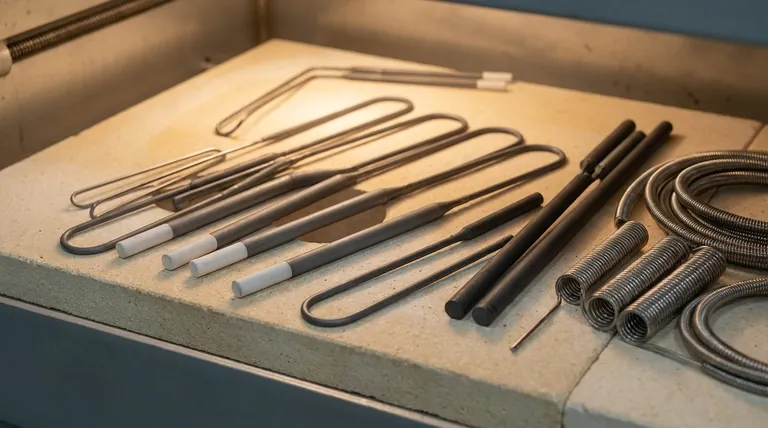
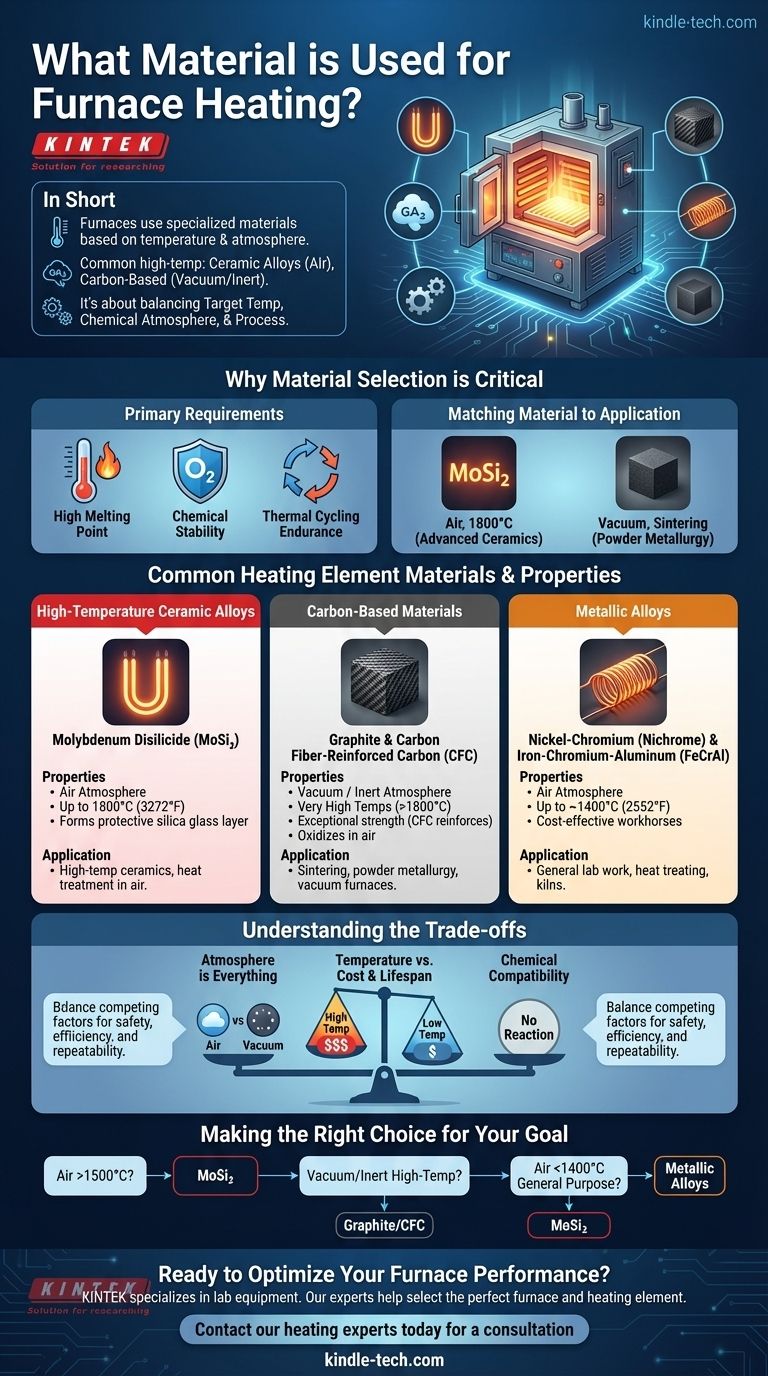
In short, furnaces use a range of specialized materials for their heating elements, chosen based on the required temperature and operating environment. The most common high-temperature materials include ceramic alloys like molybdenum disilicide for use in air, and carbon-based materials like graphite and Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Carbon (CFC) for vacuum or inert atmospheres.
The selection of a furnace heating material is not about finding a single "best" option. It is a critical engineering decision that balances the target temperature, the chemical atmosphere inside the furnace, and the specific industrial process.

Why Material Selection is Critical
The heating element is the heart of any furnace. Its job is to convert electrical energy into intense heat reliably and for thousands of hours. The material used must withstand extreme conditions without failing.
The Primary Requirements
An effective heating element material must possess three key properties: a very high melting point, chemical stability at temperature (resistance to oxidation), and the ability to endure repeated heating and cooling cycles.
Matching Material to Application
Different industrial processes require different conditions. For example, creating advanced ceramics might require 1800°C in the open air, while sintering metal powders requires a vacuum to prevent contamination. Each scenario demands a different heating material.
Common Heating Element Materials and Their Properties
While many materials exist, they generally fall into a few key categories, each suited for different tasks.
High-Temperature Ceramic Alloys
Materials like molybdenum disilicide (MoSi₂) are industry leaders for high-temperature applications that occur in an air atmosphere.
These elements are a type of cermet, combining ceramic-like heat and oxidation resistance with metal-like conductivity. They can operate at temperatures up to 1800°C (3272°F) because they form a protective layer of silica glass on their surface when heated in air.
Carbon-Based Materials
For applications in a vacuum or inert atmosphere, graphite and Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Carbon (CFC) are excellent choices.
Graphite offers exceptional strength at very high temperatures but will rapidly oxidize (burn away) if exposed to oxygen. CFC builds on this by reinforcing the graphite with carbon fibers, significantly increasing its strength and durability, making it ideal for vacuum hot press furnaces used in powder metallurgy.
Metallic Alloys
For many common furnaces operating at lower to medium temperatures (up to ~1400°C), metallic alloys are used. The most common are Nickel-Chromium (Nichrome) and Iron-Chromium-Aluminum (FeCrAl).
These are not mentioned in the high-temperature references but are the workhorses of the industry for general heat treatment, lab work, and kilns. They offer a great balance of cost and performance in air atmospheres.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a heating element always involves balancing competing factors. Understanding these compromises is key to selecting the right furnace for a given task.
Atmosphere is Everything
This is the most critical trade-off. Graphite can reach extreme temperatures but is useless in an oxygen-rich environment. Molybdenum disilicide thrives in air but may not be suitable for certain vacuum processes where its silica layer could be a contaminant.
Temperature vs. Cost and Lifespan
As a general rule, the higher the maximum operating temperature, the more expensive and potentially fragile the heating element. Elements designed for 1800°C are significantly more costly than standard FeCrAl elements that top out around 1400°C.
Chemical Compatibility
The heating element must not chemically react with the material being processed inside the furnace. This is especially important in vacuum and specialty gas environments where off-gassing from an element could ruin a sensitive product like a semiconductor or functional ceramic.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's specific requirements will dictate the correct heating element material.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperature (1500-1800°C) in an air atmosphere: Choose a furnace with molybdenum disilicide (MoSi₂) heating elements.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature processing in a vacuum or inert gas: Look for furnaces utilizing high-purity graphite or Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Carbon (CFC) elements.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heat treating (below 1400°C) in air: A furnace with robust and cost-effective FeCrAl or Nichrome elements is the standard and most practical choice.
Ultimately, the right material is the one that enables your process to run safely, efficiently, and with repeatable results.
Summary Table:
| Material | Max Temperature | Ideal Atmosphere | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) | Up to 1800°C (3272°F) | Air | High-temperature ceramics, heat treatment in air |
| Graphite / CFC | Very High (>1800°C) | Vacuum / Inert Gas | Sintering, powder metallurgy, vacuum furnaces |
| Metallic Alloys (FeCrAl, Nichrome) | Up to ~1400°C (2552°F) | Air | General lab work, heat treating, kilns |
Ready to Optimize Your Furnace Performance?
Choosing the correct heating element is critical for the safety, efficiency, and repeatability of your laboratory or industrial processes. The wrong material can lead to premature failure, process contamination, or inconsistent results.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our experts understand the intricate balance between temperature, atmosphere, and application. We can help you select the perfect furnace with the right heating element—whether you need the extreme heat of MoSi₂, the vacuum capabilities of graphite, or the cost-effectiveness of metallic alloys.
Let us help you achieve reliable and repeatable results. Contact our heating experts today for a personalized consultation to find the ideal furnace solution for your specific requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the properties of molybdenum heating element? Choose the Right Type for Your Furnace Atmosphere
- What material is used for making heating element? Choose the Right Alloy for Your Application
- What are SiC components? Transform Your Power Electronics with Superior Efficiency and Density
- What is the purpose of using a Pt-Rh thermocouple in magnesium experiments? Ensure Precise Vapor Collection
- What are the advantages of integrating electric heating cartridges with thermocouple control systems? Precision Thermal Control
- Where are heating elements located within a hot zone? Expert Guide on Placement for Optimal Uniformity
- How often do heating elements need to be replaced? Maximize Lifespan by Understanding Failure Causes
- What are the heating elements for high temperature furnaces? Select the Right Element for Your Atmosphere



















