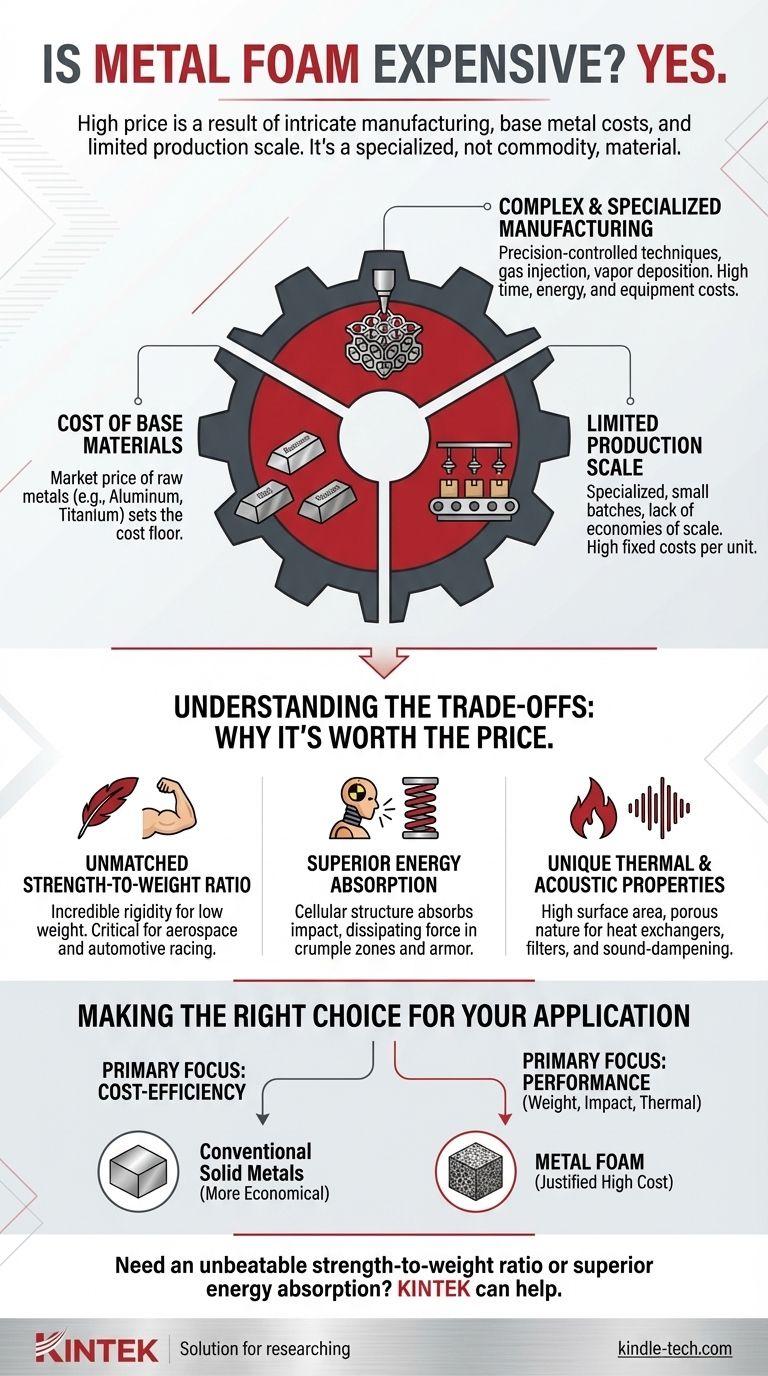
Yes, metal foam is considered an expensive material. Its high price is a direct result of intricate manufacturing techniques, the cost of the base metals used, and a relatively limited scale of production. These factors combine to make it a specialized material rather than a common commodity.
The high cost of metal foam is the most significant barrier to its widespread adoption. This cost is not arbitrary but is fundamentally linked to the complexity of its creation and the inherent value of its raw materials.

The Core Factors Driving the Cost of Metal Foam
To understand why metal foam carries a premium price, we need to look at the three primary drivers behind its cost: the manufacturing process, the raw materials, and the scale of production.
Complex and Specialized Manufacturing
The process of creating metal foam is far more involved than casting a solid piece of metal. It requires precision-controlled techniques to create the porous, cellular structure.
Common methods involve injecting gas into molten metal or using advanced processes like vapor deposition onto a polymer scaffold, which is later burned away. Each step adds significant time, energy, and equipment costs.
The Cost of Base Materials
The final foam is made from metals like aluminum, steel, or even titanium. The market price of these raw materials directly contributes to the final cost.
A foam made from an already expensive material like titanium will naturally be much more costly than one made from aluminum. The price of the base metal sets the floor for the cost of the foam.
Limited Production Scale
Metal foam is not mass-produced like steel beams or aluminum sheets. It is often created for specialized, high-performance applications in smaller batches.
This lack of economies of scale means the high fixed costs of research, development, and specialized equipment are distributed over a smaller number of units, keeping the per-unit price high.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Why Is It Ever Worth the Price?
If metal foam is so expensive, its use must be justified by properties that conventional materials cannot offer. Its value is not in being cheap, but in its exceptional performance in specific scenarios.
Unmatched Strength-to-Weight Ratio
Metal foams offer incredible rigidity and strength for their extremely low weight. This is invaluable in aerospace, automotive racing, and other fields where minimizing weight is critical to performance and efficiency.
Superior Energy Absorption
The cellular structure is exceptionally effective at absorbing impact energy. During a collision, the cells collapse at a controlled rate, dissipating force and protecting what's behind it. This makes it ideal for vehicle crumple zones or military armor.
Unique Thermal and Acoustic Properties
The high surface area and porous nature of metal foam make it effective for applications like heat exchangers, filters, and sound-dampening panels. Its unique structure allows it to perform functions that solid metals cannot.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing metal foam requires a clear understanding of your project's non-negotiable requirements versus its budget constraints.
- If your primary focus is cost-efficiency for a standard application: Metal foam is almost certainly not the right choice; conventional solid metals will be far more economical.
- If your primary focus is achieving the lowest possible weight without sacrificing strength: The high cost of metal foam may be justified, particularly in aerospace or high-performance automotive projects.
- If your primary focus is maximizing impact absorption or thermal management: The unique structural properties of metal foam provide a clear performance advantage that can warrant the investment.
Ultimately, the decision to use metal foam is a strategic trade-off between its high cost and its unparalleled performance characteristics.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Cost |
|---|---|
| Complex Manufacturing | High (Precision processes like gas injection or vapor deposition) |
| Raw Material Cost | High (Base metals like aluminum, steel, or titanium) |
| Limited Production Scale | High (Lack of economies of scale) |
| Key Justifying Properties | Strength-to-weight ratio, Energy absorption, Thermal/acoustic management |
Need a material that offers an unbeatable strength-to-weight ratio or superior energy absorption for your project? The high-performance characteristics of metal foam might be the perfect solution. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced laboratory equipment and materials to help you innovate. Our experts can help you determine if metal foam is the right choice for your specific application. Contact us today to discuss your project requirements and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory's advanced material needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Copper Foam
- High Purity Gold Platinum Copper Iron Metal Sheets
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- High Purity Zinc Foil for Battery Lab Applications
- Thermally Evaporated Tungsten Wire for High Temperature Applications
People Also Ask
- How can different materials have different heat capacity? Unlocking the Microscopic Secrets of Energy Storage
- Is copper foam safe? Discover the facts about its antimicrobial and cooling benefits
- What are the characteristics of copper foam? Unlock High-Performance Thermal and Electrical Solutions
- What are the proper storage conditions for nickel and copper foam? A Guide to Preserving Performance
- What electrostatic protection measures should be taken when using nickel and copper foam? Essential ESD Safety Protocols



















