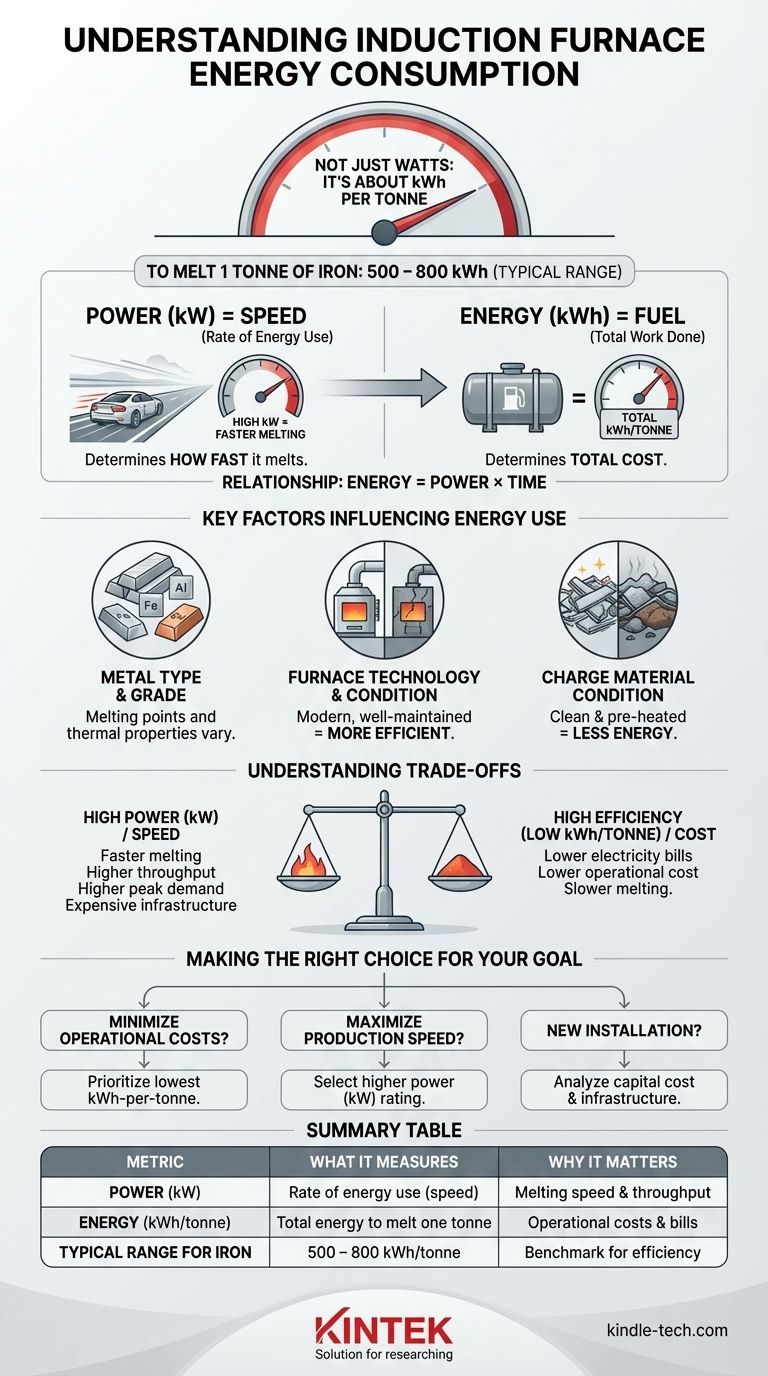
The power consumption of an induction furnace is not a single number. Instead of a fixed wattage, its performance is measured by the energy required to perform a specific task. To melt one tonne of iron, a modern induction furnace will typically consume between 500 and 800 kilowatt-hours (kWh) of electrical energy.
The most important concept to understand is the difference between power and energy. The power rating of a furnace (in kilowatts) determines how fast it can melt metal, while its energy consumption (in kilowatt-hours per tonne) determines the total cost of the operation.

Power (kW) vs. Energy (kWh): The Critical Distinction
To understand furnace performance, we must first clarify the terms. Confusing power and energy is a common source of error when evaluating industrial equipment.
What is Power (Watts/Kilowatts)?
Think of power as the rate at which energy is used. It's analogous to the speed of a car. A higher power rating, measured in kilowatts (kW), means the furnace can deliver more energy in a shorter amount of time, resulting in faster melting cycles.
What is Energy (Kilowatt-Hours)?
Energy is the total amount of work done. It's analogous to the total fuel consumed on a trip. Measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), this is the metric that appears on your electricity bill and reflects the actual cost to melt a given amount of material.
How They Connect
The relationship is simple: Energy = Power × Time. For example, a furnace with a 600 kW power rating running at full capacity for one hour will consume 600 kWh of energy. This is why the industry benchmark is "kWh per tonne"—it measures total energy efficiency for a standard task.
Key Factors Influencing Energy Consumption
The typical range of 500 to 800 kWh per tonne exists because several variables impact the furnace's overall efficiency.
Type and Grade of Metal
Different materials have different melting points and thermal properties. The provided data is for iron, but melting aluminum or copper would require a different amount of energy.
Furnace Technology and Condition
Modern, well-maintained coreless induction furnaces are significantly more efficient. Older designs or furnaces with worn-out linings will suffer greater heat loss, increasing the kWh required per tonne.
Charge Material Condition
The starting temperature and cleanliness of the material being melted (the "charge") are critical. Using cold, damp, or dirty scrap metal requires substantially more energy than using clean, pre-heated material.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing or evaluating an induction furnace involves balancing competing priorities. There is no single "best" option, only the best option for a specific operational goal.
High Power vs. High Efficiency
A furnace with a very high power rating (high kW) will melt metal quickly. This increases throughput and can reduce heat loss over time. However, this capability requires a much more robust and expensive electrical infrastructure to support the high peak demand.
Capital Cost vs. Operational Cost
A less expensive, less efficient furnace may seem attractive initially. However, its higher energy consumption (higher kWh/tonne) will result in larger electricity bills for its entire operational life, potentially costing more in the long run.
Production Speed vs. Grid Demands
Operating a high-power furnace can incur significant "demand charges" from utility providers. These are fees based on the highest peak power drawn from the grid during a billing period, regardless of total energy consumed. This financial reality must be factored into any operational plan.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your primary objective determines which metric is most important for your evaluation.
- If your primary focus is minimizing operational costs: Prioritize a furnace with the lowest possible kWh-per-tonne rating, as this directly translates to your electricity bill.
- If your primary focus is maximizing production speed: Select a furnace with a higher power rating (kW) to ensure faster melting cycles and greater output.
- If you are planning a new installation: Carefully analyze both the capital cost of the furnace and the electrical infrastructure required to support its peak power demand.
Ultimately, shifting your focus from "how many watts" to "how many kilowatt-hours per tonne" is the key to making an informed and cost-effective decision.
Summary Table:
| Metric | What It Measures | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Power (kW) | The rate of energy use (speed of melting) | Determines melting speed and production throughput |
| Energy (kWh/tonne) | Total energy consumed to melt one tonne of material | Directly impacts operational costs and electricity bills |
| Typical Range for Iron | 500 - 800 kWh/tonne | Benchmark for comparing furnace efficiency |
Ready to optimize your melting operations with an energy-efficient induction furnace?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-performance lab equipment, including induction furnaces tailored to your specific production goals. Whether your priority is minimizing operational costs with superior kWh/tonne efficiency or maximizing output with high-power melting, our experts can help you select the right solution.
Contact us today to discuss your needs and discover how KINTEK's reliable equipment can enhance your laboratory's productivity and reduce your energy expenses.
Get a personalized consultation →
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a vacuum induction melting furnace? Melt High-Purity Metals with Precision
- What principle is used to generate heat in a vacuum induction melting furnace? Achieve Clean, Efficient Metal Melting
- How does induction work in a vacuum? Achieve Ultra-Pure Metal Melting with VIM
- What is VIM in metallurgy? A Guide to Vacuum Induction Melting for High-Performance Alloys
- What is the vacuum induction method? Master High-Purity Metal Melting for Advanced Alloys



















