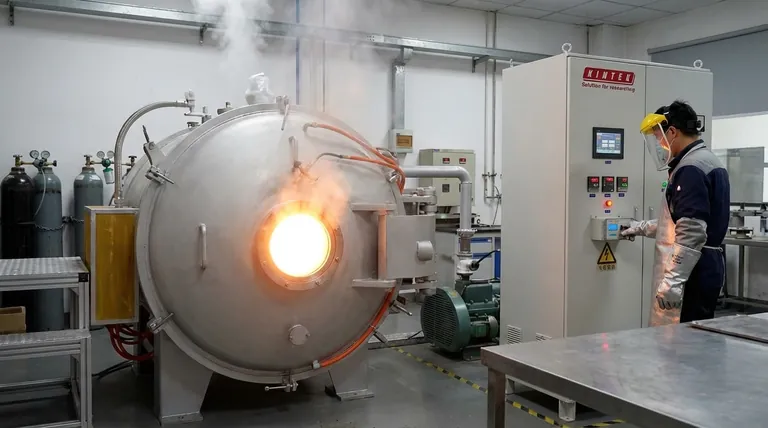
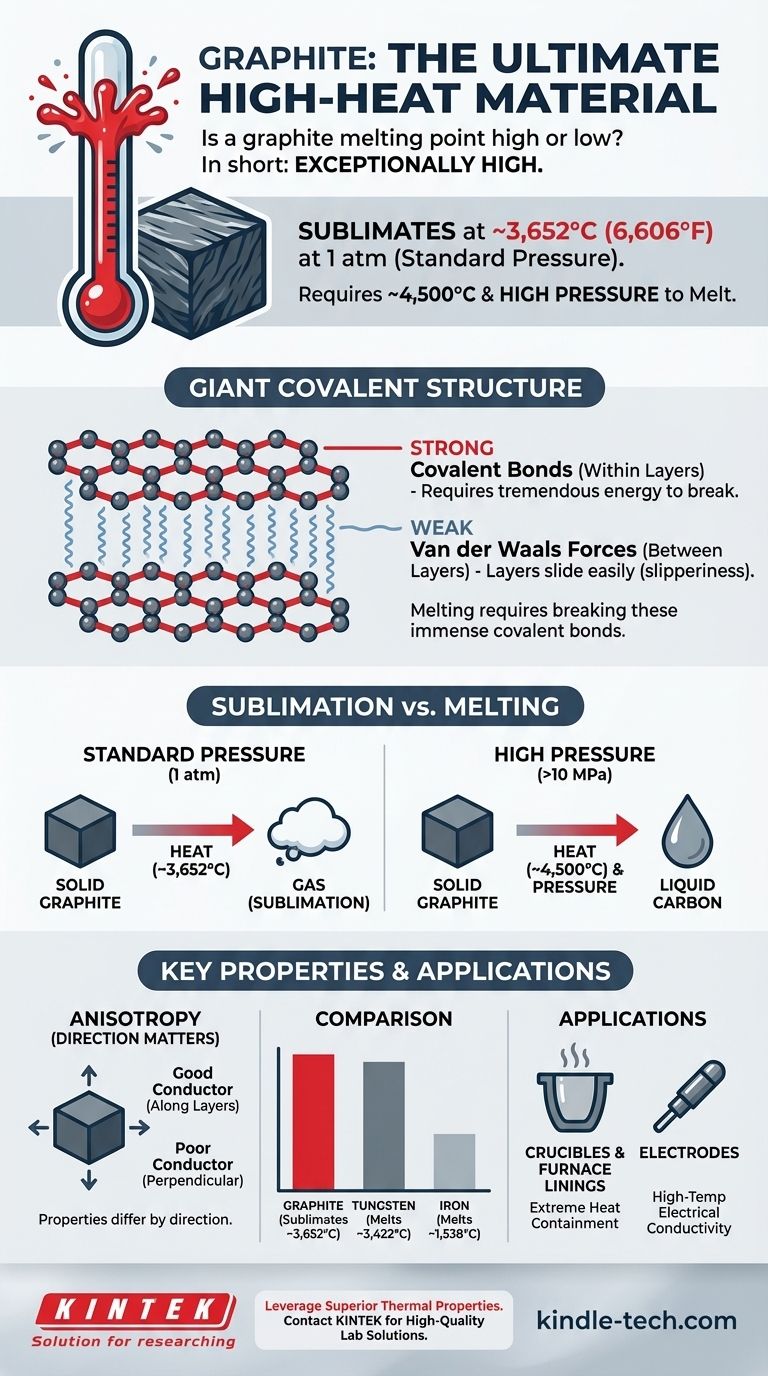
In short, graphite has an exceptionally high melting point. More accurately, at standard atmospheric pressure, it sublimates—turning directly from a solid to a gas—at an extreme temperature of around 3,652°C (6,606°F). To achieve true melting into a liquid state, both very high temperatures (~4,500°C) and high pressures are required.
The core reason for graphite's thermal resilience is its atomic structure. Melting graphite is not a matter of simply separating its layers, but of breaking the immensely strong covalent bonds that form the material itself, which requires a tremendous amount of energy.

The Giant Covalent Structure of Graphite
To understand graphite's high melting point, you must first understand its structure. It is not a simple collection of molecules, but a giant covalent structure.
Strong Covalent Bonds Within Layers
Each carbon atom in graphite is bonded to three other carbon atoms through strong covalent bonds. These atoms form a hexagonal lattice, creating vast, two-dimensional sheets or layers.
These covalent bonds are the same type of bond found in diamonds and are incredibly strong, requiring a massive amount of thermal energy to break.
Weak Forces Between Layers
While the atoms within a layer are strongly bonded, the layers themselves are held together by much weaker intermolecular forces known as van der Waals forces.
These weak forces are easily overcome, which is why graphite feels soft and slippery. This property allows layers to slide off, making graphite an excellent material for pencil lead and as a solid lubricant.
What 'Melting' Actually Means for Graphite
This distinction between the two force types is critical. The slipperiness of graphite is due to the weak forces between layers, but its melting point is dictated by the strong covalent bonds within the layers.
To transition graphite from a solid to a liquid, you must provide enough energy to break the strong covalent bonds and allow the carbon atoms to move freely. This is why it has one of the highest melting/sublimation points of any known material.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Nuances
Graphite's properties are not uniform, and its behavior under heat comes with specific conditions and limitations that are crucial for practical applications.
Sublimation vs. Melting
At normal atmospheric pressure, graphite does not melt. When heated, it reaches its sublimation point and turns directly into a gas.
A true liquid carbon phase only exists at very high pressures, starting around 10 megapascals (MPa), or about 100 times standard atmospheric pressure.
Anisotropy: Direction Matters
Graphite is an anisotropic material, meaning its properties differ depending on the direction of measurement.
It conducts heat and electricity very well along its layers but is a poor conductor perpendicular to them. This must be considered in thermal management applications.
Comparison to Diamond and Metals
Graphite's sublimation point is comparable to, and under some conditions surpasses, that of diamond—another carbon allotrope. Both are high for the same reason: breaking strong covalent bonds.
Compared to metals, graphite stands apart. For instance, iron melts at 1,538°C and tungsten, one of the highest melting point metals, melts at 3,422°C—still below graphite's sublimation point.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Understanding these principles allows you to select and use graphite effectively based on your specific goal.
- If your primary focus is extreme heat containment: Graphite is a premier choice for crucibles, furnace linings, and rocket nozzles due to its incredibly high sublimation point and structural stability at temperatures where most metals would be liquid or vapor.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature electrical conductivity: Graphite is ideal for electrodes in electric arc furnaces, as it can withstand the immense heat generated while efficiently conducting massive electrical currents.
- If your primary focus is understanding material science: Remember that a material's melting point is fundamentally linked to the strength of the bonds holding its atoms together, and graphite is a classic example of a giant covalent structure.
Ultimately, graphite's high melting point is a direct consequence of its robust atomic structure, making it one of the most thermally resilient materials known.
Summary Table:
| Property | Value / Description |
|---|---|
| Sublimation Point | ~3,652°C (6,606°F) at 1 atm |
| Melting Point | ~4,500°C (requires high pressure) |
| Key Structural Feature | Giant covalent structure with strong bonds within layers |
| Primary Thermal Limitation | Oxidation in air at temperatures above ~400°C |
Leverage Graphite's Superior Thermal Properties in Your Lab
Graphite's exceptional heat resistance makes it indispensable for high-temperature applications like furnace linings, crucibles, and electrodes.
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including premium graphite products tailored for demanding laboratory environments. Our materials ensure reliability, performance, and safety at extreme temperatures.
Ready to enhance your high-temperature processes? Contact our experts today to find the perfect graphite solution for your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the properties of graphite at high temperatures? Unlock Its Strength and Stability in Extreme Heat
- At what temperature does graphite thermal decompose? The Critical Role of Atmosphere
- What is the thermal coefficient of graphite? Unlock Its Unique Thermal Stability
- How is synthetic graphite manufactured? A Deep Dive into the High-Temperature Process
- Why can graphite withstand heat? Unlocking Its Extreme Thermal Stability for Your Lab



















