is incredibly rapid and efficient.
The Stirring Effect: Ensuring Homogeneity
A unique side effect of the powerful eddy currents is an electromagnetic stirring action within the molten bath. This natural agitation ensures the molten metal mixes thoroughly, leading to a uniform temperature and a homogenous chemical composition in the final alloy.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Parameters
While powerful, induction melting is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Its effectiveness depends on carefully managed parameters and an understanding of its inherent trade-offs.
The Critical Role of Frequency
The frequency of the power supply is a crucial variable. Lower frequencies penetrate deeper into the metal bath, making them ideal for melting large volumes of metal.
Higher frequencies concentrate the heating effect closer to the surface of the charge. This is more effective for smaller melts or specialized surface-hardening applications. Mismatched frequency leads to inefficiency.
Efficiency vs. Contamination
The primary benefit of induction is its clean, non-contact nature. Unlike an arc furnace or a gas-fired cupola, there are no electrodes or combustion byproducts to contaminate the melt. This results in a higher-purity final product.
However, in an open-air furnace, the molten metal is still exposed to atmospheric oxygen, which can cause oxidation.
The Refractory Lining
The crucible holding the molten metal is made of a refractory material, often quartz sand, that can withstand extreme temperatures. This lining is a consumable component.
It slowly erodes over time due to chemical reactions and the physical force of the stirring metal. Regular inspection and repair are critical operational realities to prevent a dangerous metal breakout.
Specialized Applications: The Vacuum Induction Furnace
To overcome the issue of atmospheric contamination, the core technology can be placed inside a sealed vessel, creating a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace.
Why Operate in a Vacuum?
By removing the air from the chamber, the melting process occurs in a vacuum or under a controlled, inert atmosphere (like argon). This completely prevents the formation of oxides and removes dissolved gases from the melt.
The Result: Ultra-High Purity Metals
VIM furnaces are essential for producing materials where purity is paramount. This includes nickel-based superalloys for jet engines, special steels, precision alloys for electronics, and reactive metals like titanium for aerospace and medical applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal induction approach depends entirely on the material being processed and the desired quality of the final product.
- If your primary focus is high-volume casting of standard metals (e.g., steel, iron, aluminum): A medium-frequency, open-air furnace provides the best balance of speed, efficiency, and operational cost.
- If your primary focus is producing high-purity superalloys or reactive metals: A Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace is non-negotiable to prevent contamination and achieve precise chemical control.
- If your primary focus is maximizing melting speed and efficiency: Carefully match the power supply's frequency and power output to the size and type of your metal charge to ensure optimal energy transfer.
By understanding the principle of direct internal heating, you can effectively leverage the speed, precision, and purity of induction technology.
Summary Table:
| Key Component | Primary Function | Impact on Melting Process |
|---|---|---|
| Power Supply | Converts grid AC to medium-frequency AC | Creates the high-power frequency needed for induction |
| Induction Coil | Generates a powerful, alternating magnetic field | Induces eddy currents within the metal charge |
| Metal Charge | Acts as a secondary winding, generating internal heat | Melts from the inside out via Joule heating |
| Refractory Lining | Contains the molten metal within the crucible | Requires regular maintenance to ensure safety |
| Frequency Setting | Controls the depth of heat penetration | Optimizes efficiency for different melt sizes and metals |
Ready to enhance your metal melting capabilities with precision and efficiency?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including induction melting furnaces tailored to your specific needs—whether for high-volume casting or ultra-high-purity applications like Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM). Our solutions deliver clean, fast, and homogeneous melts, ensuring superior results for laboratories and production facilities.
Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can optimize your melting process and drive your success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What principle is used to generate heat in a vacuum induction melting furnace? Achieve Clean, Efficient Metal Melting
- What is the difference between induction melting and vacuum induction melting? Choosing the Right Process for Purity
- How does induction work in a vacuum? Achieve Ultra-Pure Metal Melting with VIM
- What are the advantages of induction melting? Achieve Faster, Cleaner, and More Controlled Metal Melting
- What is VIM in metallurgy? A Guide to Vacuum Induction Melting for High-Performance Alloys



















