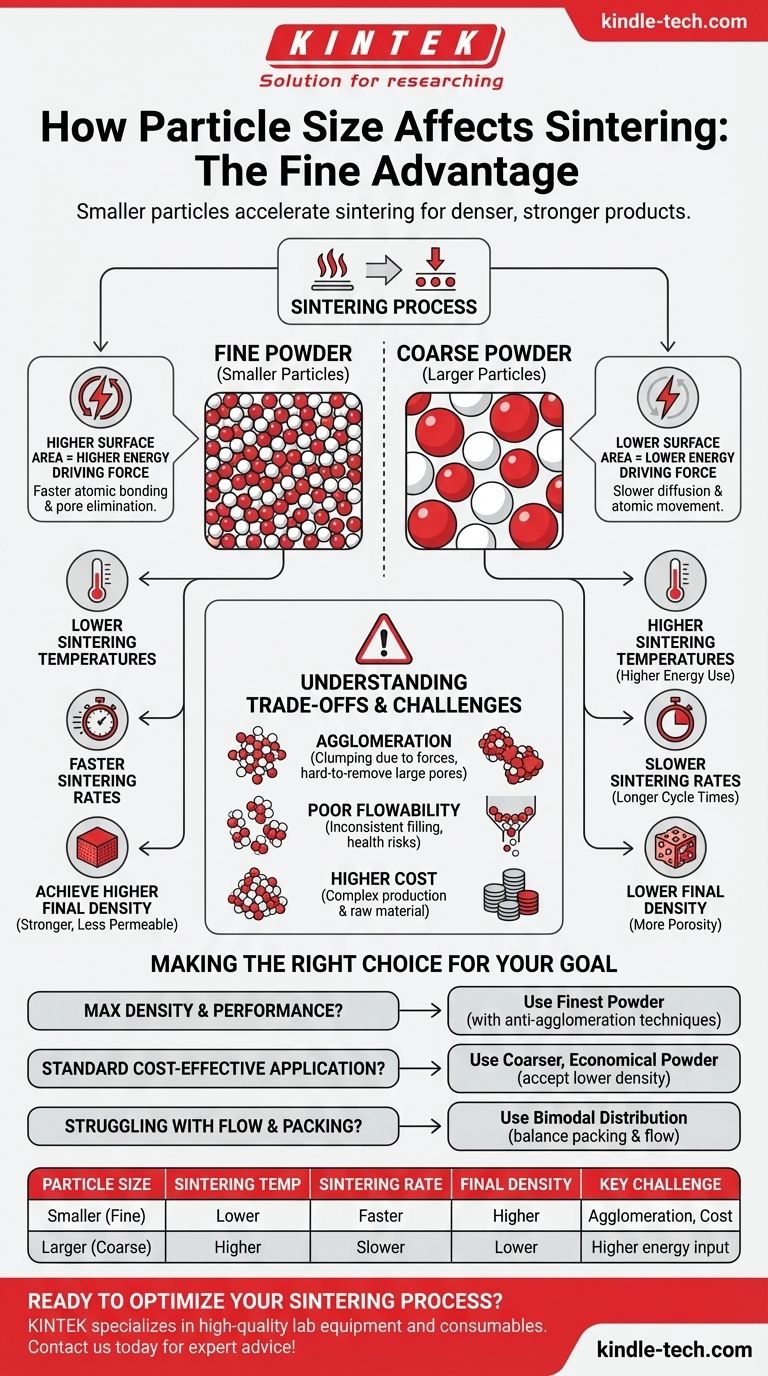
In short, smaller particle sizes fundamentally accelerate the sintering process. Using a powder with finer particles allows you to achieve a dense, solid final product more quickly and at lower temperatures. This is because the total surface area of a fine powder is vastly greater than that of a coarse powder of the same weight, which dramatically increases the driving force for densification.
The core reason particle size is so critical is that sintering is driven by the reduction of surface energy. Smaller particles possess a much higher collective surface area, providing more available energy to fuel the atomic bonding and pore elimination that defines the process.

The Driving Force Behind Sintering
Sintering as a Quest for Lower Energy
Sintering compacts a loose powder into a solid mass using heat and pressure, but importantly, this occurs below the material's melting point.
The process works because individual particles have a high amount of surface energy. The system is inherently unstable and "wants" to reduce this energy. It achieves this by forming bonds between particles and eliminating the empty spaces (pores), which reduces the total surface area.
The Power of Surface-to-Volume Ratio
The key to understanding particle size is the surface-area-to-volume ratio. Imagine a single, one-kilogram stone. Now, imagine that same stone crushed into one kilogram of fine sand.
The sand has a vastly greater total surface area than the single stone. This same principle applies to metal or ceramic powders used in sintering.
How Smaller Particles Increase Driving Force
Because a collection of smaller particles has an exponentially higher total surface area, it also has much higher total surface energy.
This higher energy state creates a stronger thermodynamic "push" for the system to consolidate. This increased driving force is why finer powders sinter more effectively.
Practical Consequences of Using Finer Powders
Lower Sintering Temperatures
With a higher driving force, the atomic diffusion required for particles to bond can occur at lower temperatures.
This is a significant advantage, as it reduces energy consumption, lowers thermal stress on equipment, and can help prevent undesirable grain growth in the final material, which often preserves mechanical strength.
Faster Sintering Rates
The process of densification happens more quickly. The atoms don't have to travel as far to form a bond between neighboring particles, and the stronger driving force accelerates this movement.
This directly translates to shorter cycle times in a manufacturing environment, increasing throughput.
Achieving Higher Final Density
The ultimate goal of most sintering operations is to eliminate porosity. Smaller particles pack together more efficiently from the start, leaving smaller initial pores.
These smaller pores are much easier to close and eliminate during the sintering cycle, resulting in a final product that is denser, stronger, and less permeable.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
The Problem of Agglomeration
While ideal in theory, very fine powders present a significant practical challenge: agglomeration.
Due to strong inter-particle forces (like van der Waals forces), fine particles have a powerful tendency to clump together. These clumps, or agglomerates, behave like large particles, creating large, stubborn pores between them that are extremely difficult to remove during sintering. This can defeat the purpose of using a fine powder.
Handling and Processing Difficulties
Extremely fine powders often have poor flowability. They do not flow smoothly from hoppers into molds, which can lead to inconsistent filling and variations in final part density.
Furthermore, fine airborne particles can pose a health and safety risk, requiring more stringent handling protocols.
The Cost Factor
Producing powders that are both extremely fine and uniform in size is a more complex and expensive process.
The cost of the raw material must be weighed against the desired performance benefits of using a finer powder.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal particle size is not a universal constant but a strategic choice based on your specific objectives and processing capabilities.
- If your primary focus is maximum density and final performance: Use the finest powder you can effectively process, but you must invest in techniques (like spray drying or using binders) to prevent agglomeration.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for a standard application: A coarser, more economical powder may be entirely sufficient, accepting slightly lower density or a need for higher sintering temperatures.
- If you are struggling with powder flow and packing: A powder with a mixed (bimodal) distribution of particle sizes can sometimes provide a practical balance, improving packing density over a coarse powder while maintaining better flow than a uniformly fine one.
By mastering the relationship between particle size and sintering, you gain precise control over the properties, cost, and efficiency of your material manufacturing process.
Summary Table:
| Particle Size | Sintering Temperature | Sintering Rate | Final Density | Key Challenge |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Smaller (Fine) | Lower | Faster | Higher | Agglomeration, Cost |
| Larger (Coarse) | Higher | Slower | Lower | Higher energy input required |
Ready to optimize your sintering process with the right powder? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for precise powder handling and sintering. Our experts can help you select the ideal materials to achieve superior density, lower costs, and faster production times. Contact us today to discuss your specific laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory High Throughput Tissue Grinding Mill Grinder
- Laboratory Hybrid Tissue Grinding Mill
- Laboratory Disc Cup Vibratory Mill for Sample Grinding
- Laboratory Jar Ball Mill with Alumina Zirconia Grinding Jar and Balls
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
People Also Ask
- How does particle size affect XRF? Achieve Accurate and Repeatable Elemental Analysis
- How does a laboratory ball mill contribute to the preparation of raw materials for bio-composite coatings? Unlock Precision
- Which tool could be used to pulverize an object? Match the Tool to Your Material's Hardness and Brittleness
- What tools are used for battery research and material processing? Enhance Your Lab's Material Prep with KINTEK
- How much balls should be loaded in a ball mill for working? Optimize Grinding with the Correct Ball Charge



















