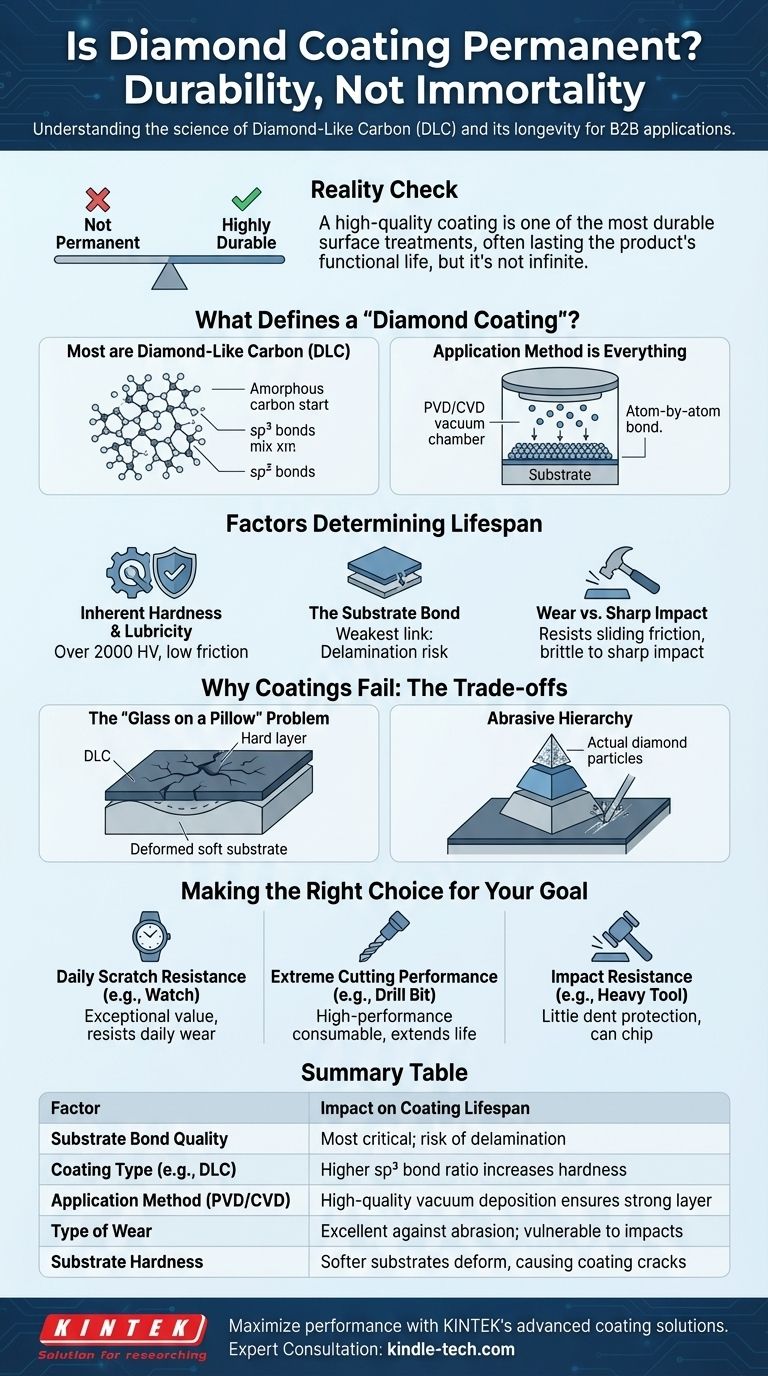
While no coating is truly permanent, a high-quality diamond coating is one of the most durable and long-lasting surface treatments available in material science. Its longevity is not infinite, but for many applications, it is designed to last the functional lifetime of the product itself. The actual durability depends entirely on the quality of the application, the type of coating, and the specific stresses it endures.
The concept of "permanence" is misleading when discussing coatings. The longevity of a diamond coating is determined not by the hardness of the coating itself, but by the strength of its bond to the underlying material and the type of wear it is subjected to.
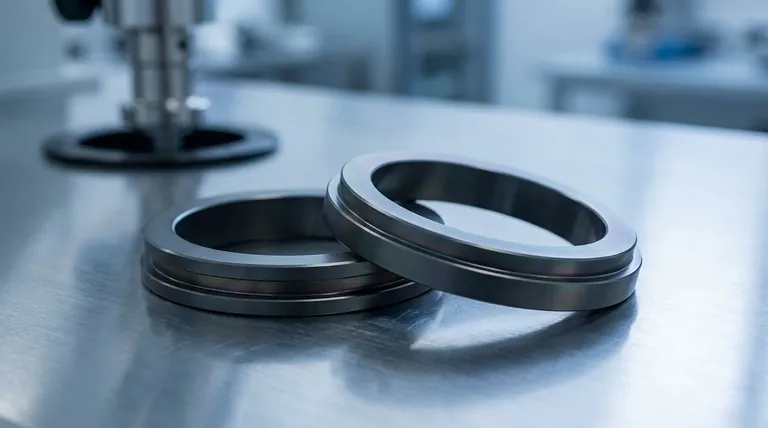

What Defines a "Diamond Coating"?
To understand its permanence, we must first clarify what a "diamond coating" is. It is rarely a layer of pure, crystalline diamond.
It's Usually Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC)
Most commercial "diamond coatings" are Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC). This is a class of amorphous carbon material that displays some of the unique properties of natural diamond.
DLC is applied in a vacuum chamber and forms an extremely hard, slick surface. It is not pure diamond but contains a mixture of diamond-type (sp³) and graphite-type (sp²) chemical bonds. The higher the ratio of sp³ bonds, the more "diamond-like" and durable the coating is.
Application Method is Everything
These coatings are applied using processes like Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) or Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). These methods deposit the coating atom by atom onto the base material (the substrate).
The key takeaway is that the coating is a distinct layer bonded to a surface. It does not become part of the material itself. This bond is the most critical factor in its longevity.
Factors That Determine Its Lifespan
A coating's durability is a balance of its own properties and how it interacts with the world.
Inherent Hardness and Lubricity
DLC coatings are exceptionally hard, often registering over 2000 HV on the Vickers hardness scale, many times harder than steel. This provides incredible resistance to abrasive wear and scratches.
They also have a very low coefficient of friction, meaning other surfaces tend to slide off them easily. This property, known as lubricity, further reduces wear.
The Weakest Link: The Substrate Bond
The single most common point of failure is not the coating wearing away, but the coating delaminating—or peeling off—from the substrate.
Proper surface preparation before the coating process is absolutely critical. A high-quality application on a well-prepared surface will create an atomic bond that is incredibly strong and resistant to peeling. A poor application will fail quickly.
Wear vs. Sharp Impact
A diamond coating provides world-class protection against sliding friction and scratching. However, it is a very thin, brittle layer.
A sharp, direct impact can cause the coating to chip or crack, especially if the underlying material is soft enough to deform from the impact.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Why Coatings Fail
True permanence is impossible because of a few key trade-offs.
The "Glass on a Pillow" Problem
Imagine placing a thin sheet of glass on a soft pillow and pressing on it. The glass itself is hard, but it will easily crack because the pillow beneath it deforms.
Similarly, a super-hard DLC coating on a relatively soft substrate (like aluminum or even some softer steels) can be damaged if the base material gets dented. The coating cannot stretch and will crack under the deformation.
Abrasive Hierarchy
While a diamond coating is harder than almost anything it will encounter, it is not invincible. It can still be scratched or worn away by materials that are harder, such as actual diamond particles or silicon carbide.
Over a very long period, even repeated friction from less-hard materials can cause microscopic wear that eventually accumulates.
Cost Dictates Quality
Creating a strong, durable bond at the atomic level is a complex and expensive process. Inexpensive products with "diamond coatings" often cut corners on surface preparation or use lower-grade DLC.
These cheap coatings are the ones that give coatings, in general, a reputation for peeling or scratching easily. A high-end application from a reputable source behaves very differently.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision should be based on a clear understanding of your expectations for the product.
- If your primary focus is daily scratch resistance (e.g., a watch case): A well-applied DLC coating from a reputable brand offers exceptional value and will resist daily wear and tear for many years, often outlasting other components.
- If your primary focus is extreme cutting performance (e.g., an industrial drill bit): View the coating as a high-performance consumable that drastically extends the tool's usable life and performance, but understand it will eventually wear and require replacement.
- If your primary focus is impact resistance (e.g., a heavy-use tool): Be aware that while extremely scratch-resistant, the coating offers little protection against dents and can chip from a sharp impact that deforms the underlying metal.
Ultimately, a diamond coating is not an assurance of indestructibility, but a technical investment in superior surface performance.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Coating Lifespan |
|---|---|
| Substrate Bond Quality | Most critical factor; determines risk of delamination |
| Coating Type (e.g., DLC) | Higher sp³ bond ratio increases diamond-like hardness |
| Application Method (PVD/CVD) | High-quality vacuum deposition ensures a strong, even layer |
| Type of Wear (Abrasion vs. Impact) | Excellent against abrasion; vulnerable to sharp impacts |
| Substrate Hardness | Softer substrates can deform, causing the hard coating to crack |
Maximize the performance and lifespan of your components with KINTEK's advanced coating solutions.
As a specialist in laboratory equipment and consumables, KINTECO understands that durability and precision are paramount. Whether you need to protect sensitive lab tooling, enhance the wear resistance of analytical components, or improve the performance of cutting instruments, our high-quality diamond-like carbon (DLC) coatings are applied using state-of-the-art PVD/CVD techniques to ensure a superior bond and long-lasting protection.
We help our laboratory and industrial customers achieve:
- Extended Component Life: Reduce wear and tear on critical parts.
- Improved Performance: Benefit from low friction and high hardness.
- Tailored Solutions: Get coatings optimized for your specific substrate and application stresses.
Don't leave your equipment's durability to chance. Contact KINTECO today for a expert consultation on how our coating services can solve your wear challenges and add value to your operations.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- Laboratory CVD Boron Doped Diamond Materials
- CVD Diamond Dressing Tools for Precision Applications
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
People Also Ask
- What are the three types of coating? A Guide to Architectural, Industrial, and Special Purpose
- How thick is CVD diamond coating? Balancing Durability and Stress for Optimal Performance
- Is diamond coating worth it? Maximize Component Life and Performance
- What is diamond coating film? A Thin Layer of Diamond for Extreme Performance
- What are diamond coated films? Enhance Materials with Super-Hard, Transparent Layers














