In a direct comparison of joint material, a properly executed weld is stronger than a brazed joint. This is because welding melts and fuses the base metals together, creating a single, continuous piece of material. However, this simple answer is misleading. The "stronger" method depends entirely on the application, the materials being joined, and the design of the joint itself, with brazing often producing a stronger overall assembly.
The critical distinction is not which process is generically "stronger," but how each method achieves its strength. Welding creates strength through fusion, while brazing creates strength through joint design and adhesion. Understanding this difference is the key to selecting the right process for your goal.

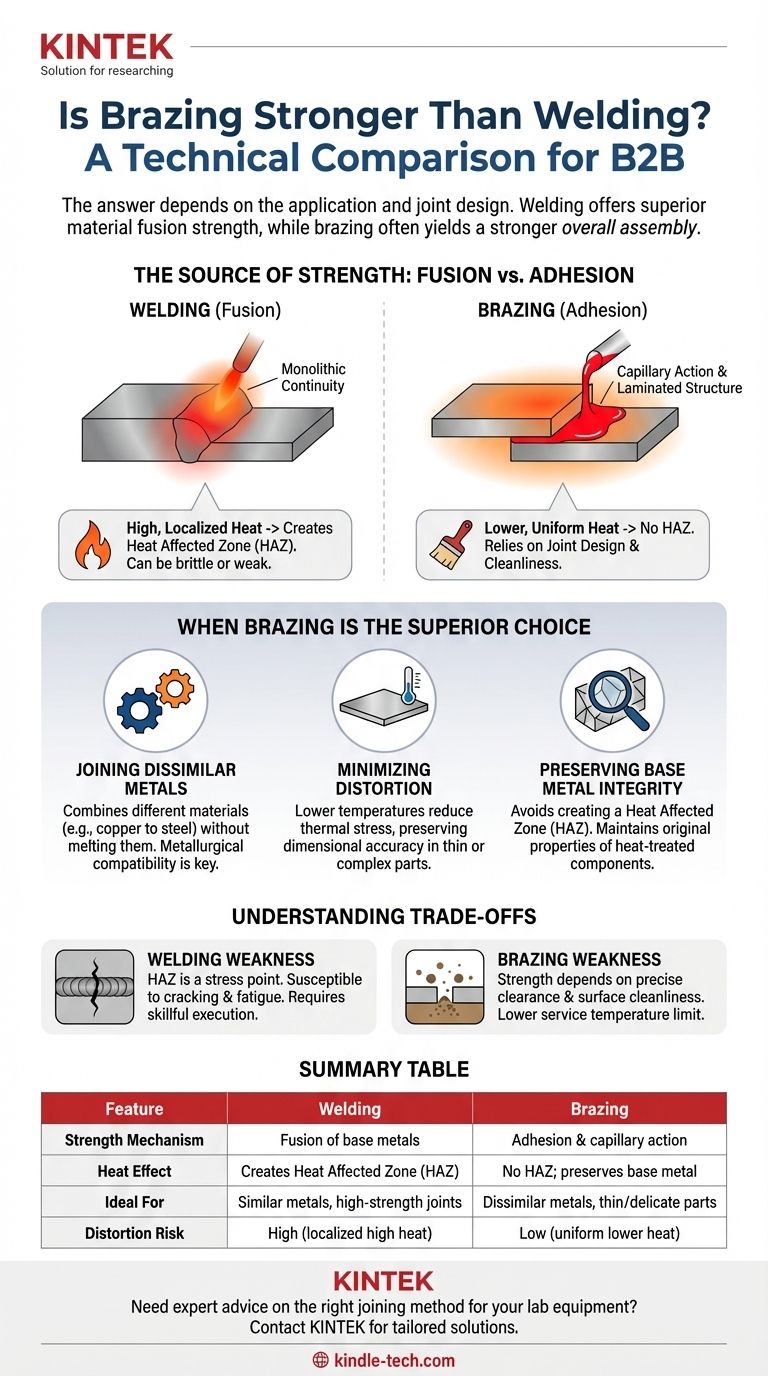
The Source of Strength: Fusion vs. Adhesion
The fundamental difference between these two processes dictates where their strengths and weaknesses lie. They are not interchangeable; they are different tools for different engineering problems.
How Welding Achieves Strength
Welding works by concentrating intense heat on the joint, melting the edges of the base metals along with a consumable filler material.
This molten pool solidifies into a single, fused structure. The resulting weld bead is, in essence, a cast metal structure that is integral to the parent parts. Its strength comes from this monolithic continuity.
A byproduct of this intense, localized heat is the Heat Affected Zone (HAZ)—an area of base metal next to the weld that was heated but not melted. The properties of the metal in the HAZ can be altered, sometimes becoming more brittle or weaker than the original material.
How Brazing Achieves Strength
Brazing works by heating the base metals to a temperature below their melting point and introducing a filler metal that melts and is drawn into the joint by capillary action.
The strength of a brazed joint does not come from the intrinsic strength of the filler metal, which is almost always weaker than the base metals. Instead, its strength comes from a combination of metallurgical bonding and superior joint design.
Brazed joints are designed with a large surface area (e.g., a lap joint instead of a butt joint). The thin layer of filler metal distributes the load across this entire area, creating an incredibly strong, laminated structure.
When a Brazed Assembly is the Superior Choice
While a weld bead itself may be stronger, there are common scenarios where the brazing process results in a more reliable and functionally stronger final product.
Joining Dissimilar Metals
Welding fundamentally different metals (like copper to steel) is extremely difficult or impossible due to differences in melting points, thermal expansion, and metallurgy.
Brazing excels at this task. By choosing a filler metal that is metallurgically compatible with both base metals, you can create a strong, reliable bond between them without having to melt either one.
Minimizing Thermal Stress and Distortion
The high, localized heat of welding induces significant thermal stress in the part, which can lead to warping and distortion, especially in thin or complex assemblies.
Brazing uses much lower temperatures, and the heat is applied more uniformly across the entire joint area. This preserves the original properties (like temper or hardness) of the base metals and dramatically reduces the risk of distortion, often resulting in a stronger, more dimensionally accurate final part.
Preserving Base Metal Integrity
The HAZ created by welding is often the weakest point in the finished assembly and a common point of failure.
Because brazing does not melt the base metals, it does not create a Heat Affected Zone. The mechanical properties of the base materials right up to the edge of the joint remain unchanged, which is a critical advantage for heat-treated or work-hardened components.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither method is perfect. Choosing correctly means understanding their inherent limitations.
The Weakness of a Welded Joint
The primary weakness of a weld is the Heat Affected Zone (HAZ). This area can be a point of stress concentration and is susceptible to cracking or embrittlement, especially under fatigue or cyclical loading. Poor welding technique can also introduce porosity or incomplete fusion, creating significant weak points.
The Weakness of a Brazed Joint
The strength of a brazed joint is critically dependent on joint clearance and cleanliness. If the gap between the parts is too large, the strength of the joint becomes that of the weaker filler metal. The surfaces must also be perfectly clean for the capillary action to work and for a proper metallurgical bond to form.
Furthermore, brazed joints have a lower service temperature limit, defined by the melting point of the filler metal.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The optimal method is the one that best manages the forces and conditions your assembly will face.
- If your primary focus is maximum raw strength in a simple, load-bearing joint (like structural steel): Welding is the superior choice, as it creates a fused, monolithic structure.
- If your primary focus is joining dissimilar metals or delicate, thin-walled components: Brazing offers a reliable and strong solution where welding would fail or damage the part.
- If your primary focus is maintaining dimensional stability and avoiding material distortion: Brazing's lower, uniform heat makes it the far better option.
- If your primary focus is creating a stress-free joint that preserves the base metal's properties: Brazing is the only choice, as it avoids creating a Heat Affected Zone.
By moving beyond a simple "stronger versus weaker" mindset, you can select the joining process that guarantees the performance and integrity of your entire design.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Welding | Brazing |
|---|---|---|
| Strength Mechanism | Fusion of base metals | Adhesion & capillary action |
| Heat Effect | Creates Heat Affected Zone (HAZ) | No HAZ; preserves base metal |
| Ideal For | Similar metals, high-strength joints | Dissimilar metals, thin/delicate parts |
| Distortion Risk | High (localized high heat) | Low (uniform lower heat) |
Need expert advice on the right joining method for your lab equipment?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored to your specific needs. Whether you're joining dissimilar metals for a custom reactor or need precise thermal processing for delicate components, our team can help you select the optimal process to ensure strength, reliability, and performance.
Contact us today to discuss your project and discover how KINTEK can enhance your laboratory's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between welding and vacuum brazing? Choose the Right Joining Method for Your Project
- What is brazing in heat treatment? Achieve Superior Joint Quality and Efficiency
- What is the cost of a vacuum brazing furnace? A guide to key factors and investment strategy
- What are the different types of brazing welding? A Guide to Choosing the Right Heat Source
- Where are vacuum furnaces used? Essential for High-Purity Heat Treatment in Critical Industries



















