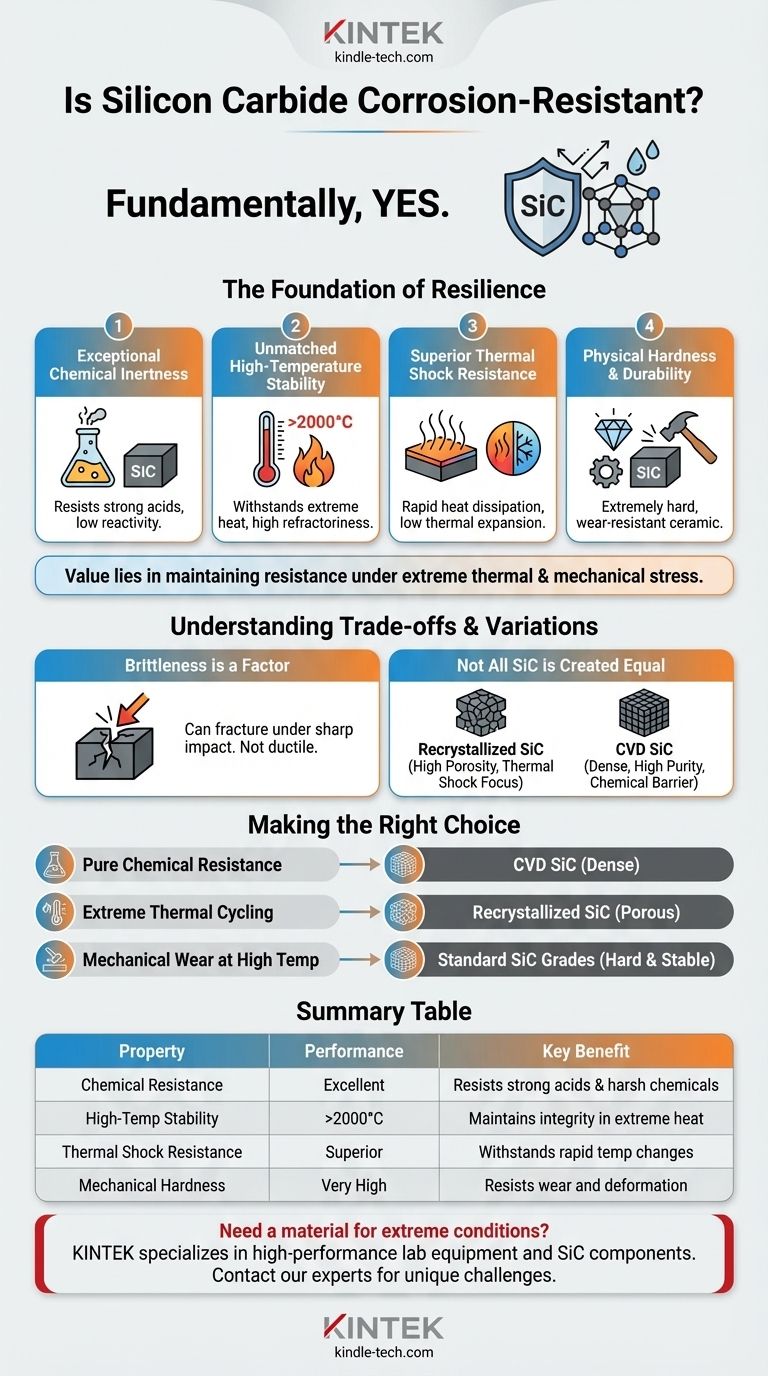
Fundamentally, yes. Silicon carbide (SiC) is renowned for its exceptional chemical stability and is considered highly corrosion-resistant. It is particularly effective against strong acids and maintains its integrity in many severe chemical environments where other materials would quickly degrade.
While silicon carbide's chemical resistance is a core feature, its true value lies in its ability to maintain this resistance under extreme thermal and mechanical stress. Understanding this combination of properties—not just chemical inertness alone—is the key to leveraging it effectively for demanding applications.

The Foundation of SiC's Resilience
Silicon carbide is not just a single-purpose material. Its usefulness comes from a powerful combination of properties that work together, making it a default choice for components in furnaces, pumps, rocket engines, and semiconductor manufacturing.
Exceptional Chemical Inertness
Silicon carbide exhibits very low reactivity with most chemicals. The references highlight that it is extremely acid-resistant, meaning it does not react with or degrade in the presence of strong acids that would dissolve most metals.
This chemical stability is fundamental to its role in processing equipment and industrial furnace linings where corrosive substances may be present.
Unmatched High-Temperature Stability
A material's corrosion resistance is only useful if it can survive the operating temperature. SiC has a very high refractoriness, capable of withstanding temperatures above 2000°C.
This allows it to function as heating elements, furnace floors, and guide rails in environments that are both thermally extreme and chemically aggressive.
Superior Thermal Shock Resistance
Many materials crack when subjected to rapid temperature changes. SiC excels here due to a unique combination of high thermal conductivity and low thermal expansion.
It rapidly dissipates heat across its structure to prevent localized hot spots, and it expands and contracts very little with temperature changes. This prevents the buildup of internal stress, making it ideal for applications like combustion nozzles and heat exchangers.
Physical Hardness and Durability
Beyond its thermal and chemical properties, SiC is an extremely hard and durable ceramic. It is not easily deformed, which contributes to its long service life in abrasive or high-pressure environments, such as in pump components.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Variations
No material is perfect, and making an informed decision requires understanding SiC's limitations and the differences between its various forms.
Brittleness is a Factor
Like most hard ceramics, silicon carbide is brittle. While it resists deformation and wear, it can fracture or shatter under sudden, sharp impacts. This is a critical design consideration, as it is not a tough, ductile material like steel.
Not All SiC is Created Equal
The manufacturing process significantly impacts the final properties of a silicon carbide component. The references point to different grades with distinct characteristics.
For example, recrystallized SiC has high porosity. This can be advantageous for thermal shock resistance but may be less ideal for applications requiring a perfect hermetic seal against corrosive gases.
In contrast, CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) SiC is theoretically dense and intrinsically pure. This dense structure provides a superior barrier to chemical attack and is essential for high-purity applications like semiconductor processing.
Properties Can Change Over Time
Even a material as stable as SiC can experience changes during its operational life. The reference to SiC resistors notes that their electrical resistance gradually increases with use.
This illustrates an important principle: you must account for how the material's properties might evolve under the specific stresses of your application over its intended lifespan.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right material depends on prioritizing your specific engineering goal. The key is to match the grade of silicon carbide to the primary challenge it will face.
- If your primary focus is pure chemical resistance: A dense, low-porosity grade like CVD silicon carbide offers the most robust barrier against corrosive agents.
- If your primary focus is performance in extreme thermal cycling: A grade like recrystallized SiC is often engineered for superior thermal shock resistance, making it ideal for kiln furniture and nozzles.
- If your primary focus is mechanical wear at high temperatures: The inherent hardness and stability of most standard SiC grades make it a default choice for furnace components, bearings, and pump parts.
By understanding the interplay of its thermal, mechanical, and chemical properties, you can confidently deploy silicon carbide in some of the world's most demanding applications.
Summary Table:
| Property | Performance | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent | Resists strong acids and harsh chemicals |
| High-Temperature Stability | >2000°C | Maintains integrity in extreme heat |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Superior | Withstands rapid temperature changes |
| Mechanical Hardness | Very High | Resists wear and deformation |
Need a material that can withstand extreme conditions? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including components made from advanced materials like silicon carbide. Whether you're facing corrosive chemicals, extreme temperatures, or demanding mechanical wear, our expertise can help you select the right solution for your laboratory's unique challenges. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's capabilities and durability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer Corrosion Resistant Cleaning Rack Flower Basket
- Professional Cutting Tools for Carbon Paper Cloth Diaphragm Copper Aluminum Foil and More
- High Purity Zinc Foil for Battery Lab Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Measuring Cylinder 10/50/100ml
- Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the strength of sintered ceramics? Achieve Maximum Density and Durability
- Why is silicon carbide more efficient? Unlock Higher Power Density with SiC's Superior Material Properties
- What is the firing temperature of alumina? Mastering the 1300°C to 1700°C Range for Optimal Results
- What is the use of SiC semiconductor? Unlock Higher Efficiency for EVs and Power Systems
- Where are ceramics used in the body? Key Applications in Orthopedics, Dentistry & Bone Repair
- What are ceramic and its applications? From Pottery to Spacecraft, Unlocking Material Potential
- What is special about ceramic? Unmatched Durability Against Heat, Wear, and Chemicals
- Why is a hexagonal Boron Nitride (h-BN) layer required for LATP? Protect Your Samples from Carbon Contamination



















