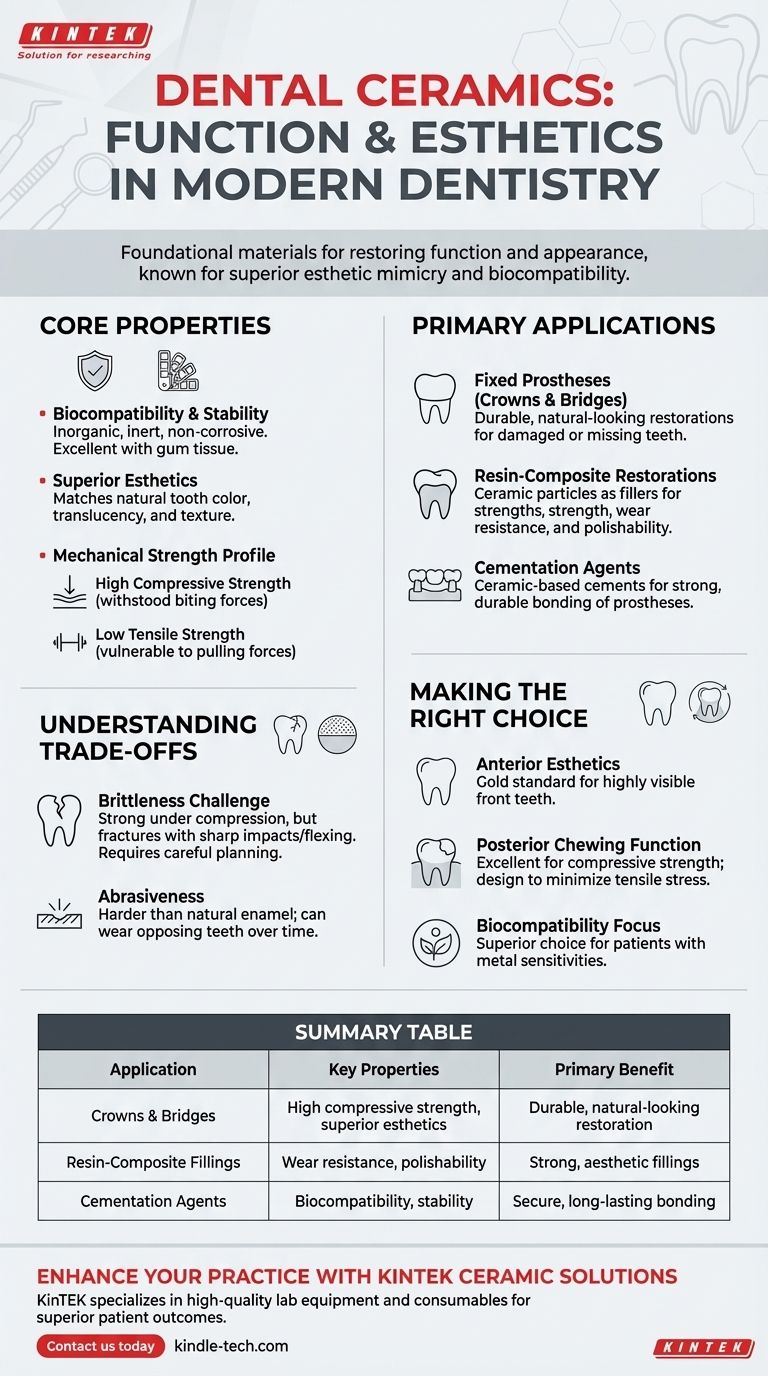
In modern dentistry, ceramics are foundational materials for restoring both the function and appearance of teeth. These inorganic, non-metallic materials are widely used for fixed prostheses like crowns and bridges, as key components in resin-composite fillings, and in specialized cementation agents.
Dental ceramics are chosen for their superior ability to mimic natural tooth enamel and their excellent biocompatibility. However, their clinical success hinges on understanding and managing their inherent brittleness.

The Core Properties of Dental Ceramics
The unique characteristics of ceramics make them highly suitable for the demanding environment of the human mouth.
Biocompatibility and Stability
As inorganic, non-metallic materials, dental ceramics are highly stable and inert. They do not corrode or react chemically within the oral cavity, making them extremely biocompatible with gum tissue.
Superior Esthetics
Perhaps the most significant advantage of ceramics is their appearance. They can be manufactured to precisely match the color, translucency, and texture of a patient's natural teeth, providing restorations that are virtually indistinguishable from real enamel.
Mechanical Strength Profile
Ceramics exhibit very high compressive strength, meaning they can withstand immense biting and chewing forces. This makes them ideal for the functional surfaces of teeth.
However, they have low tensile strength, which makes them vulnerable to forces that pull or flex the material.
Primary Applications in Clinical Practice
These properties translate into several key uses in day-to-day dentistry.
Fixed Prostheses: Crowns and Bridges
The most common application is in creating crowns (which cap a single damaged tooth) and bridges (which replace one or more missing teeth). The ceramic provides a durable and natural-looking restoration.
Resin-Composite Restorations
Ceramic particles are often used as a filler material within resin-composite fillings. These particles add strength, wear resistance, and polishability to the composite material.
Cementation Agents
Certain types of ceramic-based cements are used to permanently bond crowns, bridges, and other prostheses to the underlying tooth structure, ensuring a strong and durable connection.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, dental ceramics are not without their limitations. A successful outcome requires acknowledging these trade-offs.
The Challenge of Brittleness
The primary disadvantage of ceramics is their brittle nature. While strong under compression, they can fracture suddenly if subjected to sharp impacts or excessive flexing forces.
This means the preparation of the tooth and the design of the restoration must be meticulously planned to avoid thin areas or high-stress points.
Abrasiveness to Opposing Teeth
Because dental ceramics are extremely hard—often harder than natural tooth enamel—a ceramic crown can cause accelerated wear on the opposing natural teeth over time. This factor must be considered during treatment planning.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a ceramic material is based on balancing clinical needs with the material's inherent properties.
- If your primary focus is anterior esthetics: The unparalleled ability of ceramics to mimic natural enamel makes them the gold standard for restoring highly visible front teeth.
- If your primary focus is posterior chewing function: Ceramics are an excellent choice due to their high compressive strength, but the restoration must be designed to minimize tensile stress and prevent fracture.
- If your primary focus is biocompatibility: The inert nature of ceramics makes them a superior choice for patients with metal sensitivities or concerns about material reactivity.
Ultimately, leveraging dental ceramics effectively means balancing their unparalleled esthetic potential against their precise mechanical limitations.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Properties | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Crowns & Bridges | High compressive strength, superior esthetics | Durable, natural-looking restoration for damaged/missing teeth |
| Resin-Composite Fillings | Wear resistance, polishability | Strong, aesthetic fillings that blend with natural teeth |
| Cementation Agents | Biocompatibility, stability | Secure, long-lasting bonding for prostheses |
Enhance your dental practice with precision ceramic solutions from KINTEK.
Whether you're crafting crowns, bridges, or durable fillings, the right dental ceramics are crucial for achieving both aesthetic excellence and long-term functionality. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored to dental laboratories, ensuring you have the reliable materials needed for superior patient outcomes.
Contact us today to explore our range of dental ceramic products and discover how we can support your laboratory's success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Can you change the color of zirconia crowns? Understanding the Permanent Nature of Zirconia
- What is one of the newest applications for dental ceramics? Monolithic Zirconia for Full-Arch Bridges
- What are the white spots on zirconia after sintering? A Guide to Diagnosing and Preventing Defects
- What is the effect of zirconia sintering temperature? Master the Key to Strength and Stability
- What is the temperature of sintering zirconia? Mastering the Protocol for Perfect Dental Restorations



















