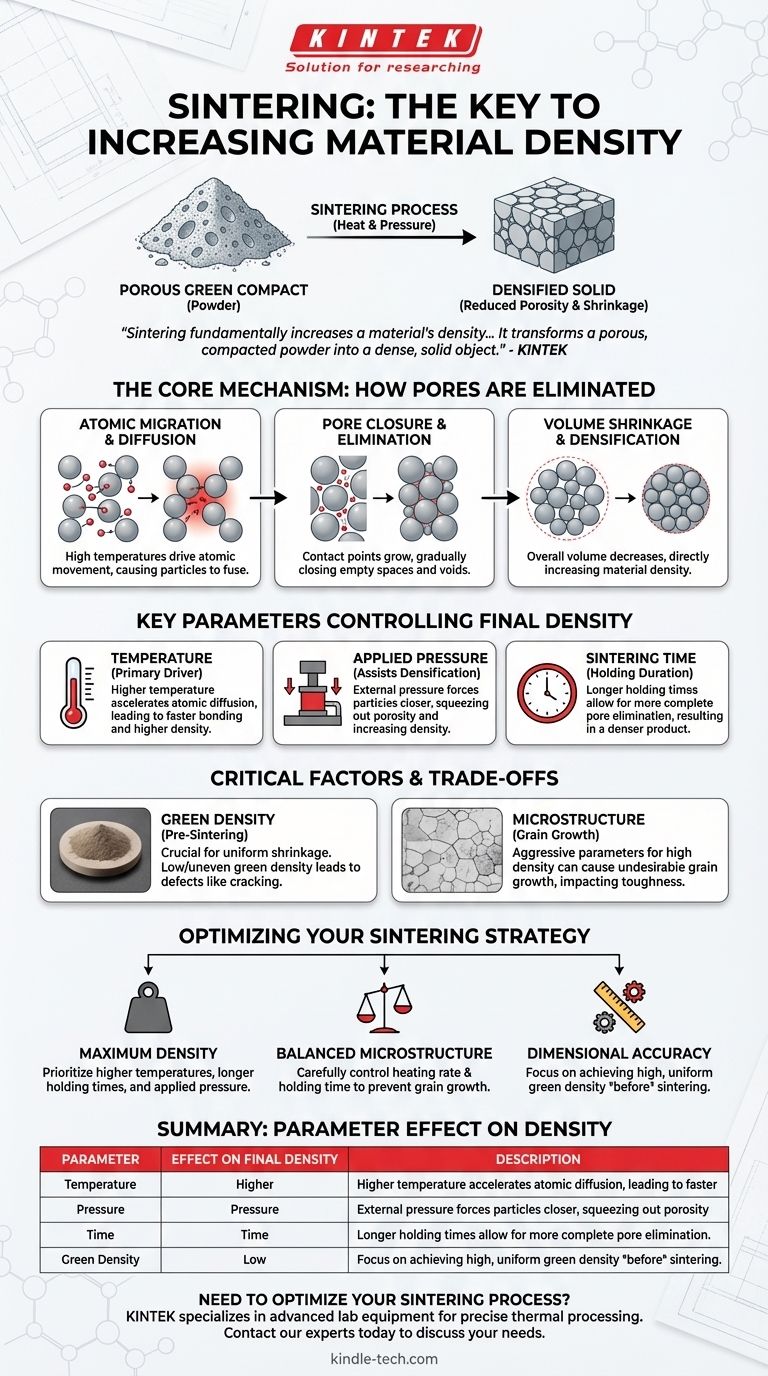
In short, sintering fundamentally increases a material's density. It is a thermal process that transforms a porous, compacted powder into a dense, solid object. By applying heat below the material's melting point, sintering causes the individual particles to bond, systematically eliminating the empty spaces (pores) between them and causing the entire part to shrink and densify.
The core purpose of sintering is densification. It is a controlled engineering process designed to reduce or eliminate the porosity inherent in a compacted powder, thereby increasing its density, strength, and other critical material properties.

The Core Mechanism: From Powder to Solid
Sintering is the critical step that converts a fragile "green" compact made of pressed powder into a robust, functional component. This transformation is driven by the reduction of empty space within the material.
The Goal of Densification
The primary objective of sintering is to achieve a dense, solid body. This process gives the material its characteristic strength and durability by creating strong metallurgical bonds between its constituent particles.
How Pores are Eliminated
At high temperatures, atoms migrate across the surfaces of the powder particles. This material transfer causes the particles to fuse together at their contact points, gradually closing the pores and voids that exist between them.
The Result is Shrinkage
As the internal pores are eliminated, the overall volume of the component decreases. This volume shrinkage is a direct and expected consequence of the increase in density. Advanced ceramics, for example, can shrink by as much as 20-25% during sintering.
Key Parameters That Control Final Density
Achieving the desired final density is not arbitrary; it is controlled by carefully manipulating several key process parameters.
Sintering Temperature
Temperature is the primary driver of the sintering process. Higher temperatures (while remaining below the melting point) accelerate the rate of atomic diffusion, leading to faster bonding, more effective pore closure, and ultimately, higher density.
Applied Pressure
In processes like hot pressing, external pressure is applied during the thermal cycle. This pressure physically forces the particles closer together, squeezing out porosity and significantly aiding the densification process.
Sintering Time (Holding Time)
The duration for which the material is held at the peak sintering temperature is critical. Longer holding times allow the atomic diffusion process more time to complete, resulting in a more thorough elimination of pores and a denser final product.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Critical Factors
While the goal is often maximum density, the process involves important considerations and potential pitfalls that must be managed.
The Importance of "Green" Density
The density and uniformity of the powder compact before sintering begins—its green density—is crucial. A low or non-uniform green density will lead to uncontrolled, uneven shrinkage, which can cause part distortion, internal stresses, or cracking.
Microstructure is Also Affected
Sintering does more than just increase density. It also fundamentally alters the material's microstructure, including its grain size, the shape of grain boundaries, and the distribution of any remaining pores. Aggressive sintering parameters that achieve high density can sometimes lead to undesirable grain growth, which may negatively impact other properties like toughness.
Optimizing Sintering for Your Density Goal
The ideal sintering strategy depends entirely on the desired outcome for the final component. You must balance the need for density against other critical material properties.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum possible density: Optimize for higher temperatures, longer holding times, and the application of external pressure where possible.
- If your primary focus is balancing density with a specific microstructure: Carefully control the heating rate and holding time to prevent excessive grain growth while still allowing for sufficient pore closure.
- If your primary focus is dimensional accuracy and repeatability: Prioritize achieving a high and perfectly uniform green density in the powder compact before the sintering process even begins.
Mastering these parameters allows you to precisely engineer the final density and properties of your material.
Summary Table:
| Sintering Parameter | Effect on Final Density |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Higher temperatures accelerate atomic diffusion, leading to faster pore closure and higher density. |
| Pressure | Applied pressure forces particles together, squeezing out porosity and aiding densification. |
| Time | Longer holding times allow more complete pore elimination, resulting in a denser product. |
| Green Density | Higher and more uniform initial density ensures controlled shrinkage and minimizes defects. |
Need to optimize your sintering process for maximum density and performance? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for precise thermal processing. Whether you're working with metals, ceramics, or advanced powders, our solutions help you achieve the perfect balance of density, strength, and microstructure. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's sintering needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace? Superior Density for Nanocrystalline Fe3Al
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing furnace? Achieve 98.9% Density in Al2O3-TiC Laminated Ceramics
- What are the advantages of vacuum sintering? Achieve Superior Purity, Strength, and Performance
- What are the key functions of a vacuum hot press sintering furnace? Produce High-Density UN Ceramic Pellets
- What technical advantages does a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace provide? Enhance Fe-Ni/Zr2P2WO12 Composite Density



















