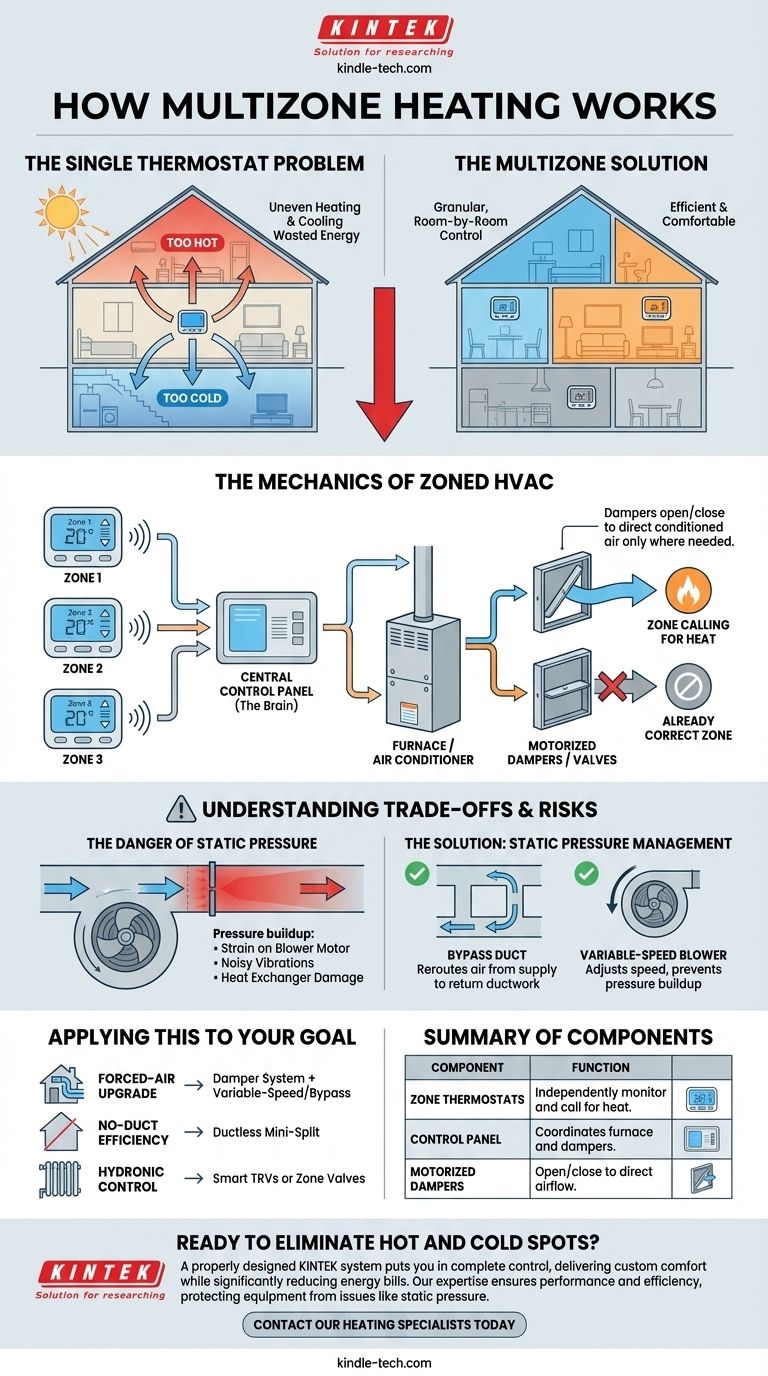
At its core, multizone heating works by dividing your home into distinct areas, or "zones," each controlled by its own thermostat. Instead of a single thermostat trying to heat the entire house to one temperature, this approach allows you to direct conditioned air only to the zones that need it. The most common method for forced-air systems uses automated dampers inside your ductwork that open and close to control airflow.
The central problem with traditional HVAC is its "one-size-fits-all" approach, which leads to uneven temperatures and wasted energy. Multizone systems solve this by giving you granular, room-by-room control, but the technology must be implemented correctly to avoid damaging your equipment.

The Problem: A Single Thermostat's Limitations
A single, centrally located thermostat can never accurately manage the temperature of an entire house. It only reads the temperature of the room it's in, leading to common frustrations.
Uneven Heating and Cooling
Rooms with large windows, top-floor bedrooms, or finished basements all have different heating and cooling needs than the hallway where the thermostat is located. This results in some areas being too hot while others are too cold.
Wasted Energy
A traditional system heats and cools the entire house, including empty guest rooms, unused offices, or storage areas. This is a significant and unnecessary energy expense.
The Mechanics of Zoned HVAC
A true multizone system is more than just closing vents; it's an integrated solution with three primary components working together.
1. Zone Thermostats
Each zone has its own thermostat. When the temperature in a specific zone drops below its set point, it sends a signal calling for heat.
2. A Central Control Panel
This is the brain of the system. It receives signals from all the zone thermostats and coordinates the furnace or air conditioner and the dampers. It decides when to turn the HVAC unit on and which zones to send air to.
3. Dampers or Valves
For a forced-air system, the control panel operates motorized dampers placed inside the ducts. These metal plates open to allow air into a zone that is calling for heat and close to block air from zones that are already at the correct temperature. For hot water (hydronic) systems, the same principle applies using zone valves to control water flow to radiators.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
While the concept is simple, a poorly designed multizone system can cause more problems than it solves. The primary concern is a buildup of air pressure.
The Danger of Static Pressure
Your furnace's blower is designed to move a specific volume of air. If most of the zone dampers are closed, the blower is trying to force the same amount of air through a much smaller opening. This spike in static pressure can strain the blower motor, cause noisy vibrations, and even damage the furnace's heat exchanger.
The Solution: Bypass Ducts and Variable-Speed Blowers
Professional installers use two key methods to manage static pressure. A bypass damper is a dedicated duct that reroutes excess air from the supply side back to the return side, relieving the pressure.
Even better, a modern variable-speed blower can automatically adjust its speed. When only one or two small zones are calling for heat, the blower runs at a much lower, more efficient speed, preventing pressure buildup from the start.
Installation Complexity
Retrofitting a zoned damper system into an existing home is a complex job. It requires cutting into ductwork, running new wiring for thermostats and dampers, and installing the control panel. This is not a simple DIY project.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Zoning is about matching the solution to your specific home and needs. There is no single best answer, only the right choice for your situation.
- If your primary focus is upgrading an existing forced-air system: A professionally installed damper system, ideally paired with a variable-speed furnace or a bypass duct, is the most direct path to zoned comfort.
- If your primary focus is maximum efficiency in a home without ducts: A ductless mini-split system is an excellent choice, as each indoor head acts as its own independent and highly efficient zone.
- If your primary focus is controlling a hot water or steam radiator system: Installing smart thermostatic radiator valves or a central system with hydronic zone valves is the correct approach.
Ultimately, a properly implemented multizone system gives you direct control over your home's comfort and energy consumption.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Zone Thermostats | Independently monitor and call for heat in specific areas. |
| Control Panel | The 'brain' that coordinates the furnace and dampers based on thermostat signals. |
| Motorized Dampers | Valves in ductwork that open/close to direct airflow only to zones needing heat. |
Ready to eliminate hot and cold spots in your home?
A properly designed multizone heating system from KINTEK puts you in complete control, delivering custom comfort room-by-room while significantly reducing your energy bills. Our expertise in precision climate control solutions ensures your system is optimized for performance and efficiency, protecting your equipment from issues like damaging static pressure.
Contact our heating specialists today for a consultation tailored to your home's unique layout and your comfort goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Gold Disc Electrode
People Also Ask
- What is the thermal expansion coefficient of molybdenum disilicide? Understanding its role in high-temperature design
- What material is used for furnace heating? Select the Right Element for Your Process
- Is molybdenum disulfide a heating element? Discover the best material for high-temperature applications.
- What is molybdenum disilicide used for? Powering High-Temperature Furnaces Up to 1800°C
- What function do molybdenum disilicide heating elements perform? Precision Heat for Pulverized Coal Research







