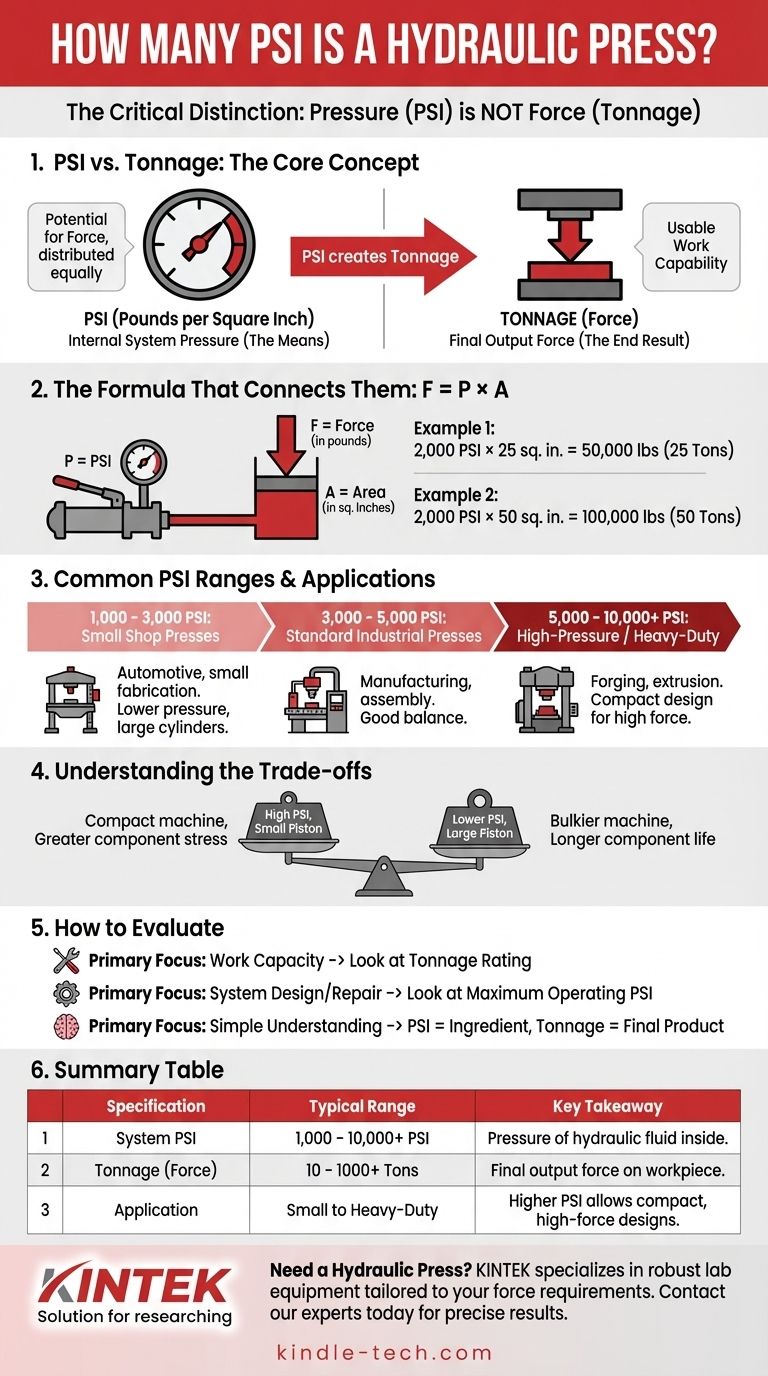
This is a common point of confusion. A hydraulic press doesn't have one single PSI value; instead, it uses a hydraulic system that operates within a specific pressure range, typically from 1,000 to 10,000 PSI, to generate its force. The PSI is the measure of pressure in the fluid, while the machine's power is rated in tonnage—the final output force it can apply.
The central takeaway is this: Pressure (PSI) is not the same as force (tonnage). A hydraulic press uses the PSI generated by its pump and applies it over the area of a piston to create a much larger output force, measured in tons.

PSI vs. Tonnage: The Critical Distinction
Understanding the difference between the pressure inside the system and the force it exerts is the key to understanding how any hydraulic press works.
What is PSI (Pressure)?
PSI, or Pounds per Square Inch, is the measure of pressure exerted by the hydraulic fluid inside the system. Think of it as the potential for force.
This pressure is generated by the hydraulic pump and, according to Pascal's Principle, is distributed equally throughout the enclosed fluid.
What is Tonnage (Force)?
Tonnage is the final, usable output force that the press ram exerts on the workpiece. This is the specification that tells you how much work the machine can actually do.
A 50-ton press can exert 100,000 pounds of force. This is the number that matters for stamping, pressing, or forging operations.
The Formula That Connects Them: Force = Pressure × Area
The magic of hydraulics lies in a simple formula. The system takes a relatively modest PSI and multiplies it over a large surface area to generate immense force.
Force (in pounds) = Pressure (in PSI) × Area (in square inches)
For example, a hydraulic system operating at 2,000 PSI acting on a piston with a face area of 25 square inches will produce 50,000 pounds of force (2,000 × 25), which is equal to a 25-ton press.
If you use that same 2,000 PSI on a larger, 50-square-inch piston, you generate 100,000 pounds of force, creating a 50-ton press. The PSI is the means, and the tonnage is the end result.
Common PSI Ranges and Their Applications
While the tonnage rating is more important, the system's maximum operating PSI can give you clues about its design and intended use.
Small Shop Presses: 1,000 - 3,000 PSI
These are typical for H-frame presses used in automotive or small fabrication shops for tasks like pressing bearings, bushings, or small parts. They achieve their tonnage (often 10-50 tons) with relatively low pressure and large cylinders.
Standard Industrial Presses: 3,000 - 5,000 PSI
This is a very common operating range for a wide variety of industrial machinery used in manufacturing, forming, and assembly. They offer a good balance of component size and force generation.
High-Pressure / Heavy-Duty Presses: 5,000 - 10,000+ PSI
Systems operating at these high pressures are used for heavy-duty applications like forging, extrusion, or deep drawing. Using higher PSI allows for more compact cylinder designs to achieve extremely high tonnage (hundreds or thousands of tons).
Understanding the Trade-offs
A press manufacturer's choice of operating pressure is a deliberate engineering decision based on balancing performance, cost, and longevity.
High PSI, Small Piston
To achieve a specific tonnage, a system using higher PSI can use a smaller, more compact piston and cylinder. This can make the machine smaller, but it places greater stress on seals, hoses, and fittings.
Lower PSI, Large Piston
A system using lower PSI needs a larger piston and cylinder to achieve the same tonnage. This results in a bulkier machine but often leads to longer component life because the system is operating under less hydraulic stress.
How to Evaluate a Hydraulic Press
Focus on the specifications that relate directly to your work.
- If your primary focus is the work capacity: Always look at the tonnage rating first, as this is the definitive measure of the press's output force.
- If your primary focus is on system design or repair: The maximum operating PSI is critical for ensuring all components (pump, hoses, seals, and valves) are correctly rated and compatible.
- If your primary focus is a simple understanding: Remember that PSI is the ingredient and tonnage is the final product; a press uses PSI to create tons of force.
By understanding the relationship between internal pressure and external force, you can confidently assess the true capability of any hydraulic press.
Summary Table:
| Specification | Typical Range | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|---|
| System PSI | 1,000 - 10,000+ PSI | The pressure of the hydraulic fluid inside the system. |
| Tonnage (Force) | 10 - 1000+ Tons | The final output force applied to the workpiece. |
| Application | Small Shop to Heavy-Duty Industrial | Higher PSI allows for more compact, high-force designs. |
Need a Hydraulic Press for Your Lab or Production Line?
Understanding the balance between PSI and tonnage is crucial for selecting the right equipment. KINTEK specializes in providing robust and reliable lab equipment, including hydraulic presses tailored to your specific force and application requirements.
We help laboratories and production facilities achieve precise and consistent results. Contact our experts today to find the perfect press for your needs and ensure your operations run with maximum efficiency and safety.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Press for XRF & KBR Pellet Press
People Also Ask
- What is the pressed powder pellet method? A Guide to Accurate FTIR Sample Preparation
- What is the advantage of KBr? Unmatched IR Transparency for Precise Spectroscopy
- How hot is a hydraulic press? Understanding the Critical Heat in Your Hydraulic System
- What is the use of KBr? Master Sample Prep for Accurate IR Spectroscopy
- Why are KBr pellets used in FTIR? Achieve Clear, Accurate Solid Sample Analysis



















