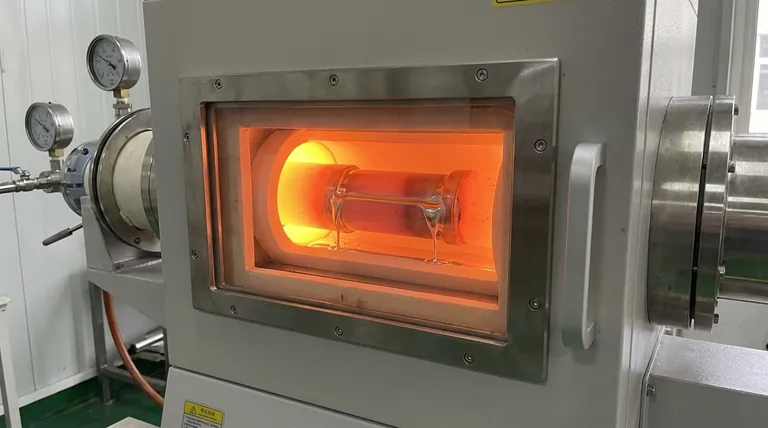
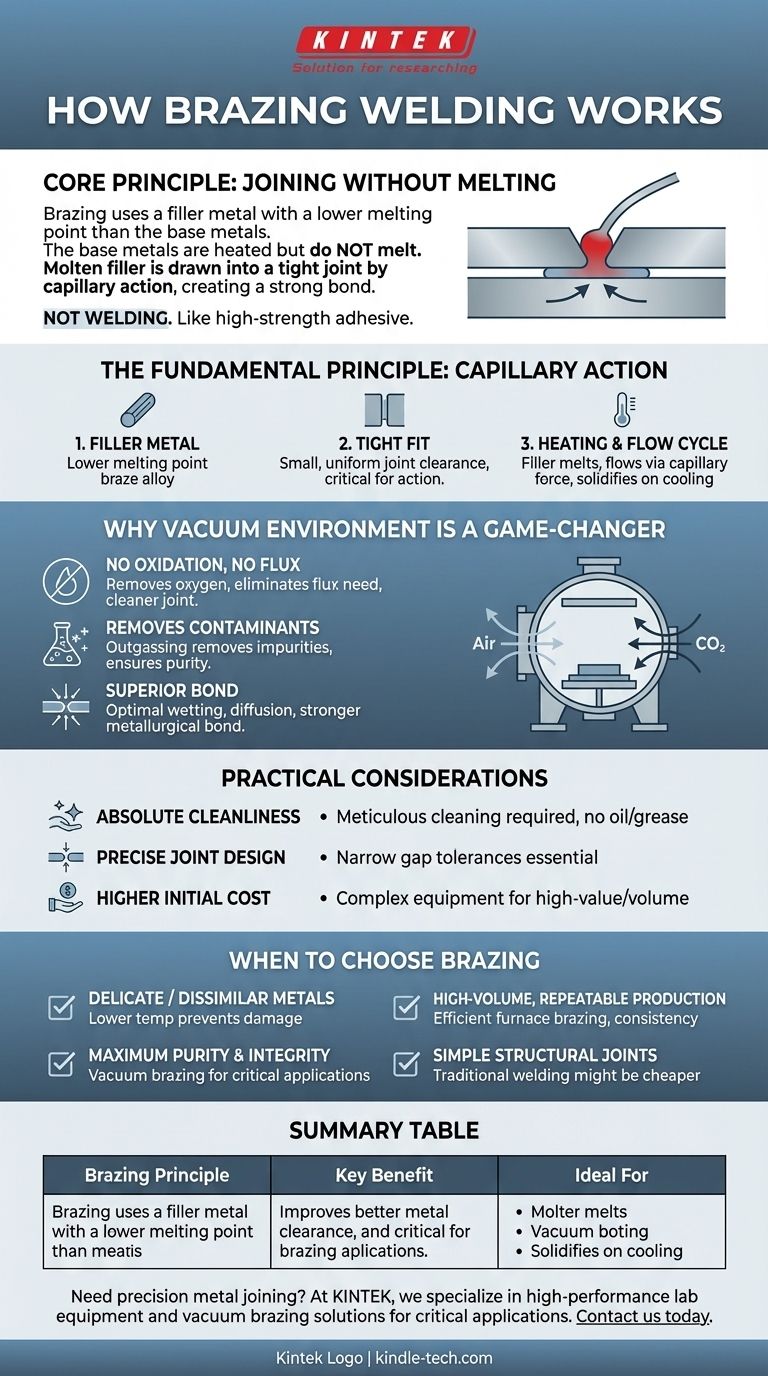
At its core, brazing is a metal-joining process that uses a filler metal with a lower melting point than the base metals being joined. The base metals are heated to a temperature high enough to melt the filler but not themselves. The molten filler is then drawn into the tight-fitting joint between the parts by capillary action, creating a strong metallurgical bond upon cooling.
Brazing is not a form of welding. Its key principle is joining metals without melting them, relying instead on a separate, lower-melting-point filler alloy to flow between and bond the pieces together, similar to how solder works but at much higher temperatures and with greater strength.

The Fundamental Principle: Capillary Action
Brazing creates exceptionally clean and strong joints by leveraging a natural physical force. Unlike welding, which fuses metals together, brazing acts more like a high-strength, metallic adhesive.
The Role of the Filler Metal
The entire process hinges on the filler metal, also known as the braze alloy. This alloy is specifically chosen to have a melting point that is significantly lower than the base metals it is intended to join.
The Importance of a Tight Fit
For brazing to work, the parts must be designed with a very small, uniform gap between them, known as the joint clearance. This precise gap is critical for enabling capillary action.
The Heating and Flow Cycle
When the entire assembly is heated in a furnace, the filler metal melts and becomes a liquid. The capillary force created by the tight joint clearance pulls this liquid filler into the gap, completely filling the space between the two base metals. Upon cooling, the filler solidifies, creating a continuous, strong bond.
Why a Vacuum Environment is a Game-Changer
While brazing can be done in various environments, performing it in a vacuum furnace fundamentally elevates the quality and integrity of the joint. This is the preferred method for high-performance applications.
Eliminating Oxidation Without Flux
In a normal atmosphere, heating metal causes it to oxidize rapidly, which prevents the filler metal from bonding properly. Traditionally, a chemical flux is used to clean these oxides away.
A vacuum furnace removes virtually all oxygen from the environment. This prevents oxidation from ever occurring, eliminating the need for flux and resulting in a much cleaner, flux-free joint with no risk of corrosive residue.
Removing Trapped Gases and Contaminants
The low-pressure environment of a vacuum furnace effectively pulls out contaminants, air bubbles, and other impurities from the metal surfaces and the joint itself. This process, known as outgassing, ensures an exceptionally pure connection.
Achieving a Superior Metallurgical Bond
Because the metal surfaces are perfectly clean and deoxidized, the molten filler metal can achieve optimal "wetting." This allows it to diffuse slightly into the base metals, forming a stronger, more integrated metallurgical bond that is free of voids or imperfections.
Understanding the Practical Considerations
While powerful, vacuum brazing is a precise industrial process with specific requirements that make it different from conventional welding.
Requirement for Absolute Cleanliness
The success of brazing depends on perfectly clean surfaces. Any oil, grease, or dirt will prevent the filler metal from flowing correctly, compromising the joint. Parts must be meticulously cleaned before entering the furnace.
Need for Precise Joint Design
Capillary action only works within a narrow range of gap tolerances. If the joint clearance is too large, the filler won't be drawn in. If it's too small, it won't be able to flow at all. This demands careful engineering of the parts being joined.
Higher Initial Equipment Cost
Vacuum furnaces are complex and expensive pieces of equipment. This makes vacuum brazing a process best suited for high-value components or high-volume production where the quality and repeatability justify the investment.
When to Choose Brazing for Your Application
Selecting the right joining method requires understanding the final goal of your component.
- If your primary focus is joining delicate or dissimilar metals: Brazing is ideal because the lower process temperature prevents damage, distortion, or melting of the parent materials.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, repeatable production: Furnace brazing is incredibly efficient, allowing thousands of joints to be created simultaneously with high consistency.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum purity and joint integrity: Vacuum brazing is the superior choice for critical applications in aerospace, medical, or electronics where failure is not an option.
- If your primary focus is creating simple structural joints at low cost: Traditional welding may be a more direct and economical solution, especially when joining thick sections of common steel.
Ultimately, understanding the principles of brazing allows you to select a joining method based on precision engineering rather than just brute force.
Summary Table:
| Brazing Principle | Key Benefit | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Uses filler metal with lower melting point | Joins without melting base metals | Delicate or dissimilar metals |
| Relies on capillary action in tight joints | Strong, clean, flux-free bonds | High-purity applications (e.g., medical, aerospace) |
| Often performed in vacuum furnaces | Prevents oxidation, removes contaminants | High-volume, repeatable production |
Need precision metal joining for your lab or production line? At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including vacuum brazing solutions that deliver clean, strong, and reliable joints for critical applications. Whether you're working with delicate components or high-volume production, our expertise ensures optimal results. Contact us today to discuss how our brazing solutions can enhance your project's integrity and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- What is the ceramic tube high temperature? From 1100°C to 1800°C, Choose the Right Material
- What tube is used for tubular furnace? Choose the Right Material for Temperature & Atmosphere
- What is the pressure on a tube furnace? Essential Safety Limits for Your Lab
- How does a tube furnace work? Master Precise Thermal and Atmospheric Control



















