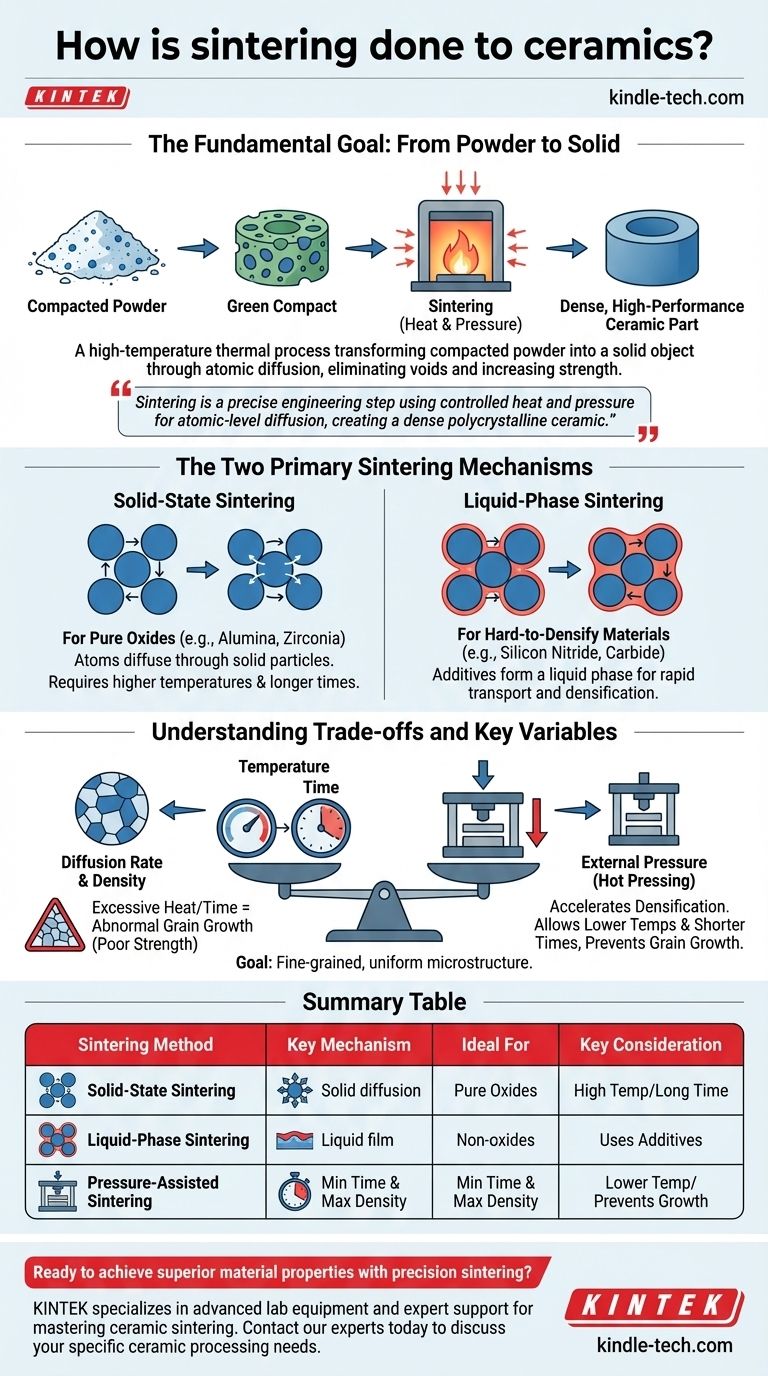
At its core, ceramic sintering is a high-temperature thermal process that transforms a compacted ceramic powder into a solid, dense object. This is achieved by heating the material to a temperature below its melting point, which causes the individual particles to fuse together through atomic diffusion, dramatically increasing the material's strength, hardness, and stability.
Sintering is not simply about heating a material. It is a precise engineering step that uses controlled heat and sometimes pressure to trigger atomic-level diffusion, eliminating the voids between powder particles to create a dense, high-performance polycrystalline ceramic.

The Fundamental Goal: From Powder to Solid
What Sintering Achieves
Sintering is the critical manufacturing step that converts a fragile, porous "green" part made of pressed powder into a robust, dense ceramic component.
The primary mechanism is mass transport, where atoms move from areas of high stress (the contact points between particles) to areas of low stress (the pores or voids). This process gradually closes the pores and bonds the particles into a solid mass.
The Starting Point: The "Green Compact"
The process begins with a "green compact," which is ceramic powder that has been pressed or molded into the desired shape.
The initial porosity of this green compact is a critical factor. A more densely packed initial state will typically result in a denser final product with less required sintering time and temperature.
The Two Primary Sintering Mechanisms
The choice of sintering method depends heavily on the type of ceramic being processed. The two main pathways are solid-state and liquid-phase sintering.
Solid-State Sintering: For Pure Oxides
This method is used for materials like alumina and zirconia. In solid-state sintering, atoms diffuse entirely through the solid particles.
Because diffusion through a solid is a relatively slow process, this method typically requires higher temperatures and longer sintering times to achieve full densification.
Liquid-Phase Sintering: For Hard-to-Densify Materials
This approach is necessary for ceramics that are very difficult to sinter via solid-state diffusion, such as silicon nitride and silicon carbide.
In this process, specific additives are mixed with the ceramic powder. At the sintering temperature, these additives melt and form a thin liquid film around the ceramic particles. This liquid phase acts as a rapid transport medium, allowing particles to rearrange and densify quickly due to capillary forces.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Variables
Successful sintering depends on the precise control of several interconnected parameters. Mismanaging these variables can lead to a component with poor mechanical properties.
The Critical Role of Temperature and Time
Temperature and time are the primary levers for controlling the sintering process. Higher temperatures and longer durations increase the rate of diffusion, leading to greater density.
However, excessive heat or time can cause abnormal grain growth, where some crystals grow much larger than others. This creates a non-uniform microstructure that can severely compromise the material's mechanical strength.
The Impact of External Pressure
Applying external pressure during heating, known as pressure-assisted sintering or hot pressing, can significantly improve the outcome.
Pressure accelerates densification by mechanically forcing particles together, which helps close pores more effectively. This allows for the use of lower sintering temperatures and shorter process times, which in turn helps prevent unwanted grain growth.
Final Properties Depend on Microstructure
Ultimately, the goal is to create a fine-grained, uniform microstructure with minimal porosity. The mechanical strength, hardness, thermal stability, and optical properties of the final ceramic are all direct functions of this sintered microstructure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The correct sintering strategy is dictated by the material you are working with and your performance objectives.
- If your primary focus is processing pure oxide ceramics (like alumina or zirconia): You will rely on solid-state sintering, requiring precise control over high temperatures and long durations to achieve full density.
- If your primary focus is densifying non-oxide ceramics (like silicon carbide): You will need liquid-phase sintering, using carefully selected additives to facilitate densification at more manageable temperatures.
- If your primary focus is minimizing process time and maximizing final density: You should consider a pressure-assisted sintering technique to accelerate pore closure and limit undesirable grain growth.
Mastering the variables of sintering is what transforms a simple ceramic powder into a high-performance engineered material.
Summary Table:
| Sintering Method | Key Mechanism | Ideal For | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solid-State Sintering | Atomic diffusion through solid particles | Pure oxides (e.g., Alumina, Zirconia) | Requires high temperatures & long times |
| Liquid-Phase Sintering | Rapid transport via a liquid film | Non-oxides (e.g., Silicon Nitride, Carbide) | Uses additives to form liquid phase |
| Pressure-Assisted Sintering | Combines heat with external pressure | Minimizing process time & maximizing density | Lower temperatures, prevents grain growth |
Ready to achieve superior material properties with precision sintering?
KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment and expert support needed to master the ceramic sintering process. Whether you are developing new materials or optimizing existing protocols, our solutions help you control critical variables like temperature and pressure to achieve the dense, high-performance ceramics your research demands.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific ceramic processing needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
People Also Ask
- What is the necessity of using ceramic plates to apply stacking pressure in a sandwich configuration? | KINTEK
- What materials can withstand very high temperature? Refractory Metals, Ceramics & Carbon Composites
- What is the temperature resistance of silicon carbide? Withstands Extreme Heat Up to 1500°C
- Why is Silicon Carbide high-conductivity ceramic used in reactors? Create a Protective Slag Layer for Biomass Systems
- What is sintered ceramic? A Durable, Non-Porous Material for Modern Surfaces
- Are ceramics durable? Unlocking Their Strength and Brittleness for Your Application
- Why is alumina used in furnaces? Achieve Unmatched Heat Resistance and Purity
- What is the purpose of multi-step processing for tape-cast green tapes? Mastering Ceramic Density & Performance



















