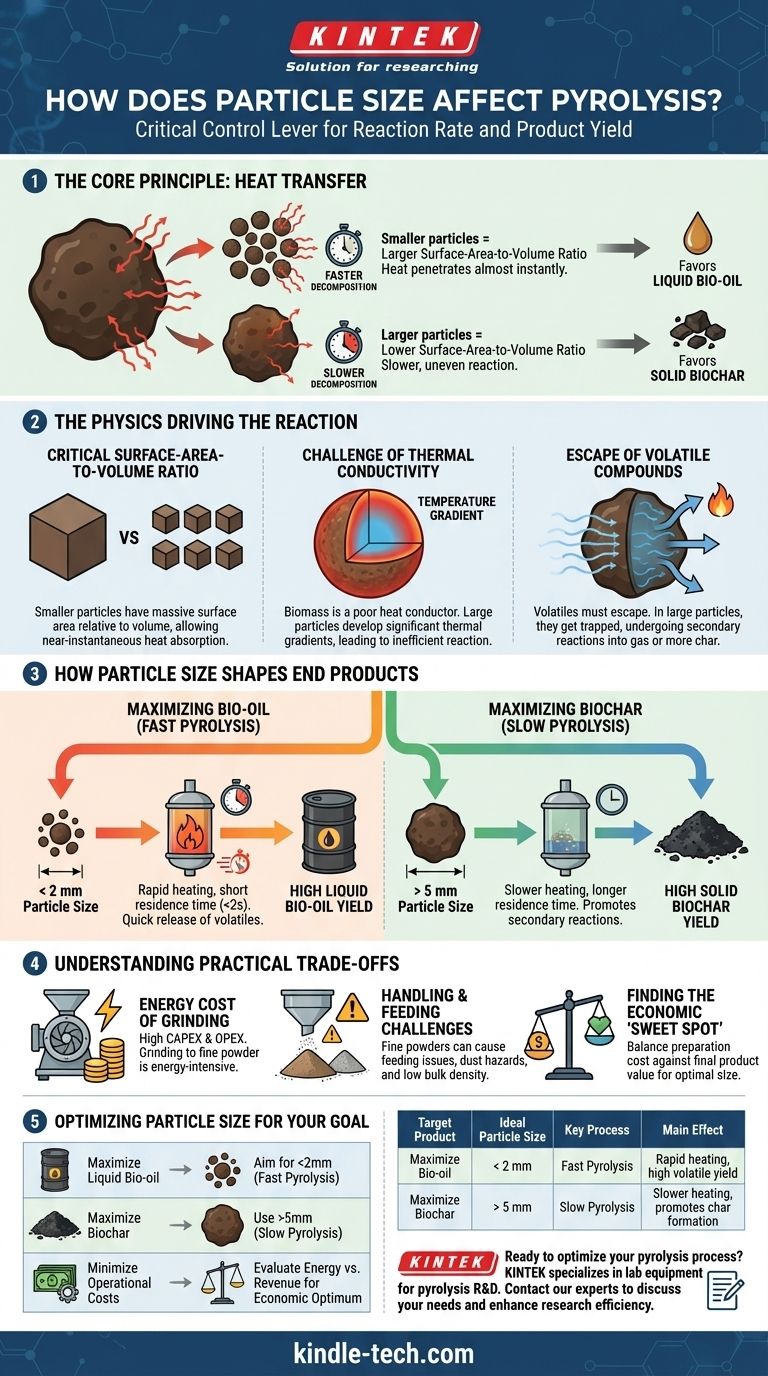
In pyrolysis, particle size is a critical control lever. It directly governs the rate and efficiency of the thermal decomposition process. As a general rule, smaller particles decompose much more quickly due to superior heat transfer, which tends to favor the production of liquid bio-oil. Conversely, larger particles react more slowly, a condition that often increases the yield of solid biochar.
The core principle is heat transfer. Smaller particles possess a much higher surface-area-to-volume ratio, allowing heat to penetrate the material almost instantly. This speed dictates the entire reaction pathway and, consequently, the final distribution of oil, char, and gas.

The Physics Driving the Reaction
The effect of particle size isn't arbitrary; it's governed by fundamental principles of heat and mass transfer. Understanding this is key to optimizing any pyrolysis system.
The Critical Surface-Area-to-Volume Ratio
Every particle has a surface that absorbs heat and an internal volume that needs to be heated. As a particle gets smaller, its surface area decreases far more slowly than its volume.
This means a small particle has a massive amount of surface area relative to its tiny internal volume. It can therefore absorb heat and transfer it to its core almost instantaneously.
The Challenge of Thermal Conductivity
Biomass and other common feedstocks are typically poor conductors of heat—they are effective insulators.
In a large particle, this creates a significant temperature gradient. The outside surface can be at the target temperature while the core remains much cooler, leading to an uneven and inefficient reaction.
The Escape of Volatile Compounds
Pyrolysis works by breaking down solid material into vapors and gases (volatiles), leaving behind solid char. These volatiles must escape the particle to be collected as bio-oil.
In large particles, these vapors have a longer, more difficult path to travel. They can become trapped within the particle's structure, where they undergo secondary reactions, often cracking into non-condensable gases or re-polymerizing into more char.
How Particle Size Shapes Your End Products
Your target product—whether it's oil, char, or gas—will determine your ideal particle size. The choice directly influences the dominant reaction conditions within the reactor.
Maximizing Bio-oil (Fast Pyrolysis)
To maximize liquid bio-oil, you need fast pyrolysis. This process requires extremely rapid heating rates and a very short residence time for the vapors (typically less than two seconds).
Small particles (often less than 2 mm) are essential for this. Their rapid heat-up ensures the entire particle reaches pyrolysis temperature almost instantly, quickly releasing volatiles before they can undergo those value-destroying secondary reactions.
Maximizing Biochar (Slow Pyrolysis)
To maximize biochar, you need slow pyrolysis. This process uses much slower heating rates and longer residence times.
Larger particles (often greater than 5 mm) are suitable here. The slow penetration of heat and the longer residence time of vapors within the particle's structure encourage the secondary reactions that lead to the formation of more stable, solid carbon (char).
Understanding the Practical Trade-offs
While smaller is often better for certain products, simply grinding your feedstock to a fine powder is not always the best overall strategy. The ideal size is an economic and engineering compromise.
The Energy Cost of Grinding
Size reduction, or comminution, is an energy-intensive process. Grinding feedstock to a very fine powder requires significant electrical energy and specialized equipment, adding to both your capital (CAPEX) and operational (OPEX) costs.
Handling and Feeding Challenges
Extremely fine powders can be difficult to work with. They can cause issues with feeding mechanisms, create dust explosion hazards, and have a low bulk density, making storage and transport inefficient.
Finding the Economic "Sweet Spot"
The goal is not necessarily to use the smallest particle possible. It is to find the optimal size that balances the cost of preparation against the value of the final product yields for your specific technology and market.
Optimizing Particle Size for Your Pyrolysis Goal
Selecting the right particle size is a strategic decision tied directly to your desired outcome and operational constraints.
- If your primary focus is maximizing liquid bio-oil yield: Aim for very small particles (typically <2 mm) to enable the rapid and uniform heating required for fast pyrolysis.
- If your primary focus is producing high-quality biochar: Use larger particles (often >5 mm) to facilitate slower, more controlled heating that encourages char formation.
- If your primary focus is minimizing operational costs: Evaluate the energy expenditure of grinding against the potential increase in revenue from a higher-value product to find your economic optimum.
Ultimately, mastering particle size is about controlling heat transfer, which gives you direct command over the final products of your pyrolysis system.
Summary Table:
| Target Product | Ideal Particle Size | Key Process | Main Effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maximize Bio-oil | < 2 mm | Fast Pyrolysis | Rapid heating, high volatile yield |
| Maximize Biochar | > 5 mm | Slow Pyrolysis | Slower heating, promotes char formation |
Ready to optimize your pyrolysis process? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for pyrolysis research and development. Whether you're focusing on bio-oil, biochar, or gas production, our expertise can help you select the right equipment to achieve precise control over particle size and reaction conditions. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's pyrolysis needs and enhance your research efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Why are high temperatures required when sintering stainless steels? Unlock Pure, High-Density Results
- How is a high-temperature calcination furnace utilized in BZY20 Sol-gel? Achieve Pure Cubic Perovskite Phases
- What are the advantages of using a rotary tube furnace for MoVOx catalysts? Elevate Uniformity and Crystallinity
- What is the range of pyrolysis? Master Temperature Control for Optimal Bio-Product Yields
- What is the difference between pyrolysis combustion and gasification? A Guide to Thermal Conversion Technologies



















