Yes, hydrogen is absolutely used in brazing. It is a core component of a specialized furnace process known as hydrogen brazing. In this method, a high-purity hydrogen atmosphere is used not as a fuel source, but as a powerful chemical agent that actively cleans the metal surfaces during the heating cycle, resulting in exceptionally strong and pure joints.
The critical insight is that in hydrogen brazing, the gas acts as a "reducing" agent, not a fuel. It chemically strips surface oxides from the parent materials, which allows the molten braze alloy to flow more freely and create a superior, high-integrity metallurgical bond.

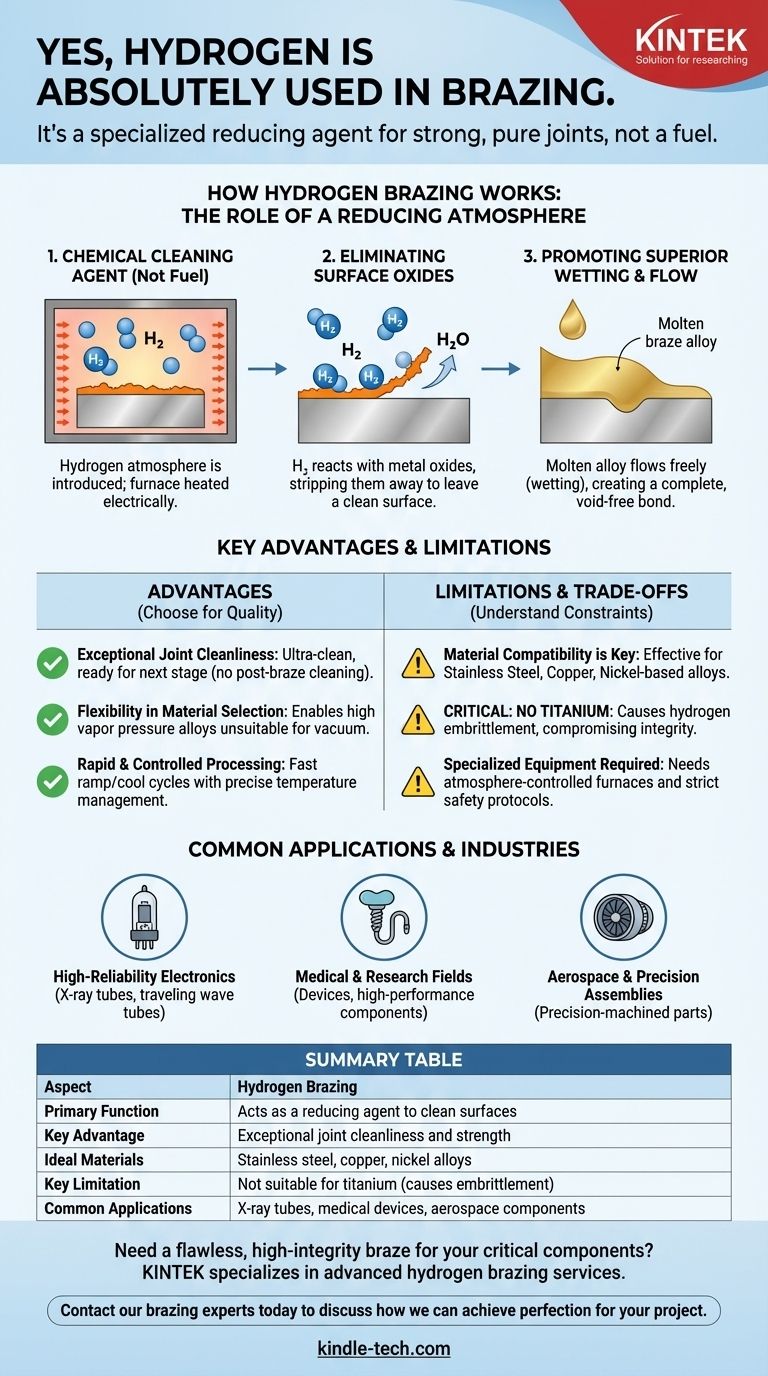
How Hydrogen Brazing Works: The Role of a Reducing Atmosphere
Hydrogen's unique chemical properties are the foundation of this process. It creates an active atmosphere within the furnace that transforms the brazing environment.
A Chemical Cleaning Agent, Not a Fuel
The purpose of the hydrogen is not to generate heat. Instead, the furnace is heated electrically while a high-purity hydrogen atmosphere is introduced.
This hydrogen atmosphere is what is known as a reducing atmosphere. Its function is to reverse the process of oxidation.
Eliminating Surface Oxides
Virtually all metals have a thin layer of oxide on their surface. This oxide layer can act as a barrier, preventing the molten braze alloy from properly adhering to the parent material.
The heated hydrogen gas reacts with these metal oxides, effectively stripping them away and leaving behind a perfectly clean, raw metal surface ready for bonding.
Promoting Superior Wetting and Flow
With the oxide barrier removed, the molten braze alloy can flow freely across the metal surfaces through capillary action. This process is called "wetting."
Superior wetting ensures the braze alloy penetrates the entire joint, creating a complete, void-free bond with maximum strength and integrity.
Key Advantages of the Hydrogen Process
Choosing hydrogen brazing provides distinct advantages, particularly for applications where quality and cleanliness are non-negotiable.
Exceptional Joint Cleanliness
The process produces ultra-clean, high-integrity assemblies. Because the cleaning happens during the brazing cycle, the finished parts are often ready for the next stage of assembly immediately, with no need for post-brazing cleaning operations.
Flexibility in Material Selection
Hydrogen brazing expands the range of usable materials. It enables the use of high vapor pressure braze alloys that would be unsuitable for brazing in a vacuum furnace.
Rapid and Controlled Processing
Modern hydrogen furnaces can be ramped to the desired temperature in minutes and feature quick, controlled cooling cycles. Integrated process control systems ensure precise temperature management for repeatable, high-quality results.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, hydrogen brazing is not a universal solution. Understanding its specific material requirements and constraints is essential for success.
Material Compatibility is Key
This process is highly effective for a range of materials, most commonly stainless steel, copper, and certain nickel-based alloys.
Critical Material Incompatibility
Hydrogen brazing cannot be used for titanium alloys. The hydrogen atmosphere causes a phenomenon known as hydrogen embrittlement in titanium, severely compromising the material's structural integrity.
Specialized Equipment is Required
Hydrogen is a flammable gas that requires specialized, atmosphere-controlled furnaces and strict safety protocols. This process is typically performed by expert providers with the necessary infrastructure and safety systems in place.
Common Applications and Industries
The benefits of hydrogen brazing make it the process of choice in demanding fields where failure is not an option.
High-Reliability Electronics
It is widely used for creating vacuum-tight seals in devices like X-ray tubes, traveling wave tubes, and other electron or ion beam devices.
Medical and Research Fields
The exceptional cleanliness of the joints is critical for medical devices and high-performance components used in scientific research and security applications.
Aerospace and Precision Assemblies
The process is ideal for joining precision-machined stainless steel components and other high-cleanliness assemblies used in the aerospace industry.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use these guidelines to determine if hydrogen brazing aligns with your project's specific requirements.
- If your primary focus is maximum cleanliness and joint integrity for sensitive electronics or medical devices: Hydrogen brazing is an exceptional choice that produces pure, strong, and reliable bonds.
- If your primary focus is brazing stainless steel or copper using high-vapor-pressure alloys: This process provides flexibility that is not possible in a vacuum atmosphere.
- If your primary focus is brazing titanium or its alloys: You must seek an alternative process, as hydrogen brazing will damage the material.
Ultimately, hydrogen brazing is a high-performance solution for applications where joint purity and metallurgical perfection are paramount.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Hydrogen Brazing |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Acts as a reducing agent to clean surfaces |
| Key Advantage | Exceptional joint cleanliness and strength |
| Ideal Materials | Stainless steel, copper, nickel alloys |
| Key Limitation | Not suitable for titanium (causes embrittlement) |
| Common Applications | X-ray tubes, medical devices, aerospace components |
Need a flawless, high-integrity braze for your critical components?
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced hydrogen brazing services for laboratories and manufacturers. Our expertise ensures superior metallurgical bonds for your most demanding applications in electronics, medical devices, and aerospace.
Contact our brazing experts today to discuss how we can achieve perfection for your project.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Non Consumable Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- When would you need to use a controlled atmosphere? Prevent Contamination and Control Reactions
- What are the effects of hydrogen (H2) in a controlled furnace environment? Mastering Reduction and Risk
- What is hydrogen annealing? Achieve Superior Material Properties with Bright Annealing
- What is a hydrogen furnace? Unlock Oxide-Free Processing for Superior Materials
- What is the temperature of a hydrogen furnace? Unlocking High-Temp, Oxide-Free Processing



















