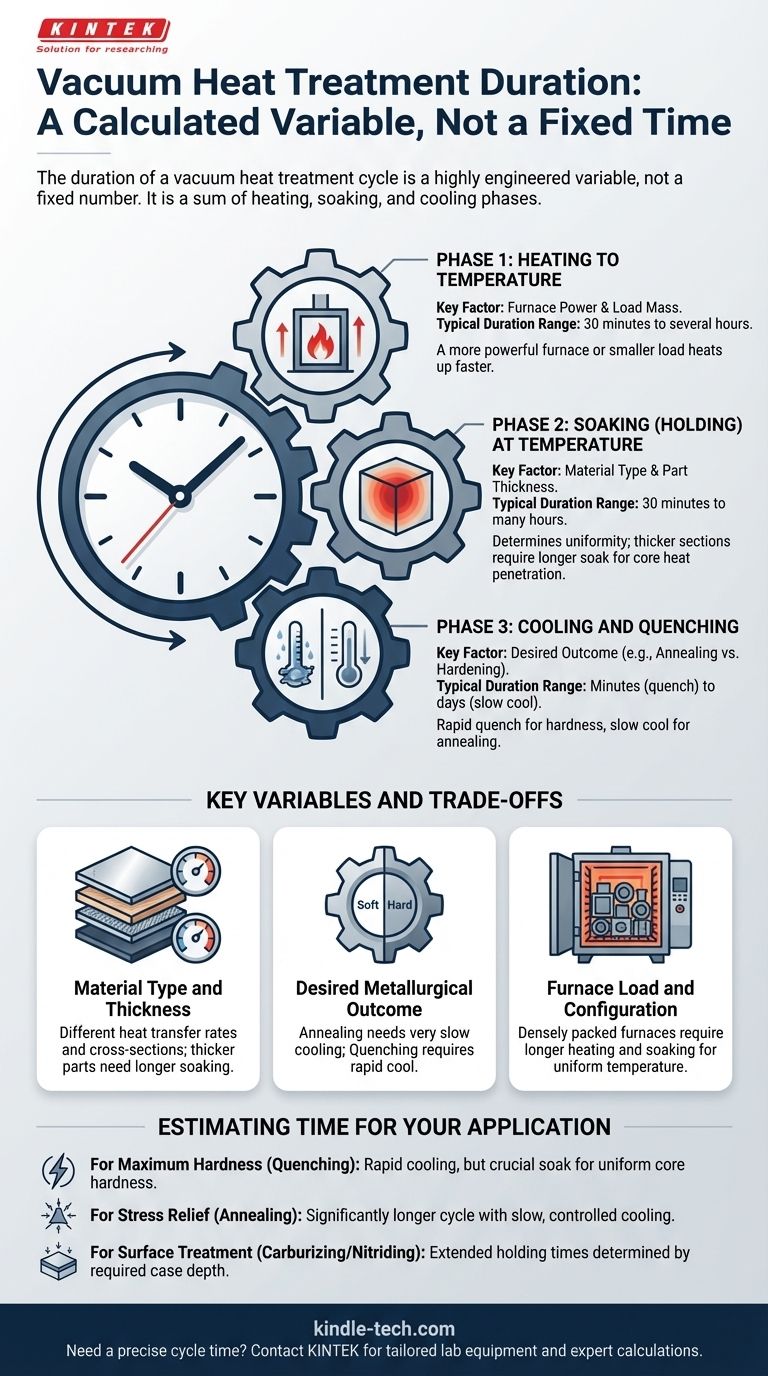
The duration of a vacuum heat treatment cycle is not a fixed number; it is a highly engineered variable determined by the specific goals of the treatment. The total time is a sum of the heating, soaking (holding), and cooling phases, each of which is calculated based on the workpiece's material, its physical dimensions, and the required metallurgical outcome.
The question isn't "how long does it take," but rather "what factors determine the cycle time for my specific application?" The duration is not a preset value but a calculated result of the material's properties, the part's geometry, and the desired final microstructure.

Deconstructing the Process: The Three Critical Phases
A vacuum heat treatment cycle is never a single step. It consists of three distinct phases, and the duration of each contributes to the total process time. Understanding these phases is the key to understanding the timeline.
Phase 1: Heating to Temperature
The initial phase involves bringing the workpiece up to the target temperature within the vacuum furnace. The time required for this step is primarily influenced by the furnace's power and the total mass of the load. A more powerful furnace or a smaller, less dense load will heat up faster.
Phase 2: Soaking (Holding) at Temperature
Once at the target temperature, the workpiece is "soaked" or held for a calculated period. This is the most critical phase for ensuring the material's internal structure transforms uniformly. The duration is determined by the part's effective thickness, not just its overall size. The goal is to ensure the thermal energy fully penetrates to the core of the thickest section.
Phase 3: Cooling and Quenching
After soaking, the material is cooled to lock in the new properties. The speed and method of cooling have a massive impact on the cycle time and the final result. A rapid gas or oil quench might take minutes, while a slow, controlled cool for annealing can add many hours or even days to the process.
Understanding the Key Variables and Trade-offs
The time for any given cycle is a direct result of balancing physical limitations with metallurgical goals. Several key variables must be considered.
Material Type and Thickness
Different materials transfer heat at different rates. More importantly, thicker cross-sections require significantly longer soaking times to ensure the core of the part achieves the same temperature and metallurgical transformation as the surface. A thin sheet will require a much shorter soak time than a thick block of the same alloy.
The Desired Metallurgical Outcome
The purpose of the treatment is the single biggest factor. A process like annealing, designed to soften the material and relieve stress, requires a very slow and controlled cooling phase that can take many hours. Conversely, a quenching process to achieve maximum hardness requires an extremely rapid cool, though the preceding heating and soaking times are still critical.
Furnace Load and Configuration
The total amount of material in the furnace—the charge—affects the cycle. A densely packed furnace will require longer heating and soaking times to ensure every part reaches a uniform temperature. Poor arrangement can create hot or cold spots, compromising the quality of the batch.
Estimating Time for Your Application
To move from a general understanding to a practical estimate, you must define your goal. The required time is a function of the desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness (quenching): The cooling phase will be rapid, but do not underestimate the time required for a proper soak to ensure uniform hardness throughout the part's core.
- If your primary focus is stress relief or softening (annealing): Be prepared for a significantly longer cycle, as the slow, controlled cooling phase is the most time-consuming and critical part of the process.
- If your primary focus is a specialized surface treatment (carburizing/nitriding): These are diffusion processes, and the holding time is determined by the required case depth, which can often extend for many hours.
Ultimately, precise timing in vacuum heat treatment is the foundation of achieving predictable, high-quality material properties.
Summary Table:
| Phase | Key Factor | Typical Duration Range |
|---|---|---|
| Heating | Furnace Power & Load Mass | 30 minutes to several hours |
| Soaking (Holding) | Material Type & Part Thickness | 30 minutes to many hours |
| Cooling/Quenching | Desired Outcome (e.g., Annealing vs. Hardening) | Minutes (quench) to days (slow cool) |
Need a precise vacuum heat treatment cycle time for your specific lab materials? At KINTEK, we specialize in providing lab equipment and consumables tailored to your unique thermal processing needs. Our experts can help you calculate the optimal heating, soaking, and cooling parameters to achieve your desired metallurgical outcomes efficiently. Contact us today to discuss your application and get a customized solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is vacuum furnace high temperature? Unlock the Range for Your Material Processing
- What is the maximum temperature in a vacuum furnace? It Depends on Your Materials and Process Needs
- What is the process of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- What are the advantages of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Purity and Control in Heat Treatment



















