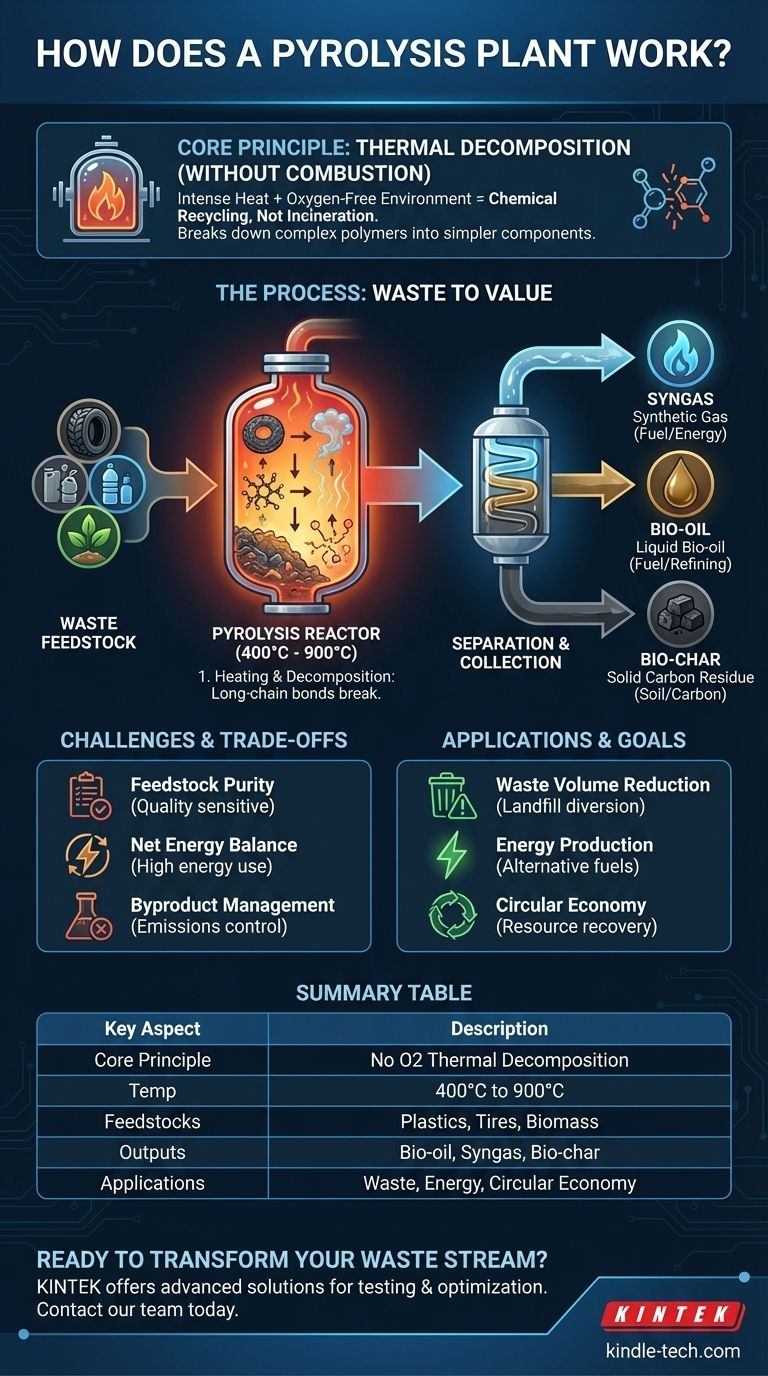
At its core, a pyrolysis plant works by using intense heat in a completely oxygen-free environment to break down waste materials. This process, known as thermal decomposition, avoids combustion (burning) and instead chemically reverts complex organic materials like plastic, tires, or biomass back into their simpler, valuable components: a synthetic gas (syngas), a liquid bio-oil, and a solid carbon residue called bio-char.
The critical concept to grasp is that pyrolysis is not incineration. It is a form of chemical recycling that operates like a reverse factory, deconstructing complex polymers and organic matter into their fundamental molecular building blocks without burning them.

The Core Principle: Thermal Decomposition Without Combustion
Pyrolysis is a thermochemical process that fundamentally alters the state of matter. It hinges on one critical condition: applying extreme heat while strictly excluding oxygen.
The Role of an Oxygen-Free Environment
By heating materials in an inert, oxygen-free atmosphere, the plant prevents combustion from occurring. Without oxygen, the material cannot burn and release pollutants in the same way.
Instead of burning, the intense heat energy targets the chemical bonds holding the large polymer molecules together.
Breaking Chemical Bonds with Heat
The temperatures inside a pyrolysis reactor, typically ranging from 400°C to 900°C, provide enough energy to break the long-chain chemical bonds in organic materials.
This process is often called thermal depolymerization or "cracking." It effectively dismantles complex structures into smaller, more stable molecules.
The Input: From Waste to Feedstock
The process is versatile and can handle a wide range of carbon-based waste.
Common feedstocks include post-consumer plastics, end-of-life vehicle tires, wood waste, agricultural biomass, and even textile scraps. The type and purity of the feedstock directly influence the quality and proportions of the final outputs.
Inside the Pyrolysis Reactor: A Step-by-Step Process
A pyrolysis plant is a closed-loop system designed to carefully manage the feedstock, heat, and output products. The central component of this system is the reactor vessel.
Step 1: Heating in the Reactor
Waste material is fed into the sealed reactor. An external heat source then raises the internal temperature to the target level for decomposition.
The design of the reactor is crucial for ensuring heat is transferred evenly and efficiently throughout the feedstock.
Step 2: Decomposition and Phase Change
As the material heats up, it breaks down. The resulting smaller molecules vaporize into a hot gas within the reactor.
This mixture of hot gases contains the valuable hydrocarbons that will become the final products.
Step 3: Separation and Collection of Products
This hot gas is piped out of the reactor and into a condensation and separation system. As the gas cools, the different components are collected.
- Bio-oil: The condensable gases cool into a liquid, often called pyrolysis oil or bio-oil, which can be refined into fuel.
- Syngas: The non-condensable gases are collected as syngas, which is often used to power the pyrolysis plant itself, creating a self-sustaining energy loop.
- Bio-char: The solid carbon-rich material left behind in the reactor is the bio-char. This can be used as a soil amendment or processed into high-value activated carbon.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While a powerful technology, the practical application of pyrolysis involves important considerations and is not a perfect solution for all scenarios.
Feedstock Quality is Critical
The process is highly sensitive to the purity of the input material. Contaminants like metals, glass, or certain types of plastics can reduce the quality of the outputs or damage the equipment.
Energy Balance and Efficiency
A pyrolysis plant requires a significant amount of energy to reach and maintain its high operating temperatures. A well-designed plant will use its own syngas output to power the process, but achieving a positive net energy balance is a key engineering challenge.
Managing Byproducts
The "no harmful byproducts" claim is an ideal. In reality, the process requires sophisticated control and cleaning systems to manage emissions and ensure the final products meet quality specifications, as contaminants from the feedstock can end up in the oil or char.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The value of a pyrolysis plant is defined by its intended purpose. Understanding your primary objective is key to evaluating its suitability.
- If your primary focus is waste volume reduction: Pyrolysis is extremely effective at converting bulky waste like tires and plastics into denser, more manageable, and valuable commodities, significantly reducing landfill burden.
- If your primary focus is energy production: The technology excels at creating bio-oil and syngas, which can serve as alternative fuels for power generation or industrial heating, turning waste into a reliable energy source.
- If your primary focus is a circular economy: The process can recover valuable carbon in the form of bio-char for agricultural use or as a precursor for materials like activated carbon, closing the loop on waste streams.
Ultimately, a pyrolysis plant provides a powerful method for transforming what was once considered a liability into a valuable resource.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Thermal decomposition in an oxygen-free environment (no combustion). |
| Typical Temperature | 400°C to 900°C. |
| Common Feedstocks | Plastics, tires, biomass, wood waste. |
| Main Outputs | Bio-oil, Syngas, Bio-char. |
| Primary Applications | Waste reduction, energy production, circular economy. |
Ready to transform your waste stream into valuable products? A pyrolysis plant is a significant investment, and choosing the right technology is critical for success. At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced laboratory equipment and analytical solutions that can help you test your feedstocks, optimize your pyrolysis process, and ensure the quality of your final products. Our experts are here to support your R&D and scaling efforts. Contact our team today to discuss how we can help you achieve your waste-to-resource goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Multi-zone Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Customizable PEM Electrolysis Cells for Diverse Research Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products



















