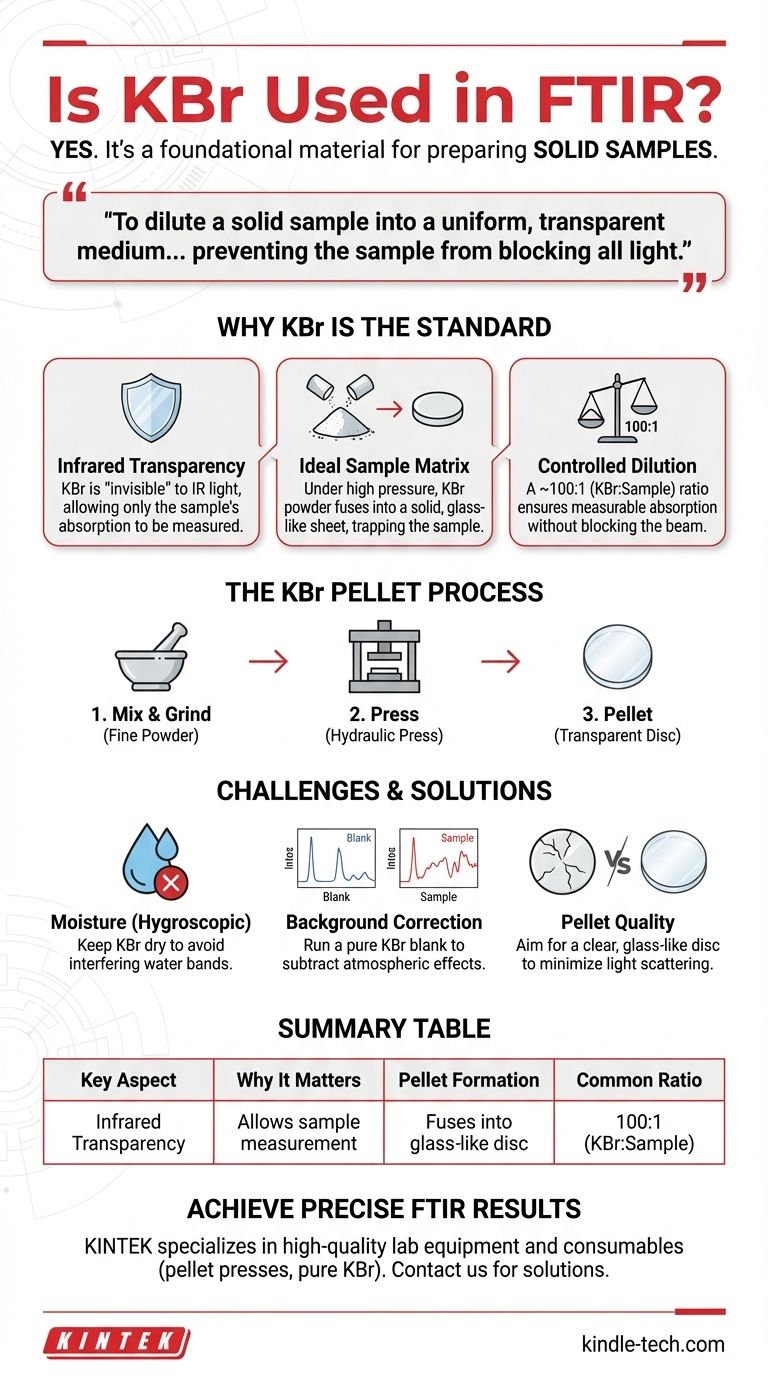
Yes, potassium bromide (KBr) is a foundational material used in FTIR spectroscopy, specifically for preparing solid samples. It acts as an inert matrix that holds the sample in the path of the infrared beam. Because KBr is transparent to infrared light, it allows the spectrometer to measure the absorption of the sample itself without interference.
The core reason for using KBr in FTIR is to dilute a solid sample into a uniform, transparent medium. This prevents the sample from being too concentrated—which would block all light—and creates an ideal state for accurate spectral analysis.

Why KBr is the Standard for Solid Sample FTIR
Infrared spectroscopy works by passing an IR beam through a substance to see which frequencies of light are absorbed. For solid samples, this presents a challenge: a chunk of opaque material will simply block the beam entirely. The KBr pellet method is the classic solution to this problem.
The Principle of Infrared Transparency
The most critical property of KBr is its transparency across the mid-infrared region. This means KBr itself does not absorb a significant amount of IR light in the range where most organic and inorganic molecules show their characteristic vibrations.
It effectively acts as a solid, invisible "window," ensuring that any absorption peaks recorded in the final spectrum belong to your sample, not the matrix holding it.
Creating the Ideal Sample Matrix
Alkali halides like KBr possess a unique physical property: when subjected to high pressure, the crystalline powder becomes plastic and fuses into a solid, glass-like sheet.
This allows you to take a tiny amount of your solid sample, mix it with KBr powder, and press it into a mechanically stable, transparent disc. The sample becomes trapped and uniformly dispersed within this disc, which is perfect for analysis.
The Importance of Controlled Dilution
A pure sample is often too concentrated for transmission FTIR. It would absorb so strongly that no light would reach the detector, resulting in a useless "flat-lined" spectrum.
The standard practice is to use a ratio of approximately 100:1 KBr to sample by weight. This extreme dilution ensures that only a small, representative amount of the sample interacts with the beam, allowing for measurable absorption without completely blocking the light.
The KBr Pellet Preparation Process
Creating a high-quality pellet is a prerequisite for a clean, reliable spectrum. The process requires careful attention to detail.
Grinding and Mixing
First, the sample and KBr powder are combined. This mixture is then finely pulverized using a pestle and mortar, preferably made of agate to reduce contamination and create a smooth, homogenous powder.
Proper grinding is essential to reduce light scattering from large particles, which can distort the spectral baseline.
Pressing the Pellet
The fine powder is loaded into a pellet press die set. For a standard 12.7 mm (½ inch) die, about 200-250 mg of the KBr mixture is used.
This die is placed in a hydraulic press and subjected to tons of pressure. During this process, a vacuum is often applied to remove trapped air and moisture, which helps create a perfectly transparent pellet.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Potential Pitfalls
While the KBr method is powerful, it is not without its challenges. Awareness of these issues is key to avoiding poor results.
The Critical Challenge of Moisture
KBr is hygroscopic, meaning it readily absorbs water from the atmosphere. If the KBr or the sample is not perfectly dry, this moisture will be incorporated into the pellet.
Water has very strong and broad absorption bands in the infrared spectrum, which can easily obscure important peaks from your sample. In humid environments, preparation inside a glovebox is often necessary.
The Need for Background Correction
No pellet is perfect. Minor imperfections or atmospheric conditions (like CO2 and water vapor) can affect the spectrum.
To correct for this, a background spectrum is always run first. This can be done with an empty pellet holder or, ideally, a "blank" pellet made of pure KBr. The instrument's software then subtracts this background from the sample spectrum, isolating the signal of your material.
Poor Pellet Quality
A pellet that is cracked, cloudy, or opaque will cause significant light scattering, leading to a noisy and steeply sloped baseline. This makes it difficult to identify small peaks and perform accurate quantitative analysis. The goal is always a disc that looks like clear glass.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Proper KBr technique is a skill that directly impacts the quality of your spectroscopic data.
- If your primary focus is spectral accuracy: Prioritize keeping your KBr powder meticulously dry, and always run a background spectrum with a pure KBr blank pellet.
- If your primary focus is sample purity: Use a high-quality agate mortar and pestle to minimize contamination during the grinding phase.
- If your primary focus is repeatability: Strictly control your sample-to-KBr ratio (typically 1%) and the pressure used to form the pellet to ensure consistent results across different samples.
Mastering the KBr pellet technique is a fundamental skill for anyone seeking to characterize solid materials using FTIR.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Why It Matters for FTIR |
|---|---|
| Infrared Transparency | KBr is transparent to IR light, allowing the sample's absorption to be measured without interference. |
| Sample Dilution | Prevents the sample from being too concentrated, which would block the IR beam entirely. |
| Pellet Formation | High pressure fuses KBr powder into a stable, glass-like disc that holds the sample uniformly. |
| Common Ratio | A typical 100:1 (KBr to sample) dilution ensures measurable absorption for accurate analysis. |
Achieve precise and reliable FTIR results with expert support from KINTEK.
Mastering the KBr pellet technique is crucial for accurate solid sample analysis. Whether your priority is spectral accuracy, sample purity, or repeatability, the right equipment and consumables make all the difference.
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for spectroscopy, including reliable pellet presses and pure KBr powder. We serve laboratories focused on material characterization, ensuring your FTIR analyses are consistent and trustworthy.
Let us help you enhance your lab's capabilities. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific FTIR needs and discover the right solutions for your research.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- kbr pellet press 2t
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Press for XRF & KBR Pellet Press
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Pellet Press Machine for Lab Use
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What is KBr disc method in IR spectroscopy? A Guide to Solid Sample Analysis
- How much sample is needed for IR? Optimize Your Analysis with Minimal Material
- Why only KBr is used in IR spectroscopy? The Truth About the Best Material for Your Sample
- What is a KBr pellet? A Guide to Preparing Solid Samples for IR Spectroscopy
- How do you prepare samples for infrared spectroscopy? Master Solid, Liquid & Gas Techniques



















