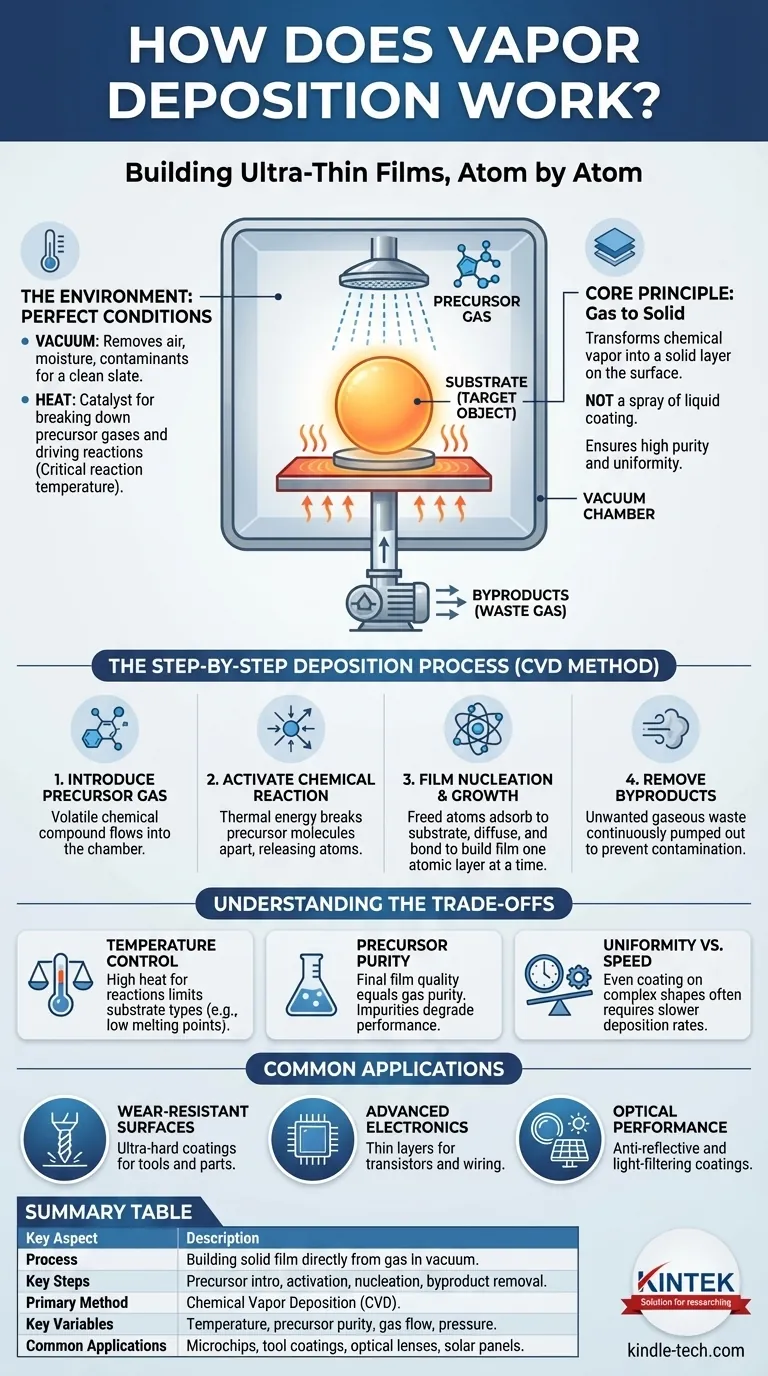
At its core, vapor deposition is a process for building an ultra-thin solid film on a surface, one layer of atoms at a time. It works by introducing a material in its gaseous state—the "vapor"—into a controlled chamber containing the object to be coated. Through a carefully managed process involving heat and pressure, this vapor reacts or condenses onto the object's surface, transforming back into a solid and forming a new, high-performance layer.
The fundamental principle of vapor deposition is not about spraying a liquid coating, but about building a solid film directly from a gas. It transforms a chemical vapor into a solid layer on a target surface, ensuring a highly pure and uniform coating that is often impossible to achieve with conventional methods.
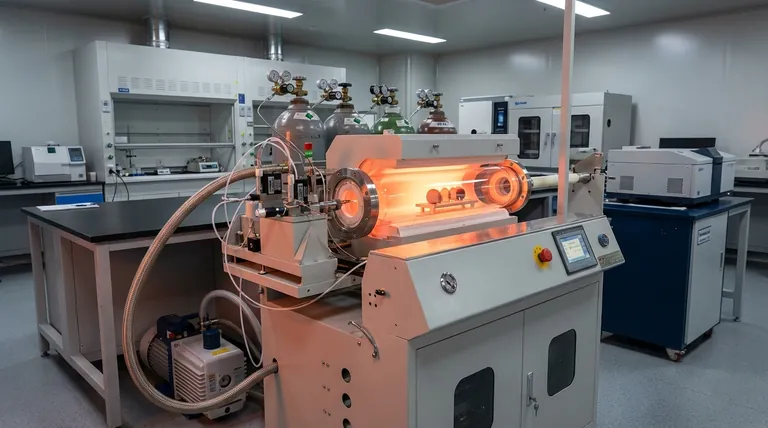

The Environment: Creating the Perfect Conditions
To achieve the necessary precision, the entire process must occur within a highly controlled environment. Each component of this environment plays a critical role in the quality of the final film.
The Role of the Vacuum Chamber
The process almost always takes place in a reaction chamber under vacuum. Creating a vacuum removes unwanted air, moisture, and other particles that could contaminate the final coating and interfere with the chemical reactions. It provides an ultra-clean slate for the deposition to occur.
The Target Object (The Substrate)
The object being coated is known as the substrate. This is the foundation upon which the new film will be built. The substrate's material and its surface condition are critical factors in how well the film adheres.
The Critical Element of Heat
Heat is the primary catalyst in Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), the most common form of this process. The chamber and substrate are heated to a specific reaction temperature, which provides the energy needed to break down the precursor gas and drive the chemical reaction on the substrate's surface.
The Step-by-Step Deposition Process
While there are several variations of vapor deposition, the chemical method (CVD) follows a clear and logical sequence of events to build the film.
Step 1: Introducing the Precursor Gas
A volatile precursor—a chemical compound that easily turns into a gas—is injected into the vacuum chamber. This precursor contains the atoms of the material that will form the final coating (e.g., silicon, titanium, carbon).
Step 2: Activating the Chemical Reaction
As the precursor gas flows over the hot substrate, the thermal energy causes it to either decompose or react with other gases present. This chemical reaction breaks the precursor molecules apart, releasing the desired atoms.
Step 3: Film Nucleation and Growth
The newly freed atoms adsorb, or stick, to the surface of the substrate. They diffuse across the surface until they find stable "growth sites," where they bond with the substrate and each other. This process repeats continuously, building up the coating one atomic layer at a time.
Step 4: Removing Byproducts
The chemical reactions often produce unwanted gaseous byproducts. These waste products are continuously pumped out of the chamber by the vacuum system, preventing them from contaminating the growing film.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Vapor deposition is a powerful but demanding technique. The quality of the outcome is directly tied to the precise control of several key variables, each with its own trade-offs.
Temperature Control is Non-Negotiable
The high temperatures required for most CVD processes are essential for the chemical reaction, but they also limit the types of materials that can be used as substrates. Materials with low melting points or those that degrade with heat cannot be coated using high-temperature CVD.
Precursor Purity Dictates Film Quality
The final film can only be as pure as the precursor gases used to create it. Any impurities in the gas will be incorporated into the film, potentially degrading its performance. This necessitates the use of expensive, high-purity chemicals.
Uniformity vs. Deposition Speed
Achieving a perfectly even coating across a complex, three-dimensional object requires careful management of gas flow and temperature. Often, ensuring high uniformity means slowing down the deposition rate, which increases process time and cost.
How This Process is Applied
The ability to create highly pure, thin, and durable films makes vapor deposition a cornerstone technology in many advanced industries.
- If your primary focus is creating wear-resistant surfaces: This process is used to apply ultra-hard coatings like titanium nitride to cutting tools, drills, and machine parts, dramatically increasing their lifespan.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing advanced electronics: Vapor deposition is absolutely essential for creating the thin layers of silicon, silicon dioxide, and other materials that form the transistors and wiring in every microchip.
- If your primary focus is enhancing optical performance: Thin films are applied to lenses, solar panels, and architectural glass to create anti-reflective, reflective, or light-filtering coatings.
By mastering the control of gases and heat, vapor deposition allows us to engineer materials from the atom up.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | Building a solid film directly from a gas in a vacuum chamber. |
| Key Steps | Precursor gas introduction, thermal activation, nucleation, byproduct removal. |
| Primary Method | Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). |
| Key Variables | Temperature, precursor purity, gas flow, and pressure. |
| Common Applications | Microchips, wear-resistant tool coatings, optical lenses, solar panels. |
Ready to engineer superior surfaces with precision coatings?
KINTEK specializes in providing the high-purity lab equipment and consumables essential for successful vapor deposition processes. Whether you are developing advanced electronics, enhancing optical components, or creating wear-resistant surfaces, our expertise and products support the precise control needed for high-quality film growth.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can help optimize your deposition process and achieve your material performance goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the factors affecting chemical bath deposition? Master pH, Temperature, and Concentration for Superior Thin Films
- Why is physical vapor deposition conducted in a high vacuum? To Ensure Purity and Performance
- What is chemical deposition method? A Guide to High-Performance Thin Film Fabrication
- What is the atmospheric pressure CVD process? A Guide to High-Purity Thin Film Deposition
- What is the advantage of chemical Vapour deposition over oxidation? Unmatched Versatility in Thin Film Deposition
- What are the steps of CVD process? A Guide to Mastering Chemical Vapor Deposition
- What is chemical vapor deposition substrate material? The Foundation for High-Quality Thin Films
- What is thin-film deposition in vacuum? Unlock Superior Surface Properties



















