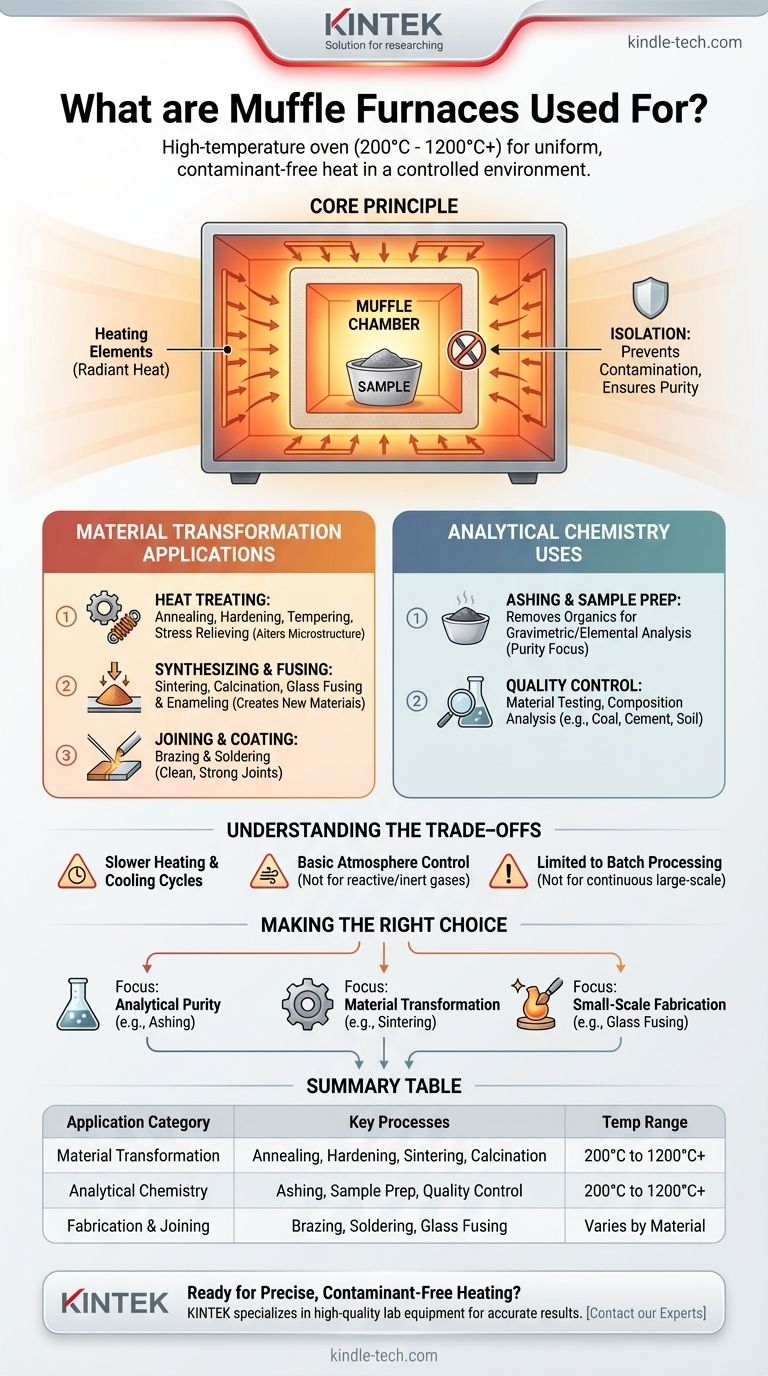
In essence, a muffle furnace is a high-temperature oven used for processes that require both extreme heat and a controlled, clean environment. It is widely used in laboratories and small-scale industrial settings to transform, analyze, or synthesize materials by heating them to temperatures typically ranging from 200°C to over 1200°C (392°F to 2192°F).
The critical function of a muffle furnace is not just to provide heat, but to provide uniform, contaminant-free heat. Its design isolates the material being heated from the actual heating elements, which is essential for applications where chemical purity and material integrity are paramount.

The Core Principle: How a Muffle Furnace Works
A standard oven heats materials directly, exposing them to the byproducts of combustion or the heating elements themselves. A muffle furnace is different.
The "Muffle" Chamber
The defining feature is the muffle—an inner chamber, typically made of high-temperature ceramic, that contains the sample. This chamber is heated from the outside by heating elements.
This design creates an "oven within an oven." The outer chamber gets hot, and that heat radiates inward to uniformly heat the sealed muffle chamber.
Why Isolation Matters
This isolation is the key. It prevents any gases, particles, or contaminants from the heating elements from interacting with the sample. This ensures that any change in the material is due solely to the application of heat, not to an unintended chemical reaction.
Primary Applications in Material Transformation
Many uses of a muffle furnace revolve around changing a material's physical or chemical properties through carefully controlled heating and cooling cycles.
Changing Material Properties (Heat Treating)
Heat treating alters the microstructure of a material, particularly metals, to make it harder, softer, or more durable.
- Annealing: Heating and slowly cooling a material to soften it, improve its ductility, and relieve internal stresses.
- Hardening & Tempering: Heating a metal to a critical temperature and then cooling it rapidly (quenching) to increase its hardness, followed by a lower-temperature heating (tempering) to reduce brittleness.
- Stress Relieving: Removing internal stresses caused by manufacturing processes like welding or machining.
Synthesizing and Fusing Materials
These processes use heat to create new materials or fuse particles together.
- Sintering: Heating a compressed powder (like ceramic or metal) to just below its melting point, causing the particles to bond together and form a solid, dense object.
- Calcination: Heating a solid material to a high temperature to drive off volatile substances, such as removing carbon dioxide from limestone to produce lime.
- Glass Fusing & Enameling: Melting glass pieces together or fusing a powdered glass coating (enamel) onto a metal or ceramic surface.
Joining and Coating
The clean, high-heat environment is also ideal for specialized joining processes.
- Brazing & Soldering: Joining metal pieces using a filler metal that has a lower melting point than the workpieces. The contaminant-free environment ensures a strong, clean joint.
Essential Uses in Analytical Chemistry
The second major category of use is preparing samples for chemical analysis, where purity is non-negotiable.
Sample Preparation via Ashing
Ashing is the primary application in analytical chemistry. It involves heating a sample to a high temperature to burn off all organic matter, leaving behind only the inorganic, non-combustible components (the "ash").
This is a critical step in gravimetric analysis or elemental analysis, where scientists need to determine the exact amount of inorganic material in a sample, such as a food product, soil, coal, or pharmaceutical.
Quality Control and Material Testing
Muffle furnaces are used to test the properties and composition of raw materials and finished goods. This includes applications like coal quality analysis, cement testing, and determining the composition of soils and aggregates for engineering purposes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly useful, a muffle furnace is not the right tool for every high-temperature task.
Slower Heating and Cooling Cycles
Because the heat must radiate through the insulated muffle chamber, these furnaces often have slower heat-up and cool-down times compared to direct-fire furnaces. This can reduce throughput in a high-volume production environment.
Basic Atmosphere Control
A standard muffle furnace creates a clean air environment, but it does not control the specific gases. If a process requires an inert atmosphere (like nitrogen or argon) or a reactive one (like hydrogen), a more specialized and expensive vacuum or atmosphere-controlled furnace is necessary.
Limited to Batch Processing
Muffle furnaces are designed for processing individual items or small batches of material. They are not suited for continuous, large-scale industrial processes, which are better served by conveyor-style tunnel kilns or rotary furnaces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if a muffle furnace is the correct tool, consider your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is analytical purity: A muffle furnace is the correct choice for ashing samples, as its isolating chamber prevents contamination and ensures accurate results.
- If your primary focus is material transformation: The furnace's ability to provide stable, uniform heat is ideal for heat treating, sintering, or calcination where precise temperature control is critical.
- If your primary focus is small-scale fabrication: The combination of high heat and a clean environment makes it perfect for creating high-quality brazed joints, enamel coatings, or fused glass art.
Ultimately, the muffle furnace is a precision instrument for tasks where controlled, uncontaminated heat is more important than raw speed or scale.
Summary Table:
| Application Category | Key Processes | Typical Temperature Range |
|---|---|---|
| Material Transformation | Annealing, Hardening, Sintering, Calcination | 200°C to 1200°C+ |
| Analytical Chemistry | Ashing, Sample Preparation, Quality Control | 200°C to 1200°C+ |
| Fabrication & Joining | Brazing, Soldering, Glass Fusing, Enameling | Varies by material |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with precise, contaminant-free heating?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including muffle furnaces designed for applications like ashing, heat treating, and sintering. Our solutions ensure the uniform, controlled heat your processes demand for accurate and reliable results.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect muffle furnace for your laboratory needs and achieve superior material transformation and analysis.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between a muffle furnace and a chamber furnace? Understand the Key Distinctions for Your Lab
- How to cool a muffle furnace? Ensure Safety and Maximize Equipment Lifespan
- What is the heating mechanism of a muffle furnace? Achieve Clean, Uniform High-Temperature Processing
- What is the difference between hot air oven and muffle furnace? Choose the Right Tool for Your Lab's Thermal Needs
- What is the mechanism of a muffle furnace? Master Precise, Contaminant-Free Heating



















