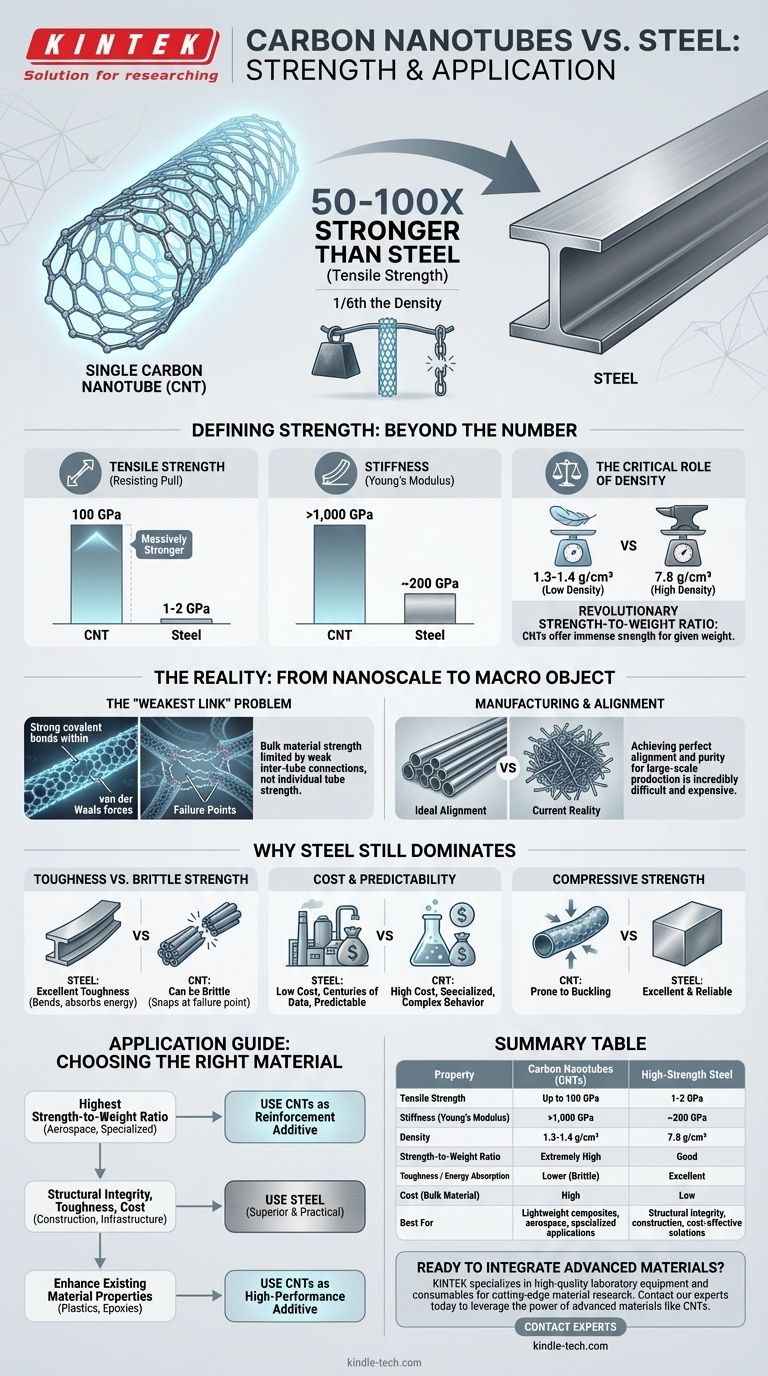
In terms of tensile strength, a single carbon nanotube is dramatically stronger than steel. The strongest individual nanotubes have been measured to be 50 to 100 times stronger than the strongest steel alloys for the same cross-sectional area. Critically, they achieve this strength while being approximately one-sixth the density of steel.
While an individual carbon nanotube possesses unparalleled tensile strength, the central engineering challenge lies in translating this nanoscale property to large-scale, usable materials. Therefore, the true advantage of carbon nanotubes is not just strength, but a revolutionary strength-to-weight ratio that remains difficult to achieve in practice.

Beyond a Simple Number: Defining "Strength"
The term "strength" can be misleading without context. Materials exhibit different types of strength, and comparing carbon nanotubes (CNTs) to steel requires looking at several key metrics.
Tensile Strength: Resisting the Pull
This is where CNTs exhibit their most famous property. Tensile strength measures a material's ability to resist being pulled apart.
The exceptionally strong covalent bonds between carbon atoms give individual CNTs a theoretical tensile strength of up to 100 gigapascals (GPa). In contrast, high-strength steel alloys typically max out around 1-2 GPa.
Stiffness (Young's Modulus): Resisting Bending
Stiffness measures a material's resistance to elastic deformation. Here again, CNTs are superior.
CNTs have a Young's Modulus of over 1,000 GPa, making them one of the stiffest materials ever discovered. Steel's Young's Modulus is much lower, around 200 GPa.
The Critical Role of Density
For applications in aerospace, automotive, and other fields where weight is critical, raw strength is less important than the strength-to-weight ratio.
The density of CNTs is about 1.3-1.4 g/cm³, whereas steel is around 7.8 g/cm³. This immense difference means that for a given weight, a CNT-based structure has the potential to be orders of magnitude stronger than a steel one.
The Challenge: From a Single Tube to a Real Object
The remarkable properties described above apply to individual, often flawless nanotubes on a microscopic scale. The primary obstacle preventing CNTs from replacing steel in bridges and buildings is translating these properties to a large, macroscopic object.
The "Weakest Link" Problem
A rope made of CNTs is not held together by the strong carbon bonds within the tubes, but by the much weaker van der Waals forces between the tubes.
These weak inter-tube connections become the failure points, meaning a bulk CNT material is significantly weaker than the individual tubes it contains. Overcoming this is a major focus of materials science research.
Manufacturing and Alignment
Creating a large object requires manufacturing trillions of nanotubes and aligning them perfectly.
Current production methods often result in tangled, impure, or short tubes, which drastically reduces the final strength of the composite material. This makes large-scale production of high-performance CNT materials incredibly difficult and expensive.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Why Steel Still Dominates
Steel's continued dominance in structural applications is not due to ignorance of better materials. It is a calculated engineering choice based on a different set of advantages.
Toughness vs. Brittle Strength
Steel possesses excellent toughness, which is the ability to absorb energy and deform without fracturing. It bends before it breaks, providing a critical safety margin in structures.
While immensely strong, CNTs can be brittle. They resist deformation up to a very high point and then may snap. Bulk CNT materials often do not exhibit the graceful failure mode of steel.
Cost and Predictability
Steel is an incredibly well-understood, isotropic (uniform in all directions), and cost-effective material.
Engineers have centuries of data on its performance, and it can be produced cheaply at a massive scale. CNTs remain an expensive, specialized material with more complex and less predictable behaviors in bulk form.
Compressive Strength
While CNTs excel under tension, their performance under compression is less remarkable. The long, thin tubes have a tendency to buckle when pushed together. Steel, as a solid bulk material, offers excellent and reliable compressive strength.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Your choice of material must be driven by the specific demands of the application, not just a single performance metric.
- If your primary focus is the highest possible strength-to-weight ratio for a specialized application (e.g., aerospace composites, ballistic protection, advanced tethers): CNTs, used as a reinforcement additive in a polymer matrix, offer performance potential far beyond any conventional metal.
- If your primary focus is structural integrity, toughness, and cost-effectiveness (e.g., building construction, bridges, infrastructure): Steel remains the superior and more practical choice due to its predictable failure modes, compressive strength, and low cost.
- If your primary focus is enhancing the properties of an existing material (e.g., creating stronger plastics or more conductive epoxies): CNTs are best viewed as a high-performance additive, not a bulk replacement for steel.
Ultimately, understanding these materials means seeing them not as direct competitors, but as highly specialized tools for fundamentally different engineering challenges.
Summary Table:
| Property | Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs) | High-Strength Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | Up to 100 GPa | 1-2 GPa |
| Stiffness (Young's Modulus) | >1,000 GPa | ~200 GPa |
| Density | 1.3-1.4 g/cm³ | 7.8 g/cm³ |
| Strength-to-Weight Ratio | Extremely High | Good |
| Toughness / Energy Absorption | Lower (Brittle) | Excellent |
| Cost (Bulk Material) | High | Low |
| Best For | Lightweight composites, aerospace, specialized applications | Structural integrity, construction, cost-effective solutions |
Ready to integrate advanced materials like carbon nanotubes into your research or production?
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality laboratory equipment and consumables to support your work with cutting-edge materials. Whether you are developing next-generation composites or enhancing material properties, our solutions can help you achieve precise and reliable results.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific laboratory needs and help you leverage the power of advanced materials.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Tube
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Centrifuge Tubes
- Multi-zone Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Professional Cutting Tools for Carbon Paper Cloth Diaphragm Copper Aluminum Foil and More
People Also Ask
- What are 4 disadvantages of brazing? Understanding the Critical Limitations of This Joining Method
- What are ceramic tubes used for? Essential Components for Extreme Heat & Electrical Insulation
- What are the disadvantages of brazing? Understanding the key limitations and trade-offs.
- What are ceramic tubes used for? Essential for Extreme Heat, Insulation & Purity
- What are the strengths of brazing? Achieve Strong, Clean, and Precise Metal Joining



















