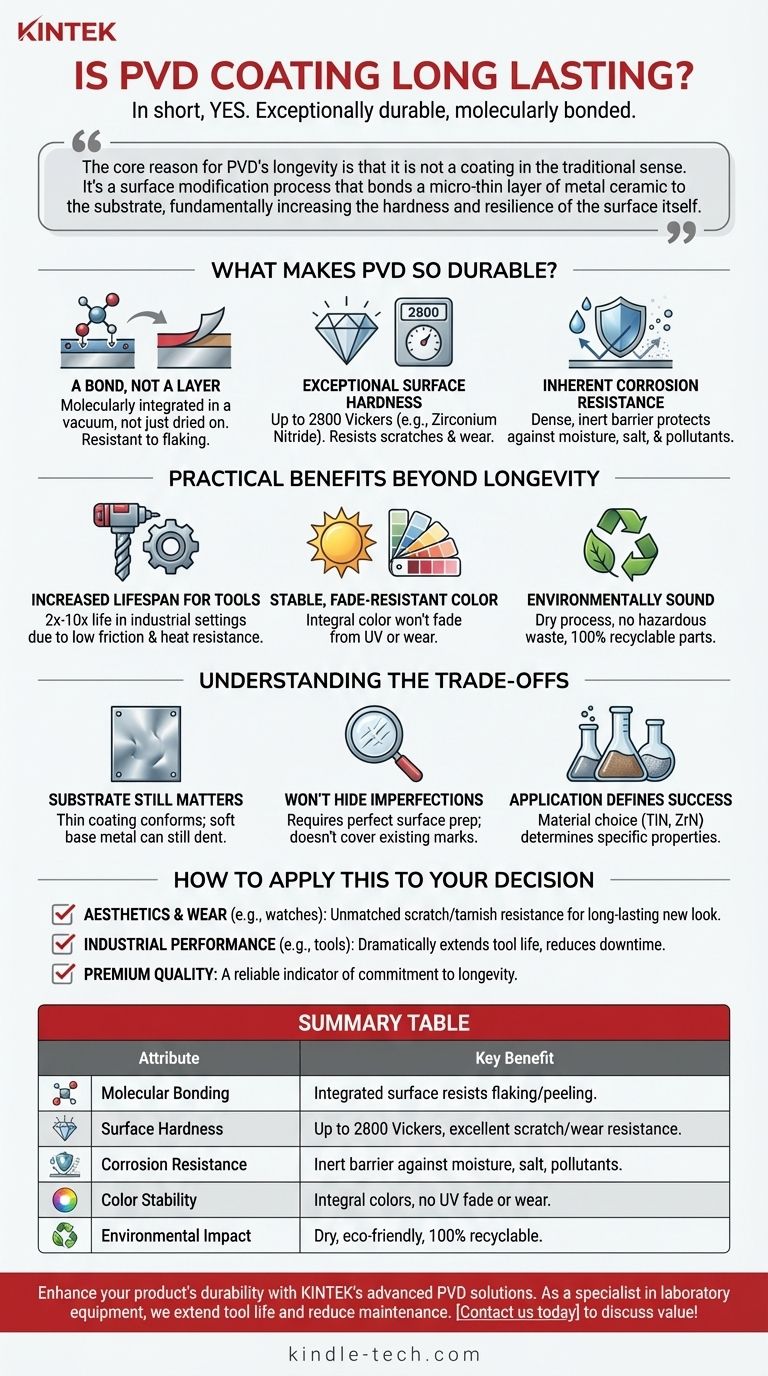
In short, yes. Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) coating is exceptionally long-lasting and is considered one of the most durable surface finishes available. Its remarkable durability comes from its unique application process, which creates a finish that is molecularly bonded to the base metal rather than being a simple layer on top. This results in superior hardness and resistance to wear.
The core reason for PVD's longevity is that it is not a coating in the traditional sense. It's a surface modification process that bonds a micro-thin layer of metal ceramic to the substrate, fundamentally increasing the hardness and resilience of the surface itself.
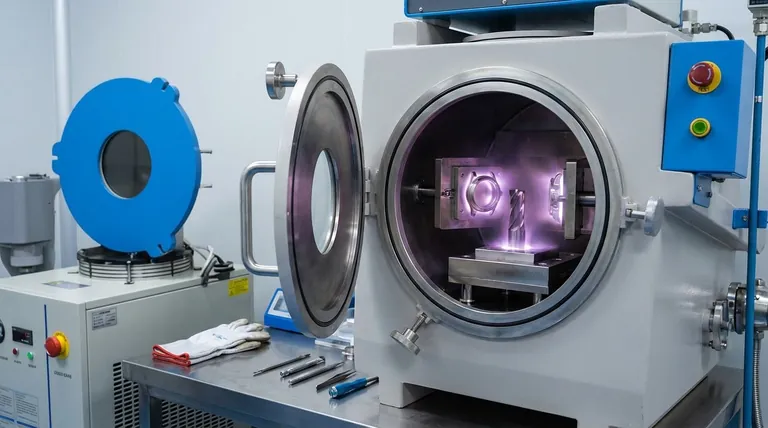

What Makes PVD So Durable?
The durability of a PVD finish isn't magic; it's a direct result of the physics behind the process. Understanding these principles shows why it outperforms traditional methods like painting or electroplating.
It's a Bond, Not a Layer
Unlike paint, which simply dries on a surface, PVD involves bonding material at a molecular level. The process takes place in a vacuum, where a solid material (like Titanium or Zirconium) is vaporized into a plasma and then deposited onto the target object.
This creates a new, integrated surface condition rather than a distinct, separate layer. Because it is bonded so tightly, it is highly resistant to flaking, peeling, or chipping.
Exceptional Surface Hardness
PVD finishes are extremely hard. For example, a PVD finish using Zirconium Nitride (often used for "Lifetime Brass" finishes) can achieve a hardness of 2800 Vickers.
This level of hardness makes the surface incredibly resistant to scratches and daily wear and tear, which is why it is favored for high-contact items like faucets, door hardware, and watch cases.
Inherent Corrosion Resistance
The dense, bonded nature of the PVD finish creates an inert barrier that protects the base metal from the effects of moisture, salt, and atmospheric pollutants.
This provides excellent resistance to corrosion and tarnishing, ensuring the color and integrity of the finish remain stable for a very long time, even in harsh environments.
Practical Benefits Beyond Longevity
The physical properties of PVD lead to tangible advantages across various applications, from consumer goods to demanding industrial environments.
Increased Lifespan for Tools
In industrial settings, applying PVD coatings to cutting tools, drills, and molds can increase their functional life by two to three times, with some applications seeing a tenfold improvement.
This is because the hard, low-friction surface reduces wear and heat buildup during operation, allowing the tool to perform better for longer.
Stable, Fade-Resistant Color
PVD can be used to deposit a wide range of colors with exceptional stability. Because the color is an integral part of the bonded finish, it will not fade from UV exposure or wear away over time like an anodized or painted finish would.
An Environmentally Sound Process
Compared to traditional electroplating methods that often use hazardous chemicals like hexavalent chromium, PVD is a dry and environmentally friendly process.
It does not produce hazardous waste, and PVD-coated components remain 100% recyclable at the end of their life.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly durable, PVD is not indestructible. Its performance is tied directly to the quality of the object it is applied to.
The Substrate Still Matters
PVD coating is extremely hard but also extremely thin (measured in microns). If the underlying metal is soft, a significant impact can still cause a dent.
The PVD finish itself will likely not chip or peel from the dented area, but the object's shape will be compromised. The coating's strength cannot compensate for a weak base material.
It Will Not Hide Imperfections
Because the PVD finish is so thin and conforms perfectly to the surface, it will not hide any underlying scratches, dings, or polishing marks. The final appearance is entirely dependent on the quality of the surface preparation before coating.
Application Defines Success
The term "PVD" describes a process, but the material used for the coating (e.g., Titanium Nitride, Zirconium Nitride) determines its specific properties. The performance depends entirely on matching the right coating material to the intended use.
How to Apply This to Your Decision
Your choice depends on what you value most in a finish. PVD excels where durability is a primary concern.
- If your primary focus is aesthetics and everyday wear (e.g., watches, faucets, jewelry): PVD offers unmatched scratch and tarnish resistance, ensuring the product looks new for years longer than traditional finishes.
- If your primary focus is industrial performance (e.g., cutting tools, mechanical components): PVD dramatically extends the operational life of the part, reducing downtime and long-term costs.
- If your primary focus is a premium, long-lasting product: Choosing a product with a PVD finish is a reliable indicator of quality and a commitment to longevity from the manufacturer.
By viewing PVD as a permanent enhancement to the metal's surface, you can confidently select it for applications that demand maximum durability and resilience.
Summary Table:
| PVD Coating Attribute | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Molecular Bonding | Creates a micro-thin, integrated surface that resists flaking and peeling. |
| Surface Hardness | Achieves up to 2800 Vickers, providing excellent scratch and wear resistance. |
| Corrosion Resistance | Forms an inert barrier against moisture, salt, and pollutants for long-term stability. |
| Color Stability | Colors are integral to the finish, preventing UV fade and wear over time. |
| Environmental Impact | A dry, eco-friendly process with no hazardous waste; coated parts are 100% recyclable. |
Enhance your product's durability and performance with KINTEK's advanced PVD coating solutions. As a specialist in laboratory equipment and consumables, we provide PVD coatings that significantly extend the lifespan of tools and components, reduce maintenance costs, and ensure superior resistance to wear and corrosion. Whether you're in manufacturing, research, or developing premium consumer goods, our expertise can help you achieve lasting quality. Contact us today to discuss how our PVD coatings can add value to your products!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- How does hot pressing work? Achieve Maximum Density for Advanced Materials
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of hot stamping? Unlock Ultra-High Strength for Automotive Parts
- What is the main function of hot press forming? Achieve Superior Strength & Precision in Manufacturing
- What is the advantage by using hot press forming? Achieve Stronger, More Complex Parts
- What is the purpose of laminating? Protect and Enhance Your Documents for Long-Term Use



















