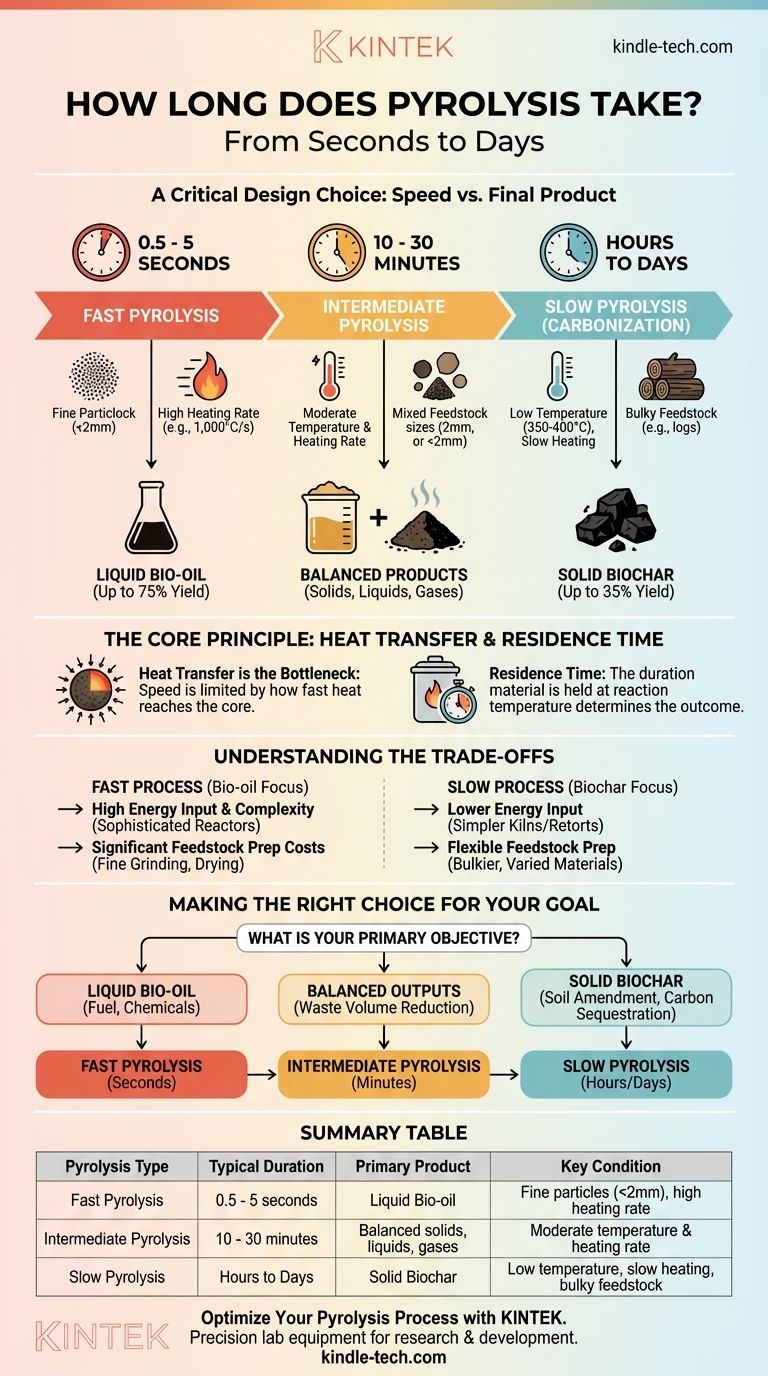
The duration of pyrolysis can range from less than two seconds to several days. This vast difference is not arbitrary; it is a direct consequence of the specific technology used and, most importantly, the desired end product. The process is engineered to be either extremely fast to maximize liquid bio-oil or intentionally slow to maximize solid biochar.
The time required for pyrolysis is not a fixed number but a critical design parameter. The central trade-off is between speed and the final product: fast processes measured in seconds are designed to produce liquid bio-oil, while slow processes measured in hours or days are designed to create solid biochar.

The Core Principle: Heat Transfer Dictates Speed
What Pyrolysis Aims to Achieve
Pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of materials at elevated temperatures in an oxygen-deprived environment. Its goal is to break down complex organic matter (like biomass, plastics, or tires) into simpler, more valuable products: a solid char, liquid oils, and combustible gases.
Why Heat Transfer Is the Bottleneck
The speed of pyrolysis is fundamentally limited by the rate at which you can heat every particle of the feedstock to the target temperature. Heat must travel from the outside of a particle to its core. This is why the physical characteristics of the feedstock and the design of the reactor are paramount.
Understanding Residence Time
Residence time is the technical term for how long the material is held at the reaction temperature inside the reactor. This is the single most important factor determining the duration of the process and the final product distribution.
The Two Extremes of Pyrolysis Duration
Fast Pyrolysis: Seconds for Liquid Bio-oil
In fast pyrolysis, the goal is to rapidly heat the feedstock to a moderate-to-high temperature (around 500°C) and then quickly cool the resulting vapors to capture them as a liquid.
- Typical Duration: 0.5 to 5 seconds of residence time.
- Conditions: Requires very small feedstock particles (typically less than 2mm) to ensure rapid heat transfer. The heating rates are extremely high (e.g., 1,000°C per second).
- Primary Product: Liquid bio-oil (yields can be up to 75% by weight).
Slow Pyrolysis (Carbonization): Hours for Solid Biochar
Slow pyrolysis, historically known as carbonization, is the process used for centuries to make charcoal. It prioritizes the production of a stable, carbon-rich solid.
- Typical Duration: Several hours to several days.
- Conditions: Uses much lower temperatures (around 350-400°C) and very slow heating rates. It can accommodate much larger feedstock pieces, like wood logs or whole tires.
- Primary Product: Solid biochar or charcoal (yields are typically around 35%).
Intermediate Pyrolysis: A Balanced Approach
As the name suggests, intermediate pyrolysis operates between the two extremes.
- Typical Duration: 10 to 30 minutes.
- Conditions: It uses moderate temperatures and heating rates, offering more flexibility in feedstock size than fast pyrolysis.
- Primary Product: It produces a more balanced distribution of solid, liquid, and gas products.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Product Yield vs. Process Speed
The decision to use a fast or slow process is entirely driven by your target product. There is no universally "better" duration. If your business model depends on selling liquid fuel, a slow, hours-long process is a failure. If your goal is to produce biochar for agriculture, a fast, seconds-long process is equally incorrect.
Energy Input and Complexity
Achieving the extremely high heating rates required for fast pyrolysis demands sophisticated and energy-intensive reactors, such as fluidized beds or ablative systems. Slow pyrolysis can be accomplished with much simpler and less energy-intensive technology, such as basic kilns or retort systems.
Feedstock Preparation Costs
Fast pyrolysis is only possible with finely ground, often pre-dried feedstock. The energy, machinery, and operational costs associated with preparing this material can be significant. Slow pyrolysis is far more forgiving, able to process bulkier, more varied, and sometimes wetter materials with minimal pre-treatment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Before asking "how long," you must first define your primary objective. The duration is a result of that choice, not an independent variable.
- If your primary focus is producing biochar for soil amendment or carbon sequestration: You will use slow pyrolysis, with process times measured in hours or days to maximize your solid yield.
- If your primary focus is creating liquid bio-oil as a fuel or chemical precursor: You must use fast pyrolysis, engineering for residence times of only a few seconds with highly prepared feedstock.
- If your primary focus is waste volume reduction with flexible product outputs: An intermediate pyrolysis process, lasting tens of minutes, may offer the most practical balance of operational simplicity and product versatility.
Ultimately, the duration of pyrolysis is a deliberate engineering choice that directly reflects the product you intend to create.
Summary Table:
| Pyrolysis Type | Typical Duration | Primary Product | Key Condition |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fast Pyrolysis | 0.5 - 5 seconds | Liquid Bio-oil | Fine particles (<2mm), high heating rate |
| Intermediate Pyrolysis | 10 - 30 minutes | Balanced solids, liquids, gases | Moderate temperature & heating rate |
| Slow Pyrolysis | Hours to Days | Solid Biochar | Low temperature, slow heating, bulky feedstock |
Ready to optimize your pyrolysis process for maximum yield? KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables for pyrolysis research and development. Whether you're targeting bio-oil, biochar, or gas production, our reactors and analytical tools help you control residence time, temperature, and feedstock preparation with accuracy. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can accelerate your sustainable energy or waste conversion projects.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the principles of a rotary kiln? Master the Mechanics of High-Temperature Processing
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- How to regenerate activated carbon? Master the 3-Stage Thermal Process for Cost Savings
- Can you restore activated carbon? Understanding the Industrial Reactivation Process
- What is the temperature of a carbon regeneration kiln? Mastering the 750-800°C Reactivation Process



















