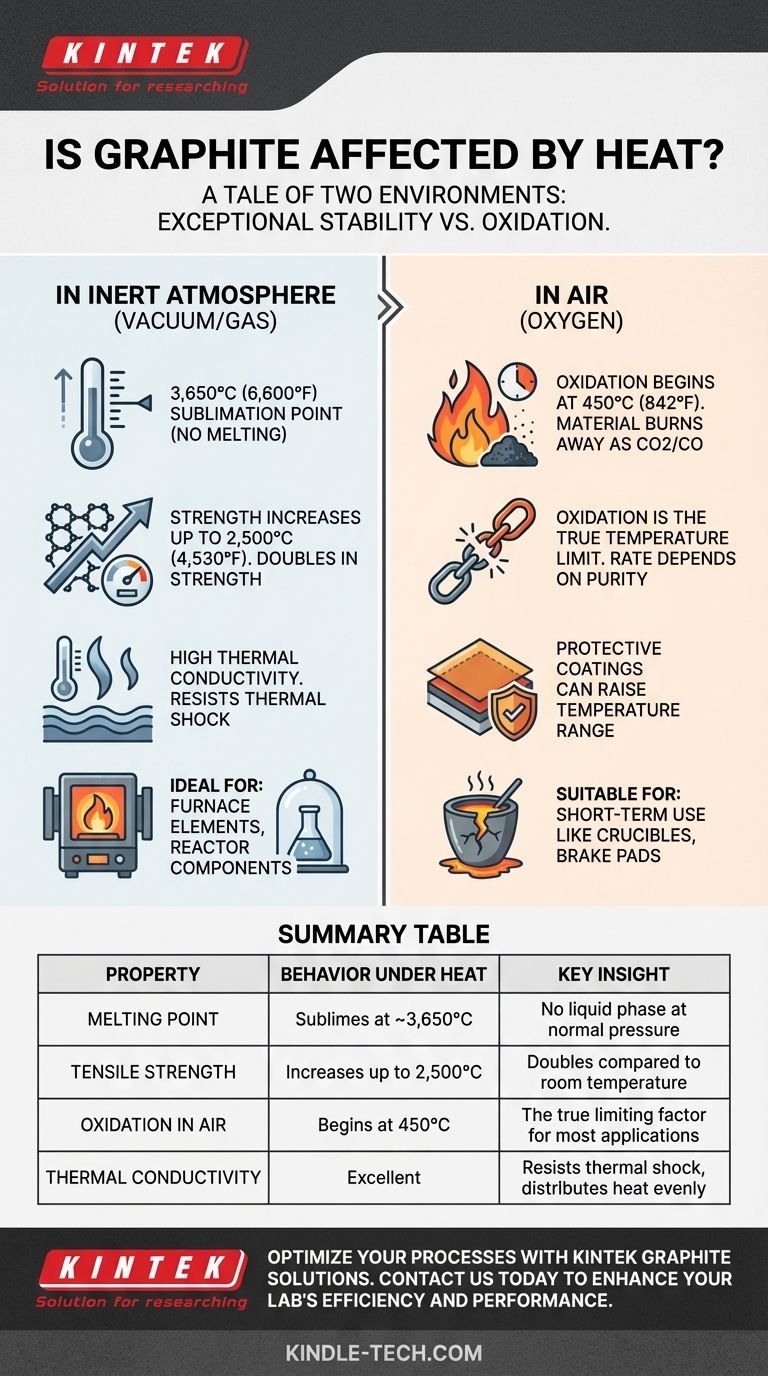
Yes, graphite is affected by heat, but it behaves unlike almost any other material. Instead of melting, graphite maintains its solid form and actually gets stronger at extreme temperatures. Its true limitation isn't the heat itself, but rather the presence of oxygen, which will cause it to burn away (oxidize) at high temperatures.
Graphite's performance under heat is a tale of two environments. It is one of the most heat-resistant materials known when protected from oxygen, but it will degrade and burn at much lower temperatures when exposed to air.

The Exceptional Thermal Stability of Graphite
Graphite’s unique atomic structure—strong carbon sheets weakly bonded to each other—gives it remarkable properties when heated.
It Sublimes, It Doesn't Melt
At normal atmospheric pressure, graphite has no melting point. Instead of turning into a liquid, it sublimes, turning directly from a solid into a gas at an incredibly high temperature of approximately 3,650°C (6,600°F).
This property makes it exceptionally stable for applications like crucibles and furnace linings, where molten metals would destroy lesser materials.
It Gets Stronger with Heat
In a complete reversal of how metals behave, graphite's tensile strength increases with temperature. It roughly doubles its room-temperature strength as it heats up to 2,500°C (4,530°F).
This counter-intuitive behavior is due to its crystalline structure, which becomes more resistant to fracture at high temperatures.
High Thermal Conductivity
Graphite is an excellent thermal conductor, meaning it efficiently dissipates heat across its structure. This prevents localized hot spots and makes it highly resistant to thermal shock—the tendency for a material to crack when subjected to rapid temperature changes.
The Critical Factor: The Surrounding Atmosphere
How graphite ultimately performs under heat is determined entirely by the gas surrounding it.
In an Inert Atmosphere: Peak Performance
When heated in a vacuum or an inert gas environment (like argon or nitrogen), graphite is stable up to its sublimation point. This is the ideal condition for its use in applications like furnace heating elements or high-temperature reactor components.
Under these protected conditions, it is one of the most capable high-temperature materials ever developed.
In Air: The Challenge of Oxidation
This is the most important limitation for real-world use. In the presence of oxygen, graphite will begin to oxidize, or burn, into carbon dioxide (CO2) and carbon monoxide (CO) gas.
This process starts at temperatures as low as 450°C (842°F) and accelerates significantly as the temperature rises. The material will literally vanish over time.
Understanding the Practical Trade-offs
When evaluating graphite for a high-temperature application, the primary concern is almost always oxidation, not melting.
Oxidation is the True Temperature Limit
For any application in open air, the functional temperature limit of graphite is defined by its rate of oxidation. A component might survive for a short time at 800°C, but it will be consumed much faster than at 500°C.
Not All Graphite is Created Equal
The temperature at which significant oxidation begins depends on the purity and structure of the graphite. Higher-purity, high-density grades of graphite are more resistant to oxidation than lower-purity, more porous grades.
Protective Coatings Can Help
For some applications, graphite components can be treated with anti-oxidation coatings. These create a barrier that can significantly raise the material's useful temperature range in air, though they add complexity and cost.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your choice depends entirely on the operating environment and desired lifespan of the component.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperature stability in a controlled environment: Graphite is an elite choice for vacuum furnaces, electrodes, or rocket nozzles where oxygen is absent.
- If your primary focus is short-term use in open air: Graphite is suitable for applications like metal casting crucibles or brake pads, where a limited lifespan due to gradual oxidation is acceptable.
- If your primary focus is thermal management: Graphite's ability to conduct heat makes it a superior material for heat sinks and spreaders in electronics, even at moderately elevated temperatures.
Ultimately, understanding the interplay between heat and atmosphere is the key to successfully using graphite in any demanding application.
Summary Table:
| Property | Behavior Under Heat | Key Insight |
|---|---|---|
| Melting Point | Sublimes at ~3,650°C | No liquid phase at normal pressure |
| Tensile Strength | Increases up to 2,500°C | Doubles in strength compared to room temperature |
| Oxidation in Air | Begins at 450°C | The true limiting factor for most applications |
| Thermal Conductivity | Excellent | Resists thermal shock and distributes heat evenly |
Optimize your high-temperature processes with the right materials. Graphite's exceptional thermal stability and strength make it a top choice for demanding applications like furnace elements, crucibles, and thermal management systems. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including premium graphite products tailored to your specific needs.
Let our experts help you select the ideal graphite solution for your project. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your laboratory's efficiency and performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How can you control temperature inside a resistance furnace? Master Precise Thermal Management
- Do diamond testers really work? Uncover the truth about their accuracy and limitations.
- What is the function of a constant temperature orbital shaker in biomass hydrolysis? Maximize Sugar Yields
- What are the types of annealing? Choose the Right Process for Your Metal's Properties
- How much does biomass cost compared to other energy sources? A Guide to Costs, Trade-offs, and Value
- What is the easiest to melt metal? Start with Tin and Pewter for Safe, Simple Casting
- What are the raw materials for bio-oil? A Guide to Selecting the Best Biomass Feedstock
- How do laboratory shakers or stirrers influence the efficiency of hydrogen production during dark fermentation?



















