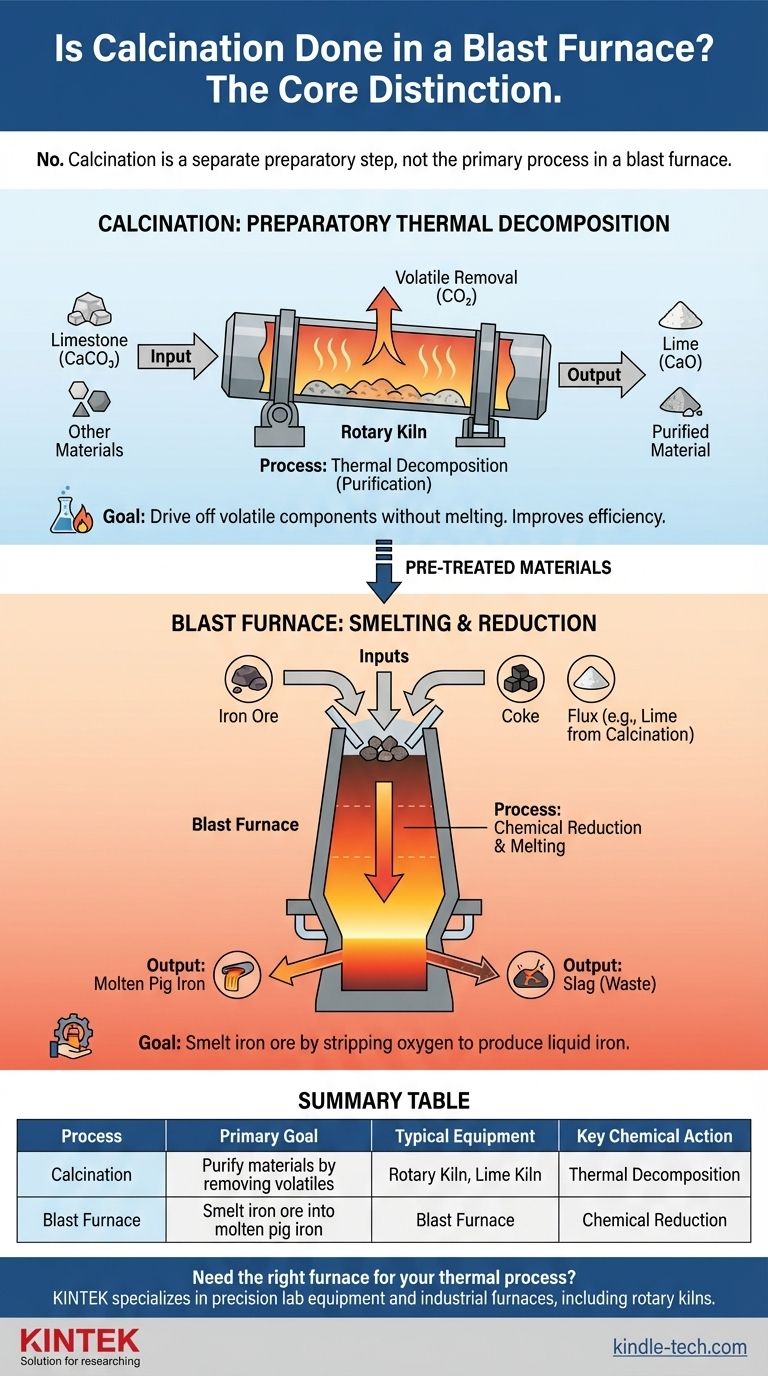
No, calcination is not the primary process performed in a blast furnace. While some decomposition occurs, a blast furnace's main purpose is smelting. Calcination is a distinct preparatory step that typically happens in a separate vessel before materials enter the blast furnace.
The core distinction is one of purpose. Calcination is a thermal pre-treatment to purify materials by removing volatile substances like carbon dioxide. A blast furnace is a massive chemical reactor designed for smelting—the reduction of iron ore into molten iron.

What is the True Purpose of a Blast Furnace?
A blast furnace is not merely an oven; it is a highly specialized, counter-current reactor at the heart of primary iron production. Its function is far more complex than simple heating.
The Goal: Smelting and Reduction
The exclusive goal of a blast furnace is to smelt iron ore. This involves a chemical reduction process, where oxygen is stripped away from iron oxides (the ore) to produce liquid iron, often called pig iron.
This is achieved by using coke (a high-carbon fuel) as both a heat source and a reducing agent. The intense heat facilitates the chemical reactions that transform solid ore into molten metal.
Key Inputs and Outputs
To achieve this, three primary materials are fed into the top of the furnace: iron ore, coke, and a flux (typically limestone). Hot air is blasted into the bottom.
The primary outputs are molten pig iron and a liquid waste product called slag, which is formed from the flux and impurities. These are drained from the bottom of the furnace.
Defining Calcination as a Separate Process
The confusion between these processes often arises because both involve high temperatures. However, their chemical goals are fundamentally different.
The Goal: Thermal Decomposition
Calcination is the process of heating a solid material to a high temperature to drive off volatile components, without melting the substance itself. It is a purification or activation step.
The classic example is heating limestone (calcium carbonate, CaCO₃) in a kiln. This drives off carbon dioxide (CO₂) and leaves behind lime (calcium oxide, CaO), which is a more effective flux.
Where Calcination Occurs
This pre-treatment is done in dedicated furnaces, such as a rotary kiln or lime kiln, before the materials are charged into the blast furnace. Performing calcination beforehand makes the blast furnace operation more efficient and controllable.
By pre-calcining the limestone and ore, the blast furnace does not have to expend energy on this initial decomposition. This allows it to dedicate all its energy to the main task of smelting.
Common Pitfalls and Clarifications
Understanding why these processes are distinct is crucial for grasping the logic of industrial metallurgy. The confusion is common but easily clarified.
Heat is the Common Denominator
Both processes rely on extreme heat. This shared characteristic is the primary source of confusion. However, the application of that heat is what defines the process—decomposition for calcination versus reduction and melting for smelting.
Process vs. Pre-treatment
Think of it as cooking a complex meal. Calcination is the prep work—like roasting garlic to mellow its flavor before adding it to a sauce. Smelting is the main event where all the prepared ingredients are combined and transformed into the final dish.
A Point of Nuance: Flux Decomposition
To be precise, some decomposition does occur inside a blast furnace. When limestone is added as a flux, the heat in the upper part of the furnace causes it to break down into lime and carbon dioxide.
However, this is a secondary reaction, not the furnace's primary purpose. The blast furnace is designed and optimized for smelting, not calcination.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To apply this knowledge correctly, always focus on the primary objective of the equipment and the stage in the production chain.
- If your primary focus is on iron production: View calcination as an optional but highly efficient preparatory step, and see the blast furnace as the non-negotiable heart of the smelting process.
- If your primary focus is on defining thermal processes: Remember that calcination purifies by removing volatiles without melting, while smelting uses a reducing agent to transform an ore into a molten metal.
Distinguishing between a preparatory treatment and the main industrial event is fundamental to understanding any complex manufacturing process.
Summary Table:
| Process | Primary Goal | Typical Equipment | Key Chemical Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calcination | Purify materials by removing volatile substances | Rotary Kiln, Lime Kiln | Thermal Decomposition |
| Blast Furnace | Smelt iron ore into molten pig iron | Blast Furnace | Chemical Reduction |
Need the right furnace for your specific thermal process? KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and industrial furnaces, including rotary kilns for calcination. Our experts can help you select the ideal equipment to optimize your material purification or smelting operations. Contact our team today to discuss your application and receive a tailored solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is the temperature in a tube furnace measured and controlled? Master Precise Thermal Processing
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- Why is a quartz tube furnace utilized in the thermal oxidation of MnCr2O4 coatings? Unlock Precise Selective Oxidation



















