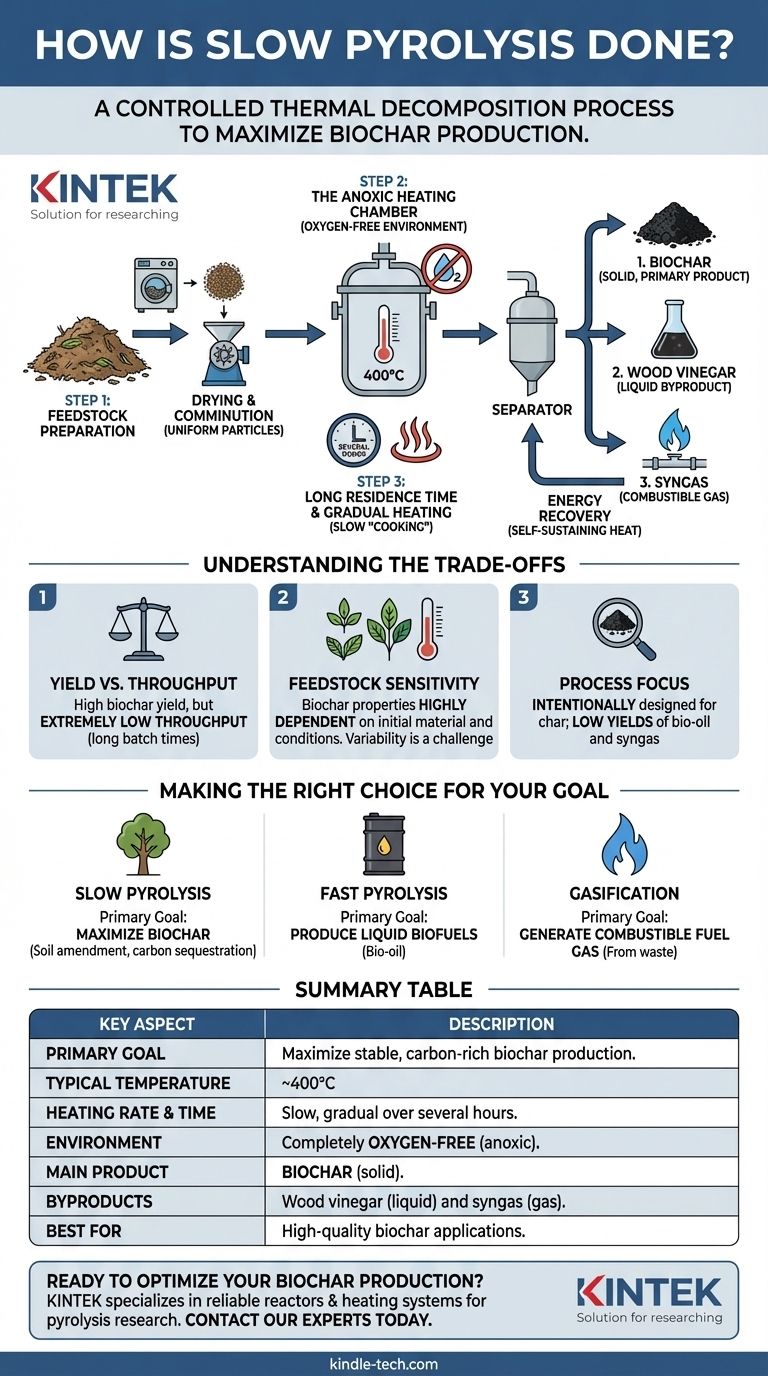
At its core, slow pyrolysis is a controlled thermal decomposition process designed to maximize the creation of a solid, carbon-rich product known as biochar. It involves heating organic material (biomass) to moderate temperatures of around 400°C over several hours in an environment completely devoid of oxygen, which prevents combustion and favors the formation of stable char.
The central principle of slow pyrolysis is control over speed. By gradually heating biomass for an extended period without air, the process intentionally prioritizes the formation of a high-quality solid (biochar) while minimizing the production of liquid and gas byproducts.
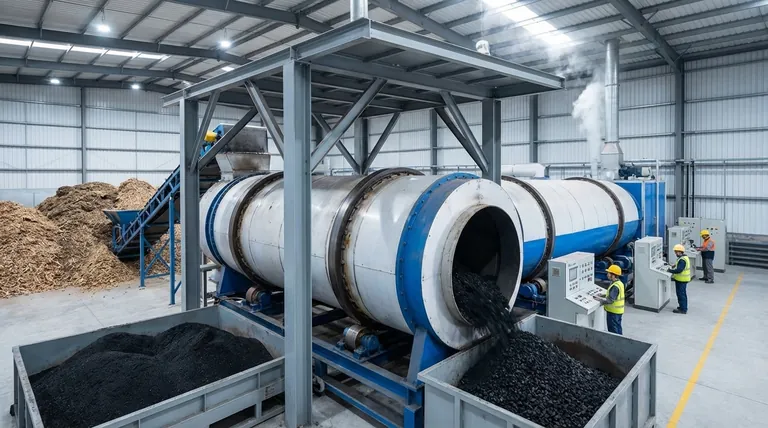

The Core Mechanism: From Biomass to Biochar
Slow pyrolysis is a deliberate, multi-stage process where each step is optimized for the final solid output. The method is more akin to a low-temperature bake than a rapid burn.
Step 1: Feedstock Preparation
Before any heating occurs, the raw biomass must be prepared. This typically involves drying to reduce moisture content and mechanical comminution (grinding or shredding) into smaller, more uniform particles.
This preparation ensures that heat is transferred evenly throughout the material, leading to a more consistent and complete pyrolytic reaction.
Step 2: The Anoxic Heating Chamber
The prepared biomass is loaded into a reactor that is then sealed to remove air. This anoxic (oxygen-free) environment is the most critical condition for pyrolysis.
Without oxygen, the biomass cannot combust. Instead, the applied heat breaks down the complex organic polymers like cellulose and lignin into simpler, more stable components.
Step 3: Long Residence Time and Gradual Heating
The reactor is heated gradually to a target temperature of approximately 400°C. The biomass is held at or around this temperature for a long residence time, often for several hours.
This slow "cooking" process allows for secondary reactions to occur, where volatile compounds can further break down and re-polymerize onto the surface of the solid, increasing the overall yield and stability of the biochar.
Step 4: Product Separation and Energy Recovery
As the biomass decomposes, it separates into three distinct products:
- A solid: The primary product, biochar or biocoal.
- A liquid: An aqueous condensate known as wood vinegar or pyroligneous acid.
- A gas: A mixture of combustible gases (syngas) like hydrogen, methane, and carbon monoxide.
A key feature of efficient slow pyrolysis systems is that the bio-gas produced can be captured and combusted to provide the necessary process heat, creating a partially self-sustaining energy loop.
Understanding the Trade-offs of This Method
While highly effective for producing biochar, slow pyrolysis involves significant trade-offs that are crucial for any practical application.
Yield vs. Throughput
The primary advantage of slow pyrolysis is its high yield of solid biochar. However, this comes at the cost of extremely low throughput. Processing a batch of biomass can take many hours, making it less suitable for applications requiring rapid waste processing.
Feedstock Sensitivity
The final properties of the biochar are highly dependent on the initial feedstock and the precise process conditions (temperature and time). This variability makes it challenging to produce a perfectly consistent product, which can complicate its valuation and marketability.
Process Focus
Slow pyrolysis is a specialized tool. It is intentionally designed to produce char, which means the yields of bio-oil and syngas are inherently low. If liquid or gaseous fuel is the desired output, other methods are far more efficient.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct thermal conversion technology depends entirely on your end goal. The term "pyrolysis" covers a wide spectrum of processes, each with a different primary output.
- If your primary focus is maximizing biochar yield for soil amendment or carbon sequestration: Slow pyrolysis is the definitive method, as it is specifically engineered to favor the creation of stable solid carbon.
- If your primary focus is producing liquid biofuels (bio-oil): You should investigate fast pyrolysis, which uses higher temperatures and seconds-long residence times to maximize the liquid yield.
- If your primary focus is generating a combustible fuel gas from waste: Gasification, which involves partial oxidation at much higher temperatures, is the more direct and efficient technology.
Understanding that slow pyrolysis is a specific tool for a specific job—creating biochar—is the key to applying it successfully.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Maximize production of stable, carbon-rich biochar. |
| Typical Temperature | ~400°C |
| Heating Rate & Time | Slow, gradual heating over several hours. |
| Environment | Completely oxygen-free (anoxic) to prevent combustion. |
| Main Product | Biochar (solid). |
| Byproducts | Wood vinegar (liquid) and syngas (gas). |
| Best For | Applications where high-quality biochar is the primary goal, such as soil amendment and carbon sequestration. |
Ready to optimize your biochar production?
The controlled, precise conditions required for efficient slow pyrolysis demand reliable lab equipment. KINTEK specializes in the reactors and heating systems needed for your pyrolysis research and development.
We provide the tools to help you:
- Achieve consistent, high-yield biochar production.
- Accurately control temperature and residence time.
- Safely manage anoxic environments.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our specialized lab equipment can advance your sustainable energy projects. Get in touch via our contact form to find the perfect solution for your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Which catalyst used in biomass pyrolysis for production of bio-oil? Select the Right Catalyst for Your Bio-Oil
- What is the byproduct of calcination? Uncovering the Gases Released in Thermal Decomposition
- What are the feedstocks for pyrolysis? Unlock the Potential of Organic Materials
- What is the difference between fast and slow pyrolysis? Choosing the Right Biomass Conversion Process
- What are the risks of pyrolysis? Key Challenges in Waste-to-Energy Conversion
- What is fast pyrolysis oil? A Guide to the Renewable Liquid Biofuel
- What is the use of biochar from pyrolysis? Unlock its potential as fuel, material, and soil amendment
- What are the outputs of pyrolysis? Unlocking the Solid, Liquid, and Gas Products from Thermal Decomposition



















