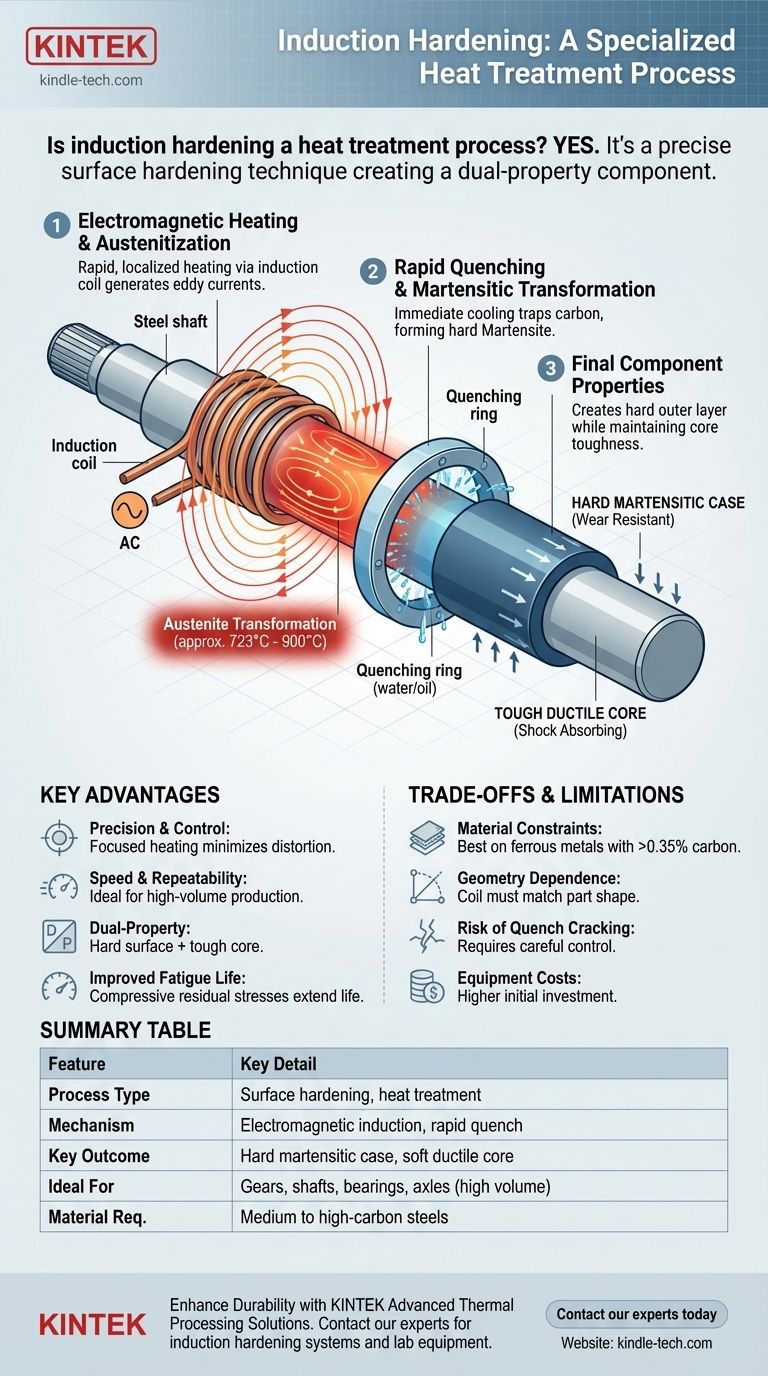
Yes, induction hardening is a distinct and highly effective form of heat treatment. It is a surface hardening process that uses electromagnetic induction to rapidly heat a targeted area of a metal part, followed by an immediate quench. This creates a hard, wear-resistant outer layer, or "case," while leaving the inner core of the material soft and ductile.
Induction hardening is not just a heat treatment; it's a strategic surface modification technique. Its primary value lies in creating components with two distinct sets of properties: a hard, wear-resistant surface to handle contact stress and a tough, ductile core to absorb shock and prevent catastrophic failure.
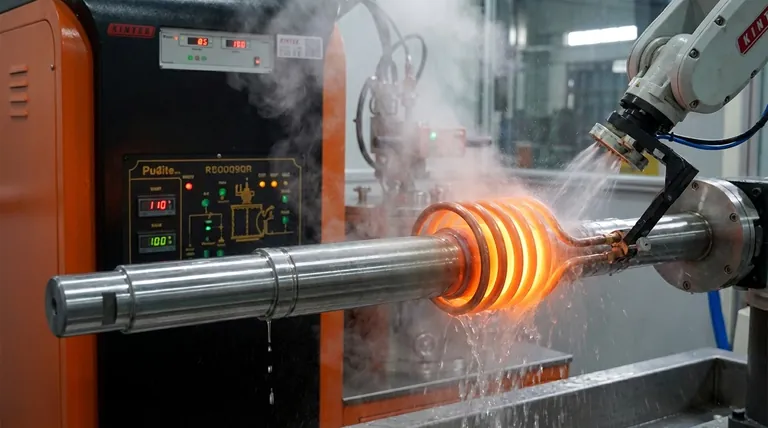
The Core Mechanism: How Induction Hardening Works
Induction hardening is an elegant process that relies on fundamental principles of physics and metallurgy. The entire cycle, from heating to cooling, can take mere seconds.
Step 1: Electromagnetic Heating
An alternating current (AC) is passed through a copper induction coil. This generates a powerful and rapidly changing magnetic field around the coil.
When a conductive part, such as a steel shaft, is placed inside this field, the magnetic field induces electrical currents within the metal itself. These are known as eddy currents.
The material's natural resistance to the flow of these eddy currents generates precise, intense, and localized heat very quickly.
Step 2: Austenitization
The heat raises the temperature of the part's surface layer above its critical transformation point (typically between 723°C and 900°C for steel).
At this temperature, the steel's crystal structure changes into a phase called austenite, where carbon becomes uniformly dissolved within the iron matrix. This step is essential for the hardening to occur.
Step 3: Rapid Quenching
Immediately after the surface reaches the target temperature, the part is cooled rapidly, or quenched. This is typically done by spraying it with water, oil, or a liquid polymer.
The quench must be fast enough to prevent the austenite from transforming back into its softer, pre-heated structures.
Step 4: Martensitic Transformation
This rapid cooling "traps" the carbon atoms within the iron's crystal lattice, forcing the austenite to transform into martensite.
Martensite is a very hard, brittle, and strong crystal structure. This martensitic layer is the "case" that gives the component its exceptional wear resistance.
Why Choose Induction Hardening? Key Advantages
Induction hardening is chosen over other methods for its unique combination of precision, speed, and the final properties it imparts to the component.
Precision and Control
Because heating is generated by a magnetic field, it can be precisely focused on only the areas that require hardening. This minimizes energy waste and reduces the risk of distortion in the rest of the part.
Speed and Repeatability
The heating cycle is extremely fast, often lasting just a few seconds. This makes induction hardening ideal for automated, high-volume production lines where process consistency is critical.
The Dual-Property Component
This is the central benefit. The process creates a hard case to resist wear, abrasion, and contact fatigue, while the unheated core remains softer and tougher, capable of withstanding impact loads without fracturing.
Improved Fatigue Life
The formation of the harder martensitic case creates beneficial compressive residual stresses on the surface. These stresses help counteract tensile stresses that lead to fatigue cracks, significantly extending the service life of parts like axles and crankshafts.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, induction hardening is not a universal solution. Its effectiveness is dependent on specific material and design factors.
Material Constraints
The process is most effective on ferrous metals with sufficient carbon content (typically medium to high-carbon steels, around 0.35% carbon or more). The carbon is the key element that enables the formation of hard martensite. Low-carbon steels require a secondary process like carburizing first.
Geometry Dependence
The shape of the induction coil must closely match the geometry of the part to ensure uniform heating. Complex or irregular shapes can be difficult to heat evenly, potentially leading to soft spots or overheating.
Risk of Quench Cracking
The extreme thermal shock from rapid heating and quenching can introduce high internal stresses. If the process is not carefully controlled, or if the material has pre-existing defects, this can lead to quench cracks.
Equipment and Tooling Costs
The initial capital investment for induction heating power supplies and the fabrication of custom coils for specific parts can be substantial compared to conventional furnace heating methods.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a heat treatment process requires matching the method's strengths to the component's engineering requirements.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of wear-resistant parts: Induction hardening's speed and repeatability make it the ideal choice for components like gears, shafts, bearings, and axles.
- If your goal is to improve fatigue strength in a specific, high-stress area: The localized heating and resulting compressive stresses from induction are uniquely suited for strengthening fillets, journals, and other stress concentration points.
- If you are working with low-carbon steel or need a chemically altered surface: You should explore case-hardening alternatives like carburizing or nitriding, which diffuse elements into the surface over a longer period.
- If the entire component needs uniform hardness and strength: A through-hardening process like quenching and tempering, which heats and cools the entire part, would be the more appropriate method.
Understanding induction hardening as a precise surface modification tool allows you to engineer components with an optimal balance of surface durability and core toughness.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Process Type | Surface hardening, a form of heat treatment |
| Mechanism | Electromagnetic induction heating followed by rapid quenching |
| Key Outcome | Hard, wear-resistant martensitic case with a soft, ductile core |
| Ideal For | High-volume production of gears, shafts, bearings, and axles |
| Material Requirement | Medium to high-carbon steels (typically >0.35% carbon) |
Need to enhance the durability and fatigue life of your components? KINTEK specializes in advanced thermal processing solutions, including induction hardening systems. Our lab equipment and consumables are designed to meet the precise needs of laboratories and manufacturers. Let us help you engineer components with the perfect balance of surface hardness and core toughness. Contact our experts today to discuss your project requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Non Consumable Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- CVD Diamond for Thermal Management Applications
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
People Also Ask
- What are the strengths of brazing? Achieve Strong, Clean, and Precise Metal Joining
- What is AC frame? Decoding the Two Meanings in Wi-Fi and Video
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of brazing? A Guide to Strong, Clean Metal Joining
- What are the different types of melting process? From Smelting to Suspension for Ultimate Purity
- What is the difference between VAR and VIM? Legacy Vimscript Variables vs. Modern Neovim API



















