To be clear, neither process is universally better. The superiority of vacuum casting over centrifugal casting, or vice versa, depends entirely on your specific project requirements, including the material you're using, the part's geometry, the level of detail needed, and your production volume. Vacuum casting excels at creating highly detailed prototypes from polyurethane resins, while centrifugal casting is ideal for producing dense, durable, and often cylindrical parts from metals or plastics.
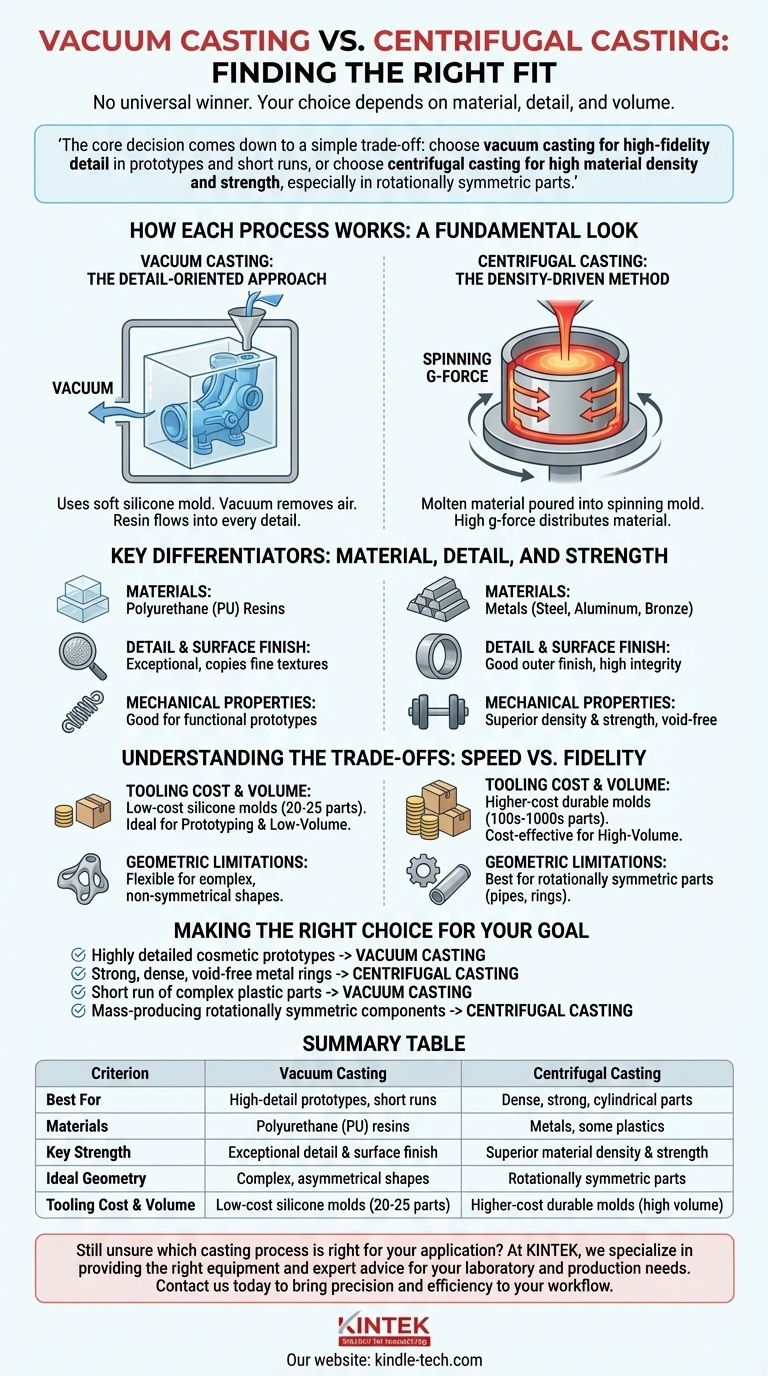
The core decision comes down to a simple trade-off: choose vacuum casting for high-fidelity detail in prototypes and short runs, or choose centrifugal casting for high material density and strength, especially in rotationally symmetric parts.

How Each Process Works: A Fundamental Look
To understand which method suits your needs, it's essential to grasp how each one operates. They use fundamentally different forces to achieve their results.
Vacuum Casting: The Detail-Oriented Approach
Vacuum casting uses a soft silicone mold, which is itself created from a high-quality master pattern (often 3D printed).
This silicone mold is placed in a chamber, and a vacuum is pulled. This removes all air from the mold.
Casting resin is then poured into the mold. The absence of air ensures the liquid material flows into every tiny crevice and feature without trapping air bubbles, resulting in a perfect replica of the master pattern.
Centrifugal Casting: The Density-Driven Method
Centrifugal casting involves pouring a molten material, typically metal or a robust plastic, into a rapidly spinning mold.
The intense rotational force (g-force) distributes the material to the outer walls of the mold cavity with immense pressure.
This pressure forces out lighter impurities and any trapped gases toward the center, resulting in a final part that is exceptionally dense, strong, and free of voids or porosity.
Key Differentiators: Material, Detail, and Strength
The right choice becomes clearer when you compare the processes across critical manufacturing criteria.
Material Compatibility: Resins vs. Metals
Vacuum casting is almost exclusively used with polyurethane (PU) resins. These resins can be formulated to mimic the properties of production plastics like ABS, nylon, or rubber.
Centrifugal casting is highly versatile, commonly used for metals (like steel, aluminum, and bronze) as well as some thermoset plastics and waxes, particularly in jewelry making.
Level of Detail and Surface Finish
Vacuum casting is the undisputed winner for detail. The combination of a high-resolution master pattern and the vacuum-assisted pour allows it to replicate extremely fine textures and complex geometries with pristine surface finishes.
Centrifugal casting produces a good surface finish on the outer diameter, but its primary strength is material integrity, not intricate surface replication.
Mechanical Properties and Part Density
Centrifugal casting produces parts with superior mechanical properties. The high pressure eliminates voids and creates a dense, uniform grain structure, significantly increasing the part's strength and durability.
Parts made via vacuum casting have properties defined by the chosen resin, which are excellent for functional prototypes but generally do not match the strength of the dense parts from centrifugal casting.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Speed vs. Fidelity
Every manufacturing process involves compromises. Understanding these will prevent costly mistakes.
Tooling Costs and Production Volume
Vacuum casting uses low-cost silicone molds. These molds are quick to make but have a short lifespan, typically lasting for only 20-25 parts. This makes the process ideal for prototyping and low-volume production.
Centrifugal casting requires a more robust, durable mold, which is more expensive and time-consuming to create. However, this mold can be used for hundreds or thousands of cycles, making it more cost-effective for higher production volumes.
Geometric Limitations
The primary limitation of centrifugal casting is geometry. It is best suited for parts that are rotationally symmetric, such as pipes, tubes, rings, and wheels.
Vacuum casting is far more flexible and can produce highly complex, non-symmetrical shapes with undercuts and intricate internal features, limited only by the ability to create a master pattern and a two-part silicone mold.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select your process based on a clear understanding of your project's primary objective.
- If your primary focus is creating highly detailed, cosmetic prototypes: Vacuum casting is the ideal choice for its superb surface replication and low initial tooling cost.
- If your primary focus is producing strong, dense, void-free metal rings or tubes: Centrifugal casting is the only viable option and will deliver superior material integrity.
- If your primary focus is a short run of complex plastic parts for fit and function testing: Vacuum casting provides a fast and cost-effective way to get high-quality parts in hand.
- If your primary focus is mass-producing durable, rotationally symmetric components: The higher upfront tooling cost of centrifugal casting is justified by its speed and lower per-unit cost at scale.
Ultimately, your choice is dictated not by which process is "better," but by which process is precisely aligned with your desired outcome.
Summary Table:
| Criterion | Vacuum Casting | Centrifugal Casting |
|---|---|---|
| Best For | High-detail prototypes, short runs | Dense, strong, cylindrical parts |
| Materials | Polyurethane (PU) resins | Metals (steel, aluminum), some plastics |
| Key Strength | Exceptional detail & surface finish | Superior material density & strength |
| Ideal Geometry | Complex, asymmetrical shapes | Rotationally symmetric parts (tubes, rings) |
| Tooling Cost & Volume | Low-cost silicone molds (20-25 parts) | Higher-cost durable molds (high volume) |
Still unsure which casting process is right for your application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the right equipment and expert advice for your laboratory and production needs. Whether you're creating detailed prototypes or manufacturing high-strength components, our team can help you select the perfect solution.
Contact us today via our Contact Form to discuss your project requirements and discover how KINTEK's expertise in lab equipment and consumables can bring precision and efficiency to your workflow.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Custom-Made Alumina Zirconia Special-Shaped Ceramic Plates for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Processing
People Also Ask
- What is the advantage by using hot press forming? Achieve Stronger, More Complex Parts
- Why is a vacuum hot-pressing furnace preferred for C_fiber/Si3N4 composites? Achieve High Density & Fiber Protection
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of hot stamping? Unlock Ultra-High Strength for Automotive Parts
- What is the purpose of laminating? Protect and Enhance Your Documents for Long-Term Use
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of hot pressing? Choose the Right Powder Metallurgy Process

















