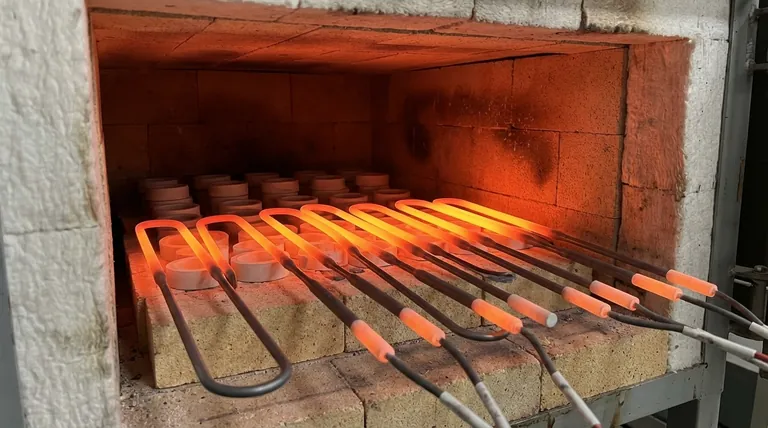
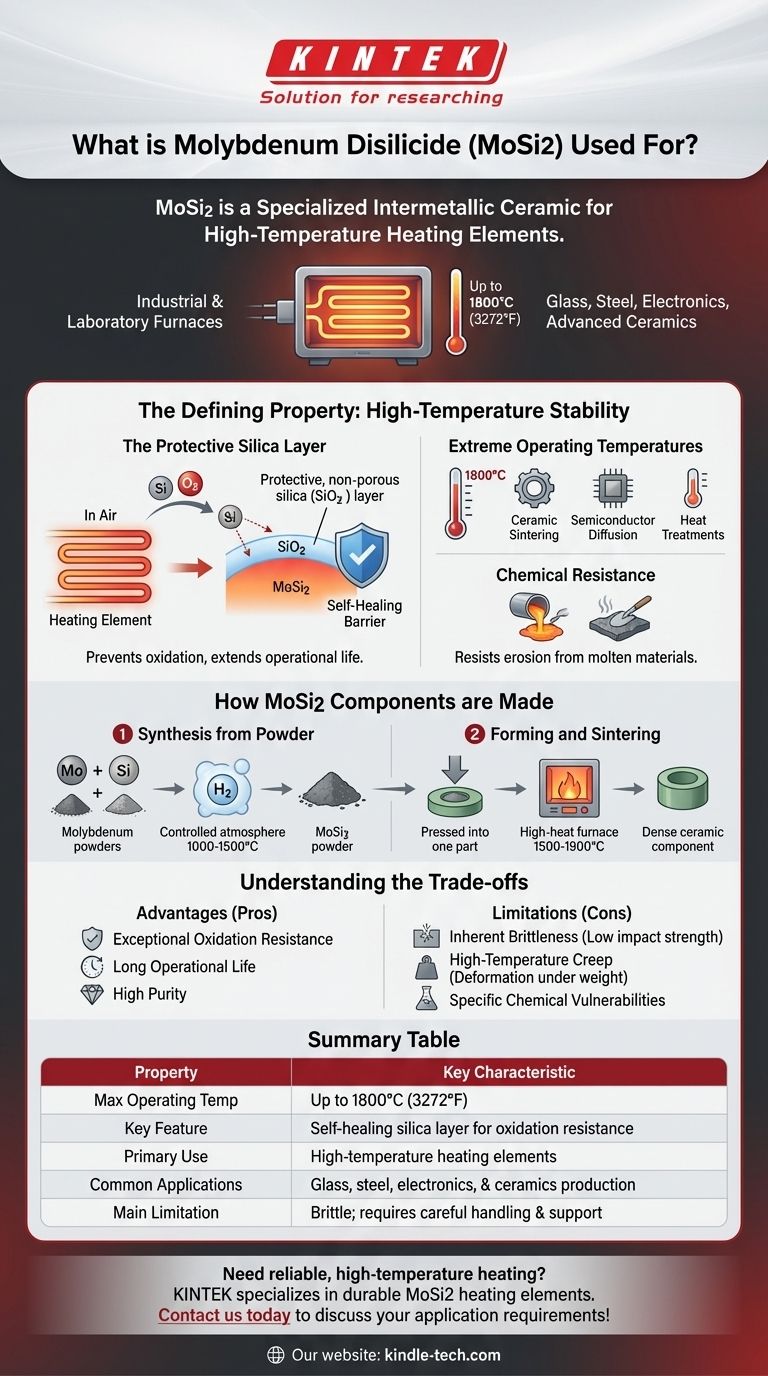
At its core, molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) is a specialized intermetallic ceramic primarily used to create high-temperature heating elements. Capable of operating at temperatures up to 1800°C (3272°F), these elements are critical components in electric furnaces for demanding industrial and laboratory applications, including the production of glass, steel, electronics, and advanced ceramics.
The defining characteristic of MoSi2 is its exceptional resistance to oxidation at extreme temperatures. This unique property stems from a self-healing protective layer of silica (SiO₂) that forms on its surface when heated, preventing the underlying material from degrading.

The Defining Property: High-Temperature Stability
The reason molybdenum disilicide is so valuable in high-heat applications is its unique behavior in the presence of oxygen. This allows it to outperform many other materials that would simply burn away.
The Protective Silica Layer
When MoSi2 is heated in air, the silicon on its surface reacts with oxygen to form a thin, non-porous layer of silicon dioxide—essentially a form of glass.
This protective coating acts as a barrier, preventing oxygen from reaching and oxidizing the molybdenum disilicide underneath. This gives the material an incredibly long operational life, even with continuous use at 1700°C.
Extreme Operating Temperatures
MoSi2 heating elements are designed for the most demanding thermal environments. Their ability to function reliably up to 1800°C makes them essential for processes like ceramic sintering, semiconductor diffusion furnaces, and complex material heat treatments.
Chemical Resistance
In addition to heat, MoSi2 stands up well to chemical attack. It resists erosion from many types of molten metal and slag, a crucial feature for applications in steel and glass manufacturing.
How MoSi2 Components are Made
Creating a functional MoSi2 product is a multi-step process that begins with raw elements and ends with a dense, precisely formed ceramic part.
Synthesis from Powder
The process starts by reacting high-purity molybdenum powder with silicon powder. This reaction is carried out in a controlled, non-oxidizing atmosphere (such as hydrogen) at temperatures between 1000°C and 1500°C.
Forming and Sintering
The resulting MoSi2 powder is then formed into the desired shape, typically for a heating element. This is done through methods like cold pressing or extrusion, often using a small amount of binder to hold the shape.
Finally, this "green" part is fired at extremely high temperatures (1500–1900°C) in a process called sintering. This fuses the powder particles together, creating a hard, dense ceramic component.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect, and MoSi2 is no exception. Its incredible thermal properties come with physical limitations that must be understood for successful implementation.
Inherent Brittleness
Like many advanced ceramics, molybdenum disilicide is very hard but also brittle, particularly at lower temperatures. It has low impact strength and cannot tolerate mechanical shock or being dropped.
High-Temperature Creep
While it resists oxidation, MoSi2 can slowly deform under its own weight when held at peak operating temperatures for long periods. This phenomenon, known as creep, must be accounted for in furnace design to ensure heating elements are properly supported.
Specific Chemical Vulnerabilities
Although it resists many substances, MoSi2 is soluble in mixtures of nitric and hydrofluoric acid. It can also be attacked by molten alkali.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting molybdenum disilicide is a decision based on the need for extreme, reliable heat in an oxidizing environment.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperature stability in air: MoSi2 heating elements are a leading choice for electric furnaces operating between 1300°C and 1800°C.
- If your primary focus is process purity and longevity: The stable, self-healing oxide layer ensures the material doesn't degrade and contaminate the furnace environment over thousands of hours.
- If your application involves mechanical stress or impact: You must account for the material's inherent brittleness in your design, ensuring elements are properly supported and handled with care.
Ultimately, molybdenum disilicide excels where reliable, long-lasting heat in an oxidizing atmosphere is the critical engineering challenge.
Summary Table:
| Property | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|
| Max Operating Temp | Up to 1800°C (3272°F) |
| Key Feature | Self-healing silica layer for oxidation resistance |
| Primary Use | High-temperature heating elements |
| Common Applications | Glass, steel, electronics, & ceramics production |
| Main Limitation | Brittle; requires careful handling & support |
Need reliable, high-temperature heating for your lab or industrial process? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, including durable MoSi2 heating elements designed for long-lasting performance in demanding environments. Our experts can help you select the right components to enhance your furnace's efficiency and purity. Contact us today to discuss your specific application requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature range of molybdenum disilicide heating elements? Choose the Right Grade for Your High-Temp Needs
- What are the properties of molybdenum heating element? Choose the Right Type for Your Furnace Atmosphere
- What is the temperature range of a MoSi2 heating element? Unlock 1900°C Performance for Your Lab
- What is the thermal expansion coefficient of molybdenum disilicide? Understanding its role in high-temperature design
- What material is used for furnace heating? Select the Right Element for Your Process



















