The maximum heat a crucible can withstand is determined entirely by its material composition, a property known as its maximum service temperature. This temperature can range from around 1600°C (2900°F) for common clay-graphite crucibles used by hobbyists to over 3400°C (6192°F) for specialized tungsten crucibles used in industrial research. The key is to select a crucible made from a material that can safely handle temperatures well above the melting point of the substance you are working with.
The most common point of failure is not exceeding the crucible's absolute temperature limit, but rather choosing the wrong material for the job or subjecting it to rapid temperature changes it cannot handle. A successful melt depends on matching the crucible's properties to the specific metal and heating method you intend to use.
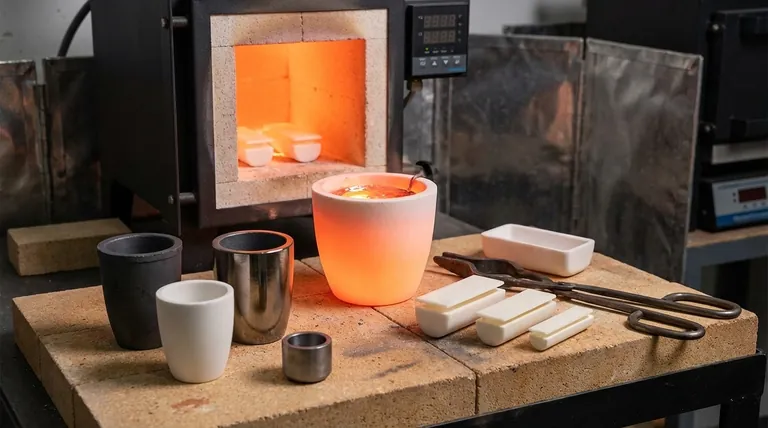

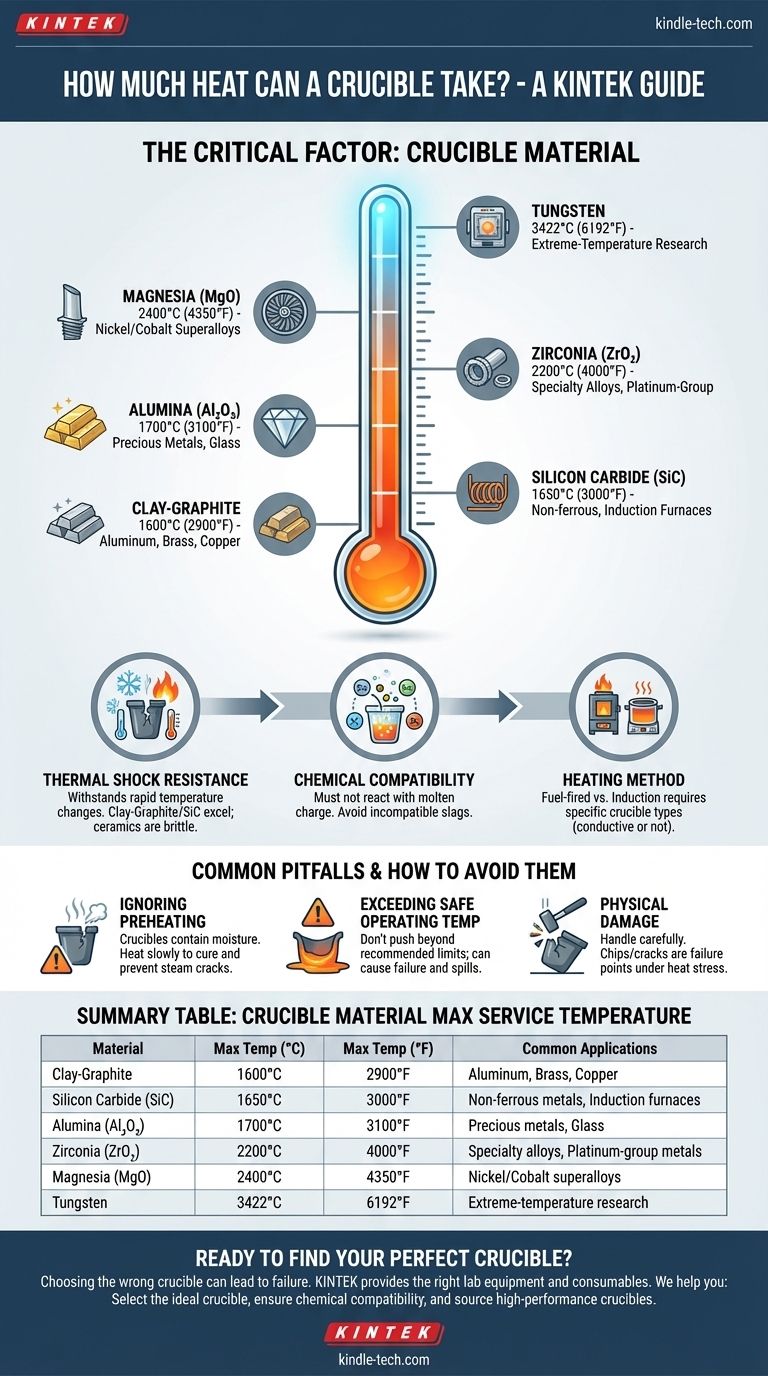
The Critical Factor: Crucible Material
The material of your crucible is the single most important variable. Each type is engineered for a specific range of temperatures, metals, and heating environments.
Clay-Graphite and Silicon Carbide
These are the workhorses for most non-ferrous foundry work.
Clay-graphite crucibles are a cost-effective and reliable choice for melting metals like aluminum, brass, and copper. Their maximum service temperature is typically around 1600°C (2900°F).
Silicon carbide (SiC) crucibles offer superior performance, with higher thermal conductivity for faster melts and a longer service life. They operate in a similar temperature range, up to 1650°C (3000°F), and are excellent for both fuel-fired and induction furnaces.
High-Temperature Ceramics
For higher purity applications, reactive metals, or steel alloys, ceramic crucibles are required.
Alumina (Al₂O₃) is a very common high-purity ceramic, ideal for melting precious metals or glass. It can withstand continuous use up to about 1700°C (3100°F).
Zirconia (ZrO₂) is used for even higher temperature applications, remaining stable up to 2200°C (4000°F). It's often chosen for melting specialty alloys, platinum-group metals, or highly reactive materials.
Magnesia (MgO) is preferred for melting nickel and cobalt-based superalloys due to its excellent resistance to basic slags. It can be used at temperatures up to 2400°C (4350°F).
Refractory Metals
These materials are used for the most extreme temperature applications, almost exclusively in vacuum or inert gas environments to prevent oxidation.
Tungsten has the highest melting point of any metal, making it the ultimate crucible material for research applications, with a maximum service temperature of 3422°C (6192°F).
Molybdenum is another high-temperature option, suitable for use up to around 2000°C (3632°F) in a controlled atmosphere.
Beyond Temperature: Factors That Cause Failure
A crucible's maximum temperature rating is only part of the story. Understanding these other factors is critical for safety and success.
Thermal Shock Resistance
This is the ability of a material to withstand rapid changes in temperature without cracking.
Crucibles made from clay-graphite and silicon carbide have excellent thermal shock resistance, which is why they are well-suited for the repeated heating and cooling cycles of foundry work.
Ceramic crucibles are generally more brittle and must be heated and cooled slowly and evenly to prevent catastrophic failure.
Chemical Compatibility
The crucible material must not react with the molten charge inside it.
For example, using a silica-based crucible to melt an alloy that produces a basic slag will cause the crucible to rapidly degrade and fail, regardless of the temperature. The chemical inertness of the crucible relative to your specific material is non-negotiable.
Heating Method
The way you apply heat matters.
Fuel-fired furnaces (propane, natural gas) heat the crucible externally. Most materials work well in this environment.
Induction furnaces use magnetic fields to heat the material. This requires either a crucible made of a conductive material (like graphite or silicon carbide) or placing a non-conductive ceramic crucible inside a conductive "susceptor" sleeve.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Choosing the right crucible is only the first step. Proper use is essential to prevent failure and ensure safety.
Ignoring Preheating Procedures
New crucibles, especially clay-graphite models, contain residual moisture from manufacturing. They must be heated slowly and gently (cured) the first time to drive this moisture out. Heating a new crucible too quickly will cause the trapped water to turn to steam and crack it.
Exceeding the Safe Operating Temperature
There is a difference between a material's melting point and its maximum safe service temperature. Pushing a crucible beyond its recommended operating range can cause it to soften, deform, or fail, resulting in a dangerous spill of molten material.
Physical Damage
Never drop tools into a hot crucible or handle it roughly. Even a small chip or crack can become a catastrophic failure point when the crucible is brought to temperature under the stress of a full charge.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select your crucible based on a clear understanding of your specific task and materials.
- If your primary focus is melting aluminum, brass, or copper: A clay-graphite crucible provides the best balance of performance and cost. A silicon carbide crucible is a worthwhile upgrade for longer life and faster melts.
- If your primary focus is melting gold, silver, or other precious metals: A high-purity fused silica or alumina crucible is required to prevent contamination of your final product.
- If your primary focus is melting steel or specialty alloys: You must use a specialized ceramic crucible, such as magnesia or zirconia, carefully matched to the unique chemistry of your alloy.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature research in a vacuum: A refractory metal crucible made of tungsten or molybdenum is the only suitable choice.
Matching your crucible's capabilities to your specific application is the most critical step for ensuring a safe and successful melt.
Summary Table:
| Crucible Material | Max Service Temperature (°C) | Max Service Temperature (°F) | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clay-Graphite | 1600°C | 2900°F | Aluminum, Brass, Copper |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | 1650°C | 3000°F | Non-ferrous metals, Induction furnaces |
| Alumina (Al₂O₃) | 1700°C | 3100°F | Precious metals, Glass |
| Zirconia (ZrO₂) | 2200°C | 4000°F | Specialty alloys, Platinum-group metals |
| Magnesia (MgO) | 2400°C | 4350°F | Nickel/Cobalt superalloys |
| Tungsten | 3422°C | 6192°F | Extreme-temperature research |
Ready to Find Your Perfect Crucible?
Choosing the wrong crucible can lead to failed melts, contaminated materials, or even dangerous equipment failure. KINTEK specializes in providing the right lab equipment and consumables for your specific application.
We can help you:
- Select the ideal crucible material based on your target metal, temperature, and heating method.
- Ensure chemical compatibility to prevent contamination and crucible degradation.
- Source high-performance crucibles from trusted manufacturers for safety and reliability.
Don't risk your materials or your safety. Let our experts guide you to the perfect solution.
Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does an Alumina Crucible play in the high-temperature solid-state synthesis of Na3OBr? Ensure Sample Purity
- Why is the use of high-purity alumina crucibles necessary for NMC powders? Ensure Purity in Cathode Synthesis
- What are the functional advantages of using high-purity alumina crucibles? Achieve Precise Oxidation Data
- What role do high-purity alumina crucibles play in high-temperature steam oxidation? Ensure Data Integrity up to 1350°C
- How does the use of corrosion-resistant ceramic crucibles ensure the chemical purity of materials? | KINTEK



















