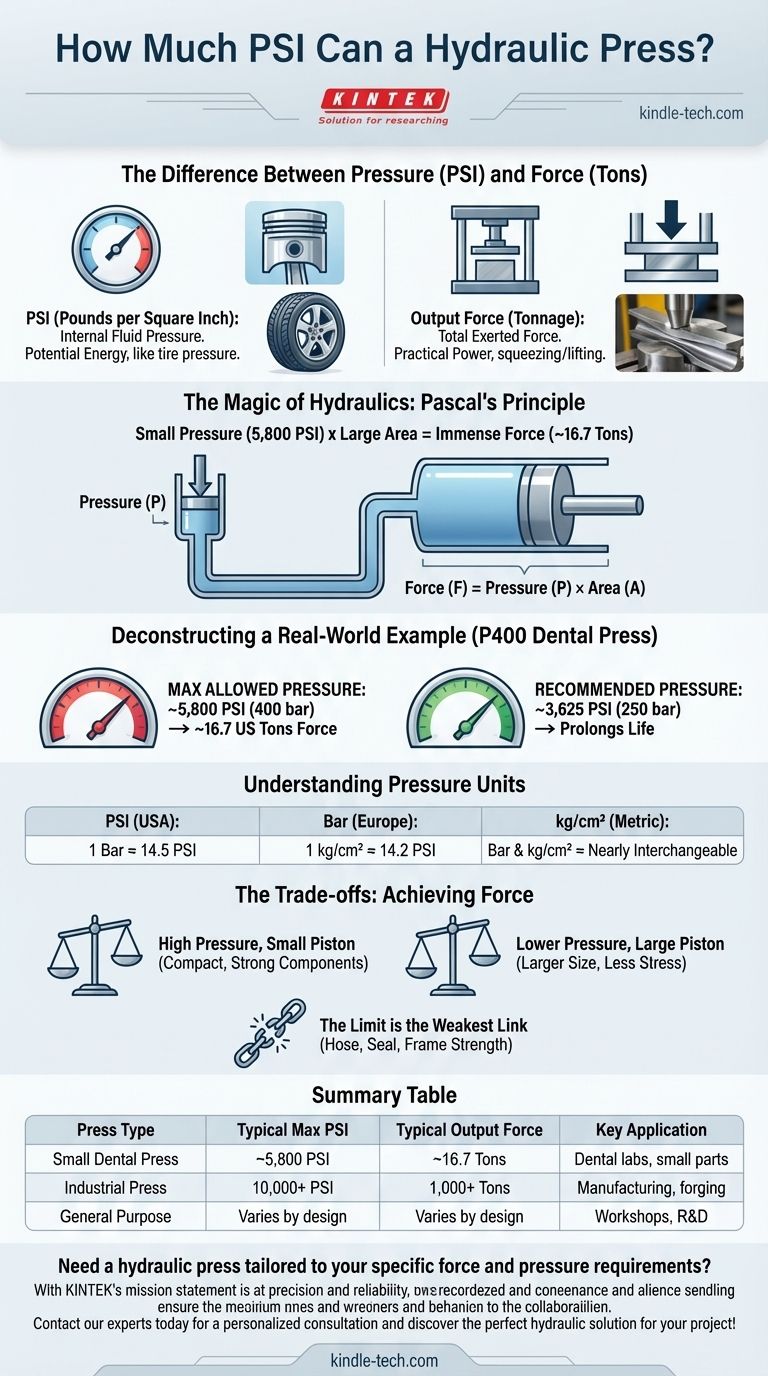
The maximum pressure of a hydraulic press is entirely dependent on its design and purpose. For example, a small dental press might be rated for a maximum of 400 bar, which is approximately 5,800 PSI. However, massive industrial presses can operate at pressures well over 10,000 PSI to generate thousands of tons of force.
The most critical metric for a hydraulic press is not its internal fluid pressure (PSI) but its total output force, typically measured in tons. This force is the result of the system's PSI acting on the surface area of its main piston.

The Difference Between Pressure (PSI) and Force (Tons)
To understand the capabilities of a press, it's crucial to distinguish between the pressure within its hydraulic lines and the force it ultimately delivers.
What is Hydraulic Pressure (PSI)?
PSI (Pounds per Square Inch) measures the amount of force exerted by the hydraulic fluid on every square inch of the system's interior.
Think of it like the air pressure in a car tire. The pressure itself doesn't lift the car; it's the potential energy waiting to be used.
What is Output Force (Tonnage)?
Output force, often called tonnage, is the total force the press exerts on the object being worked on.
This is the practical result you care about—the actual squeezing, shaping, or lifting power of the machine.
The Key Relationship: Pascal's Principle
The magic of hydraulics lies in a simple formula: Force = Pressure × Area.
A modest amount of pressure can generate immense force if it acts upon a large enough area. This is why a press with 5,800 PSI can generate a force of over 15 tons if that pressure is applied to a piston with a sufficiently large surface.
Deconstructing a Real-World Example
Using the specifications for a P400 dental press, we can see these principles in action.
Maximum vs. Recommended Pressure
The press is rated for a maximum allowed pressure of 400 bar (~5,800 PSI), which produces a force of 15,200 kg (about 16.7 US tons).
However, the manufacturer specifies a maximum recommended pressure of 250 bar (~3,625 PSI) for continuous use. Operating at this level prolongs the life of seals, hoses, and mechanical components.
Understanding Different Pressure Units
You will encounter several units for pressure when looking at press specifications.
- PSI (Pounds per Square Inch): Common in the United States.
- Bar: Common in Europe. 1 bar is roughly equal to atmospheric pressure at sea level. (1 bar ≈ 14.5 PSI).
- kg/cm² (Kilograms per square centimeter): An older metric unit, functionally very similar to the bar. (1 kg/cm² ≈ 14.2 PSI).
For most practical purposes, you can consider bar and kg/cm² to be nearly interchangeable.
Understanding the Trade-offs
A press's design is a balance of engineering and economic choices. It isn't always about achieving the highest possible PSI.
Why Not Just Maximize PSI?
Higher hydraulic pressure demands much stronger and more expensive components. The cylinder walls must be thicker, the seals more robust, and the pump more powerful to handle the increased stress.
The Role of Piston Size
Engineers can achieve high output force in two ways:
- High Pressure, Small Piston: Requires a very strong system but can be compact.
- Lower Pressure, Large Piston: Requires less robust components but the overall machine will be larger and the piston may move more slowly.
The Limit is the Weakest Link
The maximum PSI of a hydraulic press is ultimately determined by the weakest component in the system. This could be a hose rating, a seal's tolerance, or the physical strength of the steel frame.
How to Evaluate a Hydraulic Press
When assessing a press for your needs, focus on the right metrics.
- If your primary focus is total pressing power: Look for the force rating in tons or kilograms. This is the most important indicator of the machine's capability.
- If you are comparing different machines: Convert all pressure ratings (bar, kg/cm², PSI) into a single, consistent unit to make an accurate comparison.
- If your primary focus is safety and longevity: Plan to operate the press at the manufacturer's recommended pressure, not its absolute maximum rating.
Understanding the relationship between internal pressure and output force is the key to selecting and operating any hydraulic press safely and effectively.
Summary Table:
| Press Type | Typical Maximum PSI | Typical Output Force (Tons) | Key Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Small Dental Press | ~5,800 PSI | ~16.7 tons | Dental labs, small parts |
| Industrial Press | 10,000+ PSI | 1,000+ tons | Manufacturing, forging |
| General Purpose | Varies by design | Varies by design | Workshops, R&D |
Need a hydraulic press tailored to your specific force and pressure requirements?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs with precision and reliability. Whether you're in a research lab, a dental practice, or an industrial setting, we can help you select the right press to ensure safety, longevity, and optimal performance for your applications.
Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation and discover the perfect hydraulic solution for your project!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Press for XRF & KBR Pellet Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Manual Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- What are the preventive maintenance of hydraulic systems? Extend Equipment Life and Maximize Uptime
- Why is a laboratory hydraulic press used for 380 MPa in composite anodes? Unlock Peak Battery Performance
- What is the significance of using a laboratory hydraulic press or pelletizer when processing torrefied biomass?
- What is the purpose of using a laboratory hydraulic press for pre-pressure? Enhance Sintering Precision & Density
- What are three ways to reduce production time in compression molding? Optimize Design, Preheat, and Automate
- What is the ratio of KBr and sample in IR? Achieve Perfect Sample Concentration for Clear IR Spectra
- What role does a laboratory hydraulic press or pelletizer play in biochar fuels? Powering Sustainable Energy Innovation
- What are hydraulic presses used for? Powering Industries with Immense, Controlled Force



















