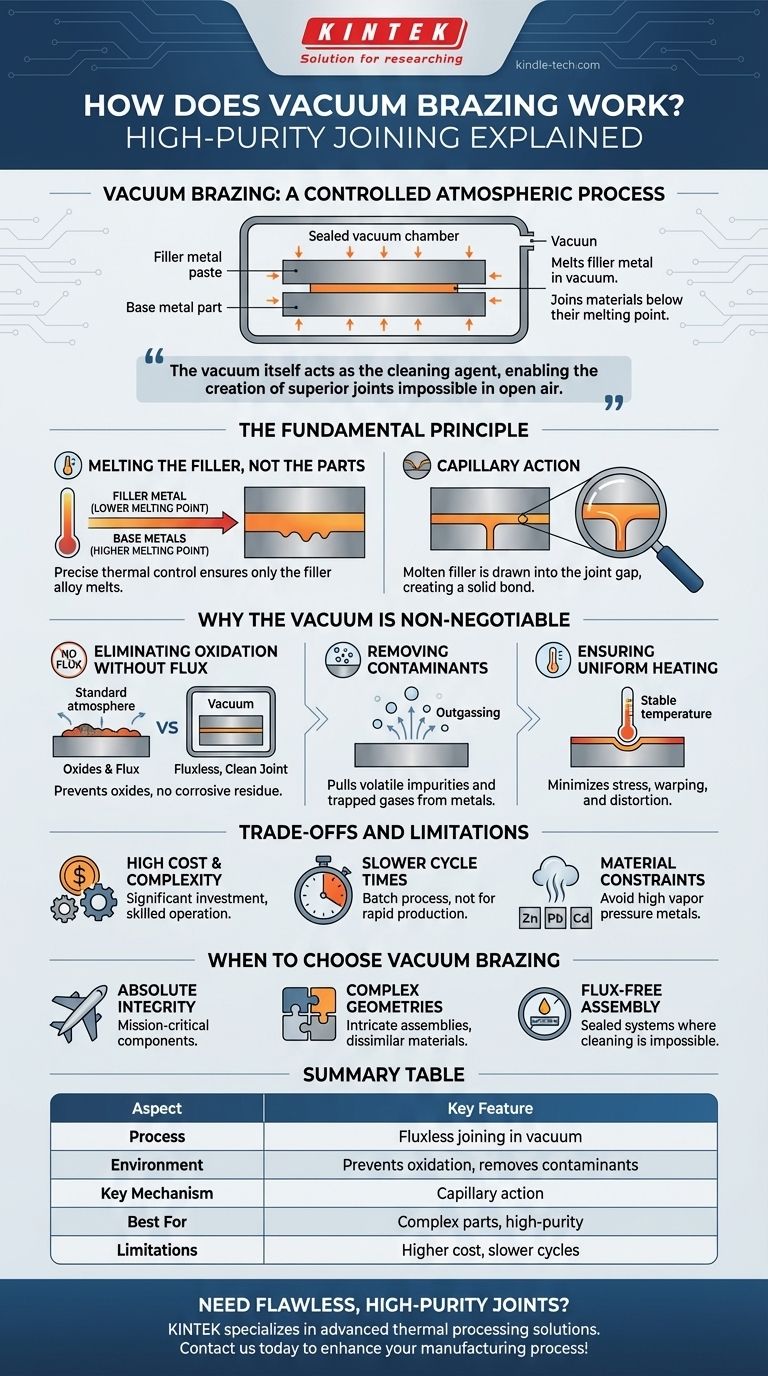
At its core, vacuum brazing is a high-purity method for joining materials by melting a filler metal between them inside a vacuum chamber. The process heats an assembly to a temperature high enough to melt the filler metal, but below the melting point of the components being joined. The vacuum environment prevents oxidation and removes contaminants, resulting in an exceptionally strong, clean, and flux-free bond.
The critical insight is that vacuum brazing isn't just a joining technique; it's a controlled atmospheric process. The vacuum itself acts as the cleaning agent, enabling the creation of superior joints that would be impossible to achieve in open air.

The Fundamental Principle: Melting the Filler, Not the Parts
Vacuum brazing operates on a simple but precise thermal principle. The success of the entire process hinges on the distinct melting points of the materials involved.
The Role of the Filler Metal
The filler metal (also called a brazing alloy) is the key ingredient. It is specifically chosen to have a melting point significantly lower than the base metals (the parts being joined).
This filler metal, often in the form of a paste, foil, or wire, is placed at the joint before the heating process begins.
The Importance of Temperature Control
The entire assembly is heated uniformly inside a vacuum furnace. The temperature is carefully raised above the melting point of the filler metal but is kept safely below the melting point of the base metals.
This ensures the components being joined remain solid and dimensionally stable, while only the filler alloy becomes liquid.
Capillary Action: The Driving Force
Once the filler metal melts, a natural phenomenon called capillary action takes over. The liquid alloy is automatically drawn into the tight gap between the base metal parts, much like a paper towel wicks up water.
This action ensures the joint is completely filled, creating a solid, continuous metallic bond once the assembly cools.
Why the Vacuum is Non-Negotiable
The use of a vacuum chamber is what elevates this process beyond standard brazing. The low-pressure environment is not passive; it actively contributes to the quality of the joint.
Eliminating Oxidation Without Flux
In a normal atmosphere, heating metals causes them to form oxides on their surfaces, which prevent a strong bond. Traditional brazing fights this with a chemical flux, which leaves behind a corrosive residue that must be cleaned.
Vacuum brazing is fluxless. By removing nearly all the oxygen from the chamber, the vacuum prevents oxides from forming in the first place. It can even remove existing light oxides from the metal surfaces.
Removing Contaminants
The vacuum actively pulls volatile impurities and trapped gases out of the base metals as they are heated. This process, known as outgassing, purifies the joint area and eliminates potential sources of weakness or porosity.
Ensuring Uniform Heating
A vacuum furnace provides extremely even and stable heating. This controlled thermal environment minimizes stress on the components, reducing the risk of warping or distortion, which is especially critical for complex or delicate assemblies.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, vacuum brazing is a specialized process with specific considerations. It is not the right solution for every application.
High Initial Cost and Complexity
Vacuum furnaces represent a significant capital investment. They are complex machines that require skilled operators and rigorous maintenance schedules, making the process more expensive than conventional joining methods.
Slower Cycle Times
Heating an entire furnace chamber, allowing the components to "soak" at the brazing temperature, and then cooling it back down is a time-consuming batch process. This makes it less suitable for high-volume, rapid production compared to methods like automated welding.
Material Constraints
Certain materials are not suitable for vacuum brazing. Metals with high vapor pressures, such as zinc, lead, or cadmium, can vaporize in the vacuum at brazing temperatures. This can contaminate the furnace and compromise the joint integrity of the part itself.
When to Choose Vacuum Brazing
The decision to use vacuum brazing should be driven by the demands of the final application.
- If your primary focus is absolute joint integrity and cleanliness: It is the ideal choice for mission-critical components in aerospace, medical implants, and high-performance scientific equipment where failure is not an option.
- If your primary focus is joining complex geometries or dissimilar materials: It excels at creating strong bonds in intricate assemblies or between materials like metal and ceramic that cannot be welded.
- If your primary focus is creating a flux-free assembly: It is essential for internal components of sealed systems, such as vacuum tubes or sensors, where post-braze cleaning is impossible.
Ultimately, vacuum brazing is the definitive choice when process control, purity, and metallurgical quality are more important than cost or production speed.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Feature |
|---|---|
| Process | Fluxless joining in a vacuum chamber |
| Environment | Prevents oxidation, removes contaminants |
| Key Mechanism | Capillary action draws molten filler metal |
| Best For | Complex geometries, dissimilar materials, high-purity applications |
| Limitations | Higher cost, slower cycle times, material constraints (e.g., zinc, cadmium) |
Need flawless, high-purity joints for your critical components? KINTEK specializes in advanced thermal processing solutions, including vacuum brazing systems tailored for aerospace, medical, and laboratory equipment. Our expertise ensures superior bond integrity, cleanliness, and performance for your most demanding applications. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your manufacturing process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the process of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock Purity in High-Temperature Processing
- What is vacuum brazing? The Ultimate Guide to High-Purity, Flux-Free Metal Joining
- Does brazing require heat? Yes, it's the catalyst for creating strong, permanent bonds.
- What are vacuum furnaces used for? Unlock Ultimate Material Purity and Performance



















