At its core, sintering is a thermal process that fuses ceramic powder particles into a solid, dense object. It achieves this by applying high heat, sometimes with pressure, to consolidate the material without melting it. This transformation is driven by atomic diffusion, where atoms migrate between particles, eliminating the pores between them and creating a strong, unified structure.
The true purpose of sintering is not just to bond particles together, but to fundamentally re-engineer the material's internal microstructure. It's the critical step that transforms a loose powder into a high-performance polycrystalline ceramic with specific, desirable properties.

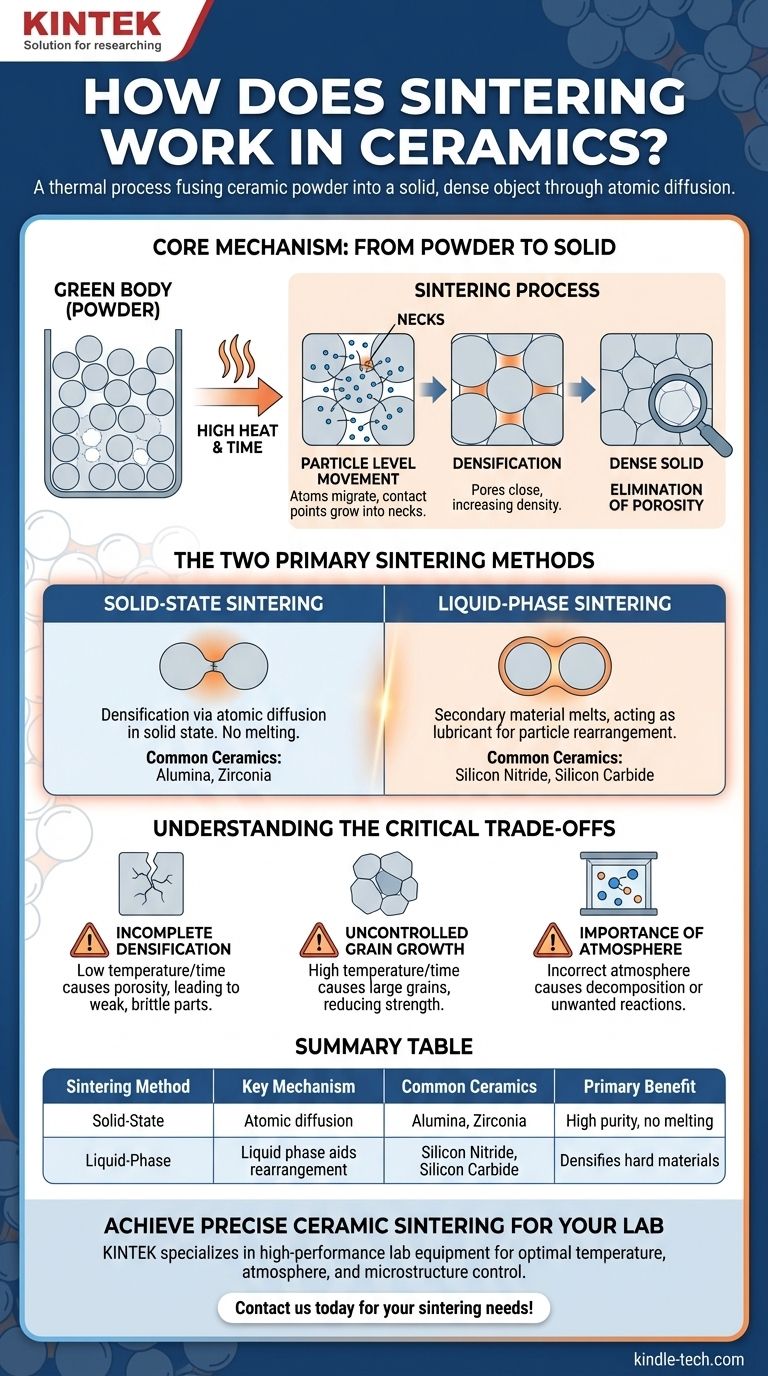
The Core Mechanism: From Powder to Solid
Sintering is the bridge between a shaped powder, often called a "green body," and a finished, durable ceramic component. The process is governed by precise atomic-level movements.
What Happens at the Particle Level?
Under high heat, atoms in the ceramic particles become more mobile. They begin to move and migrate across the boundaries where particles touch, a process known as diffusion. This mass transfer causes the contact points between particles to grow into "necks."
As these necks widen, the particles pull closer together. This movement gradually closes the empty spaces, or pores, that existed in the original powder compact.
The Goal: Densification
The primary objective of sintering is densification. By eliminating porosity, the process dramatically increases the material's density. This results in a porcelain body with a stable shape, uniform internal structure, and significantly improved mechanical strength.
The Two Primary Sintering Methods
Ceramics are sintered using one of two main approaches, chosen based on the material's intrinsic properties.
Solid-State Sintering
This is the most common method, used for ceramics like alumina and zirconia. In solid-state sintering, densification occurs entirely through atomic diffusion in the solid material. No melting is involved. The particles fuse directly with one another as material migrates to fill the voids.
Liquid-Phase Sintering
This method is used for harder-to-densify ceramics like silicon nitride and silicon carbide. It involves adding a small amount of a secondary material that melts at the sintering temperature.
This temporary liquid phase coats the ceramic particles. It acts as a lubricant, allowing particles to slide and rearrange more easily due to capillary forces, which accelerates densification. The liquid then solidifies upon cooling, becoming part of the final ceramic matrix.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
While sintering is essential, its success hinges on precise control. The process is not merely about applying heat; it's about managing a delicate balance to achieve the desired outcome.
The Risk of Incomplete Densification
If the temperature is too low or the time is too short, the diffusion process will be incomplete. This leaves behind significant porosity, resulting in a weak, brittle component that fails to meet performance requirements for applications like cutting tools or insulators.
The Challenge of Uncontrolled Grain Growth
Conversely, if the temperature is too high or held for too long, the grains within the ceramic can grow excessively large. While the part may be dense, large grains can often reduce mechanical strength and fracture toughness. The goal is a dense material with a fine, uniform grain structure.
The Importance of Atmosphere
The atmosphere inside the furnace is a critical parameter. It can prevent or promote chemical reactions with the ceramic material. An incorrect atmosphere can lead to decomposition or unwanted chemical changes, compromising the material's final properties, such as its electrical insulating capability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The control of sintering parameters directly dictates the final properties of the ceramic, making it the most important step in fabrication.
- If your primary focus is high-purity components: Solid-state sintering is the preferred method, as it avoids the introduction of additives that could act as contaminants.
- If your primary focus is densifying very hard materials: Liquid-phase sintering is often the only practical way to achieve full density and superior mechanical properties.
- If your primary focus is maximum performance: Precise control over temperature, time, and atmosphere is non-negotiable to create the ideal microstructure for strength, hardness, and thermal stability.
Ultimately, mastering the sintering process is what unlocks the full engineering potential of advanced ceramic materials.
Summary Table:
| Sintering Method | Key Mechanism | Common Ceramics | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solid-State Sintering | Atomic diffusion in solid state | Alumina, Zirconia | High purity, no melting |
| Liquid-Phase Sintering | Liquid phase aids particle rearrangement | Silicon Nitride, Silicon Carbide | Enables densification of hard materials |
Ready to achieve precise ceramic sintering for your lab? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables for advanced ceramic processing. Our sintering furnaces and expertise ensure optimal temperature control, atmosphere management, and microstructural results for materials like alumina, zirconia, and silicon nitride. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's sintering needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
People Also Ask
- What is the construction of a muffle furnace? A Deep Dive into Its Core Systems
- What are muffle furnaces used for? Achieve Precise, Contaminant-Free High-Temperature Processing
- How accurate is the muffle furnace? Achieve ±1°C Control and ±2°C Uniformity
- What is the precaution for muffle furnace? Essential Safety Protocols for Lab Excellence
- What is the temperature range of a laboratory muffle furnace? Find the Right Model for Your Application



















