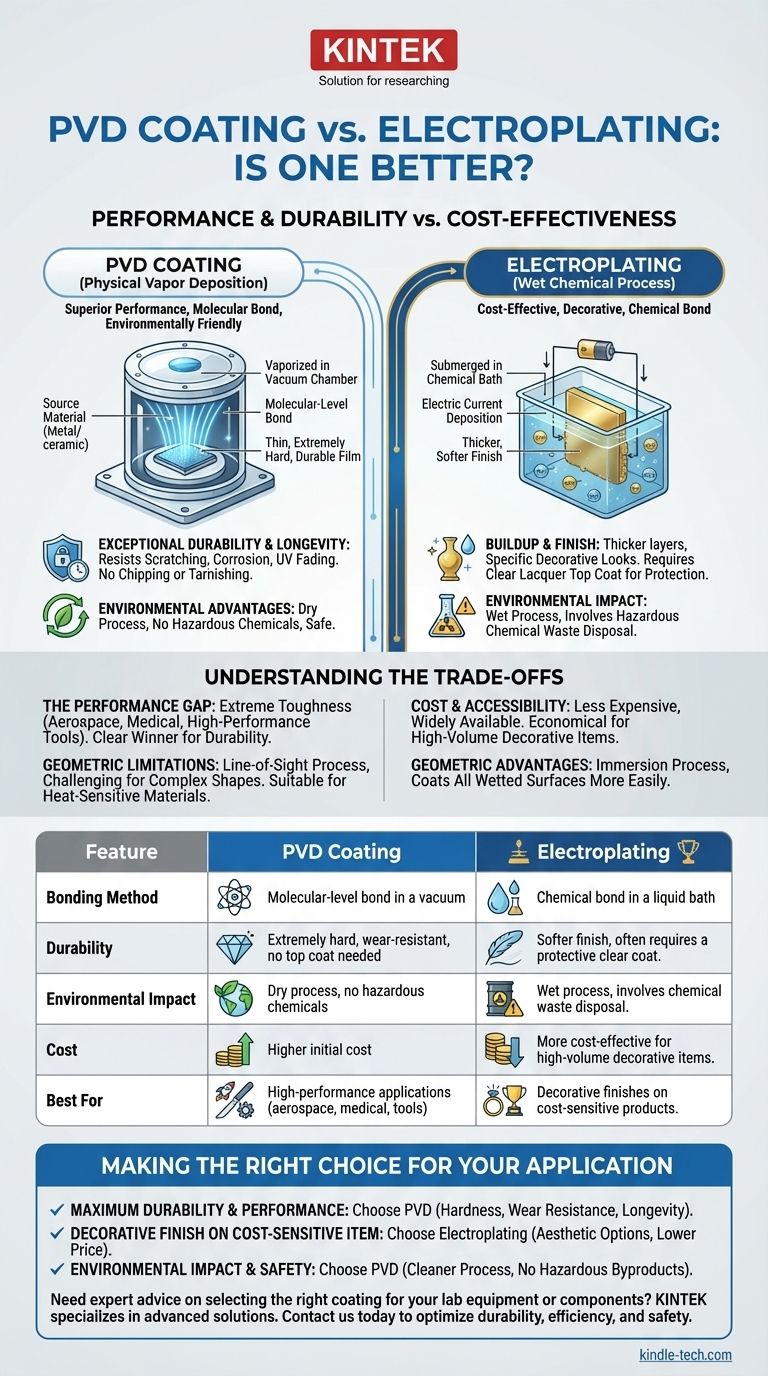
In terms of pure performance and durability, Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is almost always superior to traditional electroplating. PVD creates a harder, more corrosion-resistant, and longer-lasting surface by bonding a thin film coating to the substrate at a molecular level. While electroplating remains a common method, it relies on a weaker chemical bond and often requires a protective clear coat that can degrade over time.
The question isn't simply which process is "better," but which is appropriate for your specific application. PVD offers superior physical properties and environmental safety, while electroplating provides a cost-effective solution for a wide range of decorative and functional uses.

What is PVD? The Molecular Bonding Process
Physical Vapor Deposition is not a simple coating; it's a high-tech process that fundamentally alters the surface of a material. It is performed in a high-vacuum environment.
The Deposition Process
Solid source material—often a high-purity metal or ceramic—is vaporized through methods like sputtering or thermal evaporation. This vapor then travels through the vacuum chamber and condenses onto the substrate, forming a very thin, dense, and highly-adhered film.
Key Characteristics: Hardness and Durability
The resulting PVD coating is exceptionally hard and wear-resistant. Because the bond is molecular, it does not chip, fade, or tarnish easily. This makes it ideal for products that face high wear, friction, or exposure to the elements.
Environmental Advantages
PVD is a dry, environmentally friendly process. Unlike electroplating, it does not use or produce hazardous chemicals, eliminating the need for complex waste disposal.
How Does Electroplating Compare? The Wet Chemical Process
Electroplating is a much older, well-established "wet" process that uses an electric current to deposit a layer of metal onto a conductive surface.
The Electrochemical Process
The part to be coated (the substrate) is submerged in a chemical bath containing dissolved metal ions. When a direct current is applied, these ions are attracted to the substrate, where they are "reduced" back into a solid metal and form a layer on the surface.
Key Characteristics: Buildup and Finish
Electroplated layers can be thicker than PVD coatings and are often chosen for their specific decorative appearance, such as chrome or polished brass. However, these finishes are softer and often require a clear lacquer top coat for protection, which itself can yellow, scratch, or fail over time.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between PVD and electroplating requires a clear understanding of their respective strengths and weaknesses. The "better" choice is entirely dependent on your project's goals.
The Performance and Durability Gap
For applications demanding extreme toughness, PVD is the clear winner. Its resistance to scratching, corrosion, and UV fading is far superior to electroplating. It is the standard in demanding industries like aerospace, medical implants, and high-performance cutting tools.
The Cost and Accessibility Factor
Electroplating is generally a less expensive and more widely available process. For high-volume, cost-sensitive decorative items where extreme durability is not the primary concern, it remains an economically viable and effective solution.
Geometric and Substrate Limitations
PVD is a "line-of-sight" process, meaning it can be challenging to uniformly coat highly complex shapes with deep recesses. Electroplating, being an immersion process, can coat all wetted surfaces more easily. However, PVD can be applied at lower temperatures, making it suitable for some heat-sensitive materials that might be damaged by other processes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your decision should be guided by the primary requirements of your product or component.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability and performance: PVD is the superior choice for its hardness, wear resistance, and longevity.
- If your primary focus is a decorative finish on a cost-sensitive item: Electroplating offers a wide range of aesthetic options at a lower price point.
- If your primary focus is environmental impact and workplace safety: PVD provides a significantly cleaner and safer process with no hazardous byproducts.
Ultimately, aligning the technology with your specific performance and budget requirements will ensure you make the most effective choice.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PVD Coating | Electroplating |
|---|---|---|
| Bonding Method | Molecular-level bond in a vacuum | Chemical bond in a liquid bath |
| Durability | Extremely hard, wear-resistant, no top coat needed | Softer finish, often requires a protective clear coat |
| Environmental Impact | Dry process, no hazardous chemicals | Wet process, involves chemical waste disposal |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | More cost-effective for high-volume decorative items |
| Best For | High-performance applications (aerospace, medical, tools) | Decorative finishes on cost-sensitive products |
Need expert advice on selecting the right coating for your lab equipment or components? At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables, including solutions for surface treatment applications. Whether you're developing high-performance tools or decorative items, our team can help you choose the optimal coating technology to enhance durability, efficiency, and safety. Contact us today to discuss your specific needs and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory's success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells
- How are PECVD and CVD different? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thin-Film Deposition Process



















