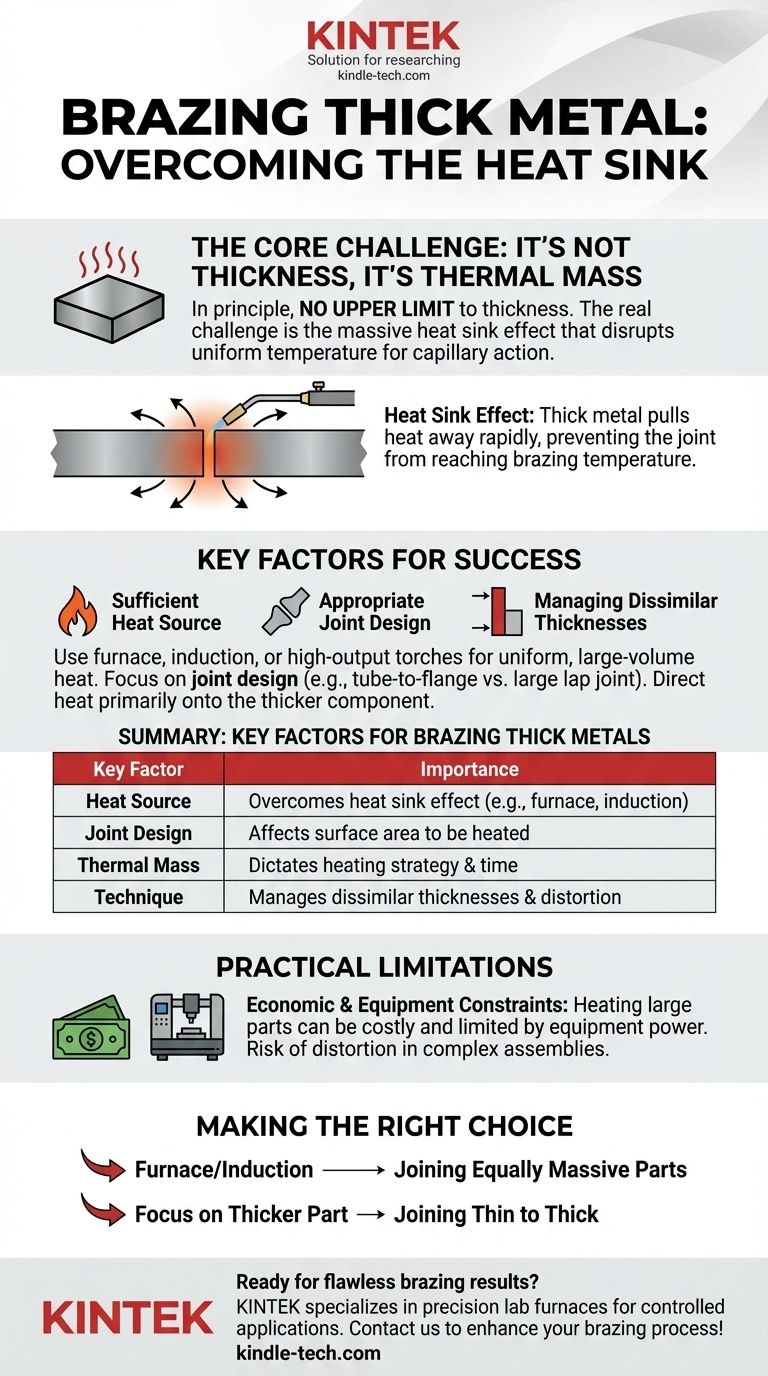
In principle, there is no upper limit to the thickness of metal you can braze. The true limiting factor is not the dimension of the metal itself, but your ability to deliver sufficient and uniform heat to the entire joint area. Success depends on overcoming the immense heat sink effect of a thick component to bring the joint to the proper brazing temperature.
The challenge of brazing thick metal isn't the material's thickness, but its thermal mass. Your success is determined entirely by your heating method's ability to overcome this heat sink and achieve a uniform temperature across the joint for proper filler metal flow.

Why Mass, Not Thickness, is the Real Challenge
Brazing operates on the principle of capillary action, where molten filler metal is drawn into the tight gap between two base metals. For this to work correctly, the entire joint area must be at a uniform temperature slightly above the filler metal's melting point. Thick materials disrupt this process due to their ability to absorb and conduct heat away from the joint.
The Heat Sink Effect
A thick piece of metal acts as a massive heat sink. It rapidly pulls thermal energy away from the point of heat application.
If your heat source (like a torch) cannot supply heat faster than the metal dissipates it, you will never reach the required brazing temperature at the joint interface.
The Need for Uniform Temperature
For capillary action to function, both pieces of metal forming the joint must be at the correct temperature.
If one piece is hot and the other is too cool, the filler metal will melt and bond to the hot side but will fail to wet or flow onto the cool side, resulting in an incomplete and weak joint.
The Danger of Thermal Gradients
Heating a localized spot on a very thick plate creates a steep thermal gradient—a sharp difference in temperature between the hot zone and the surrounding cold metal.
This can cause the filler metal to flow unevenly and, in some materials, can introduce significant internal stresses that may lead to distortion or cracking during cooling.
Key Factors for Brazing Thick Sections
Successfully brazing thick components is a matter of controlling the heat. This requires careful consideration of your equipment, joint design, and technique.
Sufficient Heat Source and Method
A small handheld torch is inadequate for thick sections. You need a method capable of delivering a large volume of heat evenly.
Effective methods include furnace brazing, where the entire assembly is heated slowly in a controlled atmosphere, or induction heating, which uses magnetic fields to generate heat directly and rapidly within the parts. Large, multi-head torch setups can also be used for localized, high-output heating.
Appropriate Joint Design
The design of the joint is critical. A lap joint between two thick plates requires heating a very large surface area.
In contrast, brazing a small-diameter tube into a thick flange is more manageable, as you can focus heat on the more massive flange component.
Managing Dissimilar Thicknesses
A common and challenging scenario is brazing a thin component to a thick one. The key is to direct the majority of your heat onto the thicker part.
By heating the larger heat sink first and more aggressively, you allow its temperature to rise. The thin part will come up to temperature much more quickly with only residual heat, preventing it from overheating while the thick part catches up.
Understanding the Practical Limitations
While theoretically possible, brazing extremely thick sections has practical and economic trade-offs that must be considered.
Economic Viability
Heating a very large, multi-ton component in a furnace for several hours may be technically possible, but it can be prohibitively expensive in terms of energy and time.
At a certain scale, welding processes often become a more practical and economical choice for joining massive sections.
Equipment Constraints
Your capabilities are ultimately limited by your equipment. The size of your furnace, the power of your induction coil, or the output of your torches will define the practical upper limit of what you can successfully braze.
Risk of Distortion
The significant thermal cycles required to heat and cool massive parts can lead to warping and distortion, especially in complex assemblies. This risk must be evaluated and managed through proper support and controlled cooling rates.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if brazing is the right approach for your thick-section application, consider your primary objective and the components involved.
- If your primary focus is joining two equally massive parts: Your best option is a method that provides enveloping heat, such as furnace or induction brazing, to ensure a slow, uniform temperature rise across the entire assembly.
- If your primary focus is joining a thin part to a thick part: Concentrate your heat source on the thicker component, allowing it to act as the primary heat reservoir, and let the thin component heat up via conduction and ambient energy.
- If your primary focus is evaluating brazing vs. welding: Consider the required joint properties, the potential for distortion, and the total cost of the operation, including heating time and equipment usage.
Ultimately, successful brazing is less about the thickness of the metal and more about the intelligent management of thermal energy.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Importance for Brazing Thick Metals |
|---|---|
| Heat Source | Determines if you can overcome the heat sink effect (e.g., furnace, induction). |
| Joint Design | Affects the surface area that needs to be heated uniformly. |
| Thermal Mass | The real challenge; dictates heating strategy and time. |
| Technique | Crucial for managing dissimilar thicknesses and preventing distortion. |
Ready to achieve flawless brazing results on your thick-section components? The right equipment is key to managing thermal mass and ensuring uniform heating. KINTEK specializes in precision lab furnaces and heating systems ideal for controlled brazing applications. Our experts can help you select the perfect solution for your specific metal joining challenges. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your brazing process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a vacuum oven play in the drying process of ZIF-67 precursors? Ensure Purity for High-Quality Synthesis
- Why is a vacuum oven necessary for treating composite cathode plates? Ensure Solid-State Battery Stability
- What are the methods of heat treatment of steel? Engineer Your Steel's Properties for Any Application
- What is the difference between heat treat and vacuum heat treat? Achieve Pristine, Contamination-Free Results
- Where are vacuum furnaces used? Essential for High-Purity Heat Treatment in Critical Industries
- What is the use of microwave sintering? Achieve Faster, More Uniform Ceramic Processing
- What are the advantages of brazing? Achieve Superior Joint Integrity for Complex Assemblies
- What is the maximum temperature in a vacuum furnace? It Depends on Your Materials and Process Needs



















