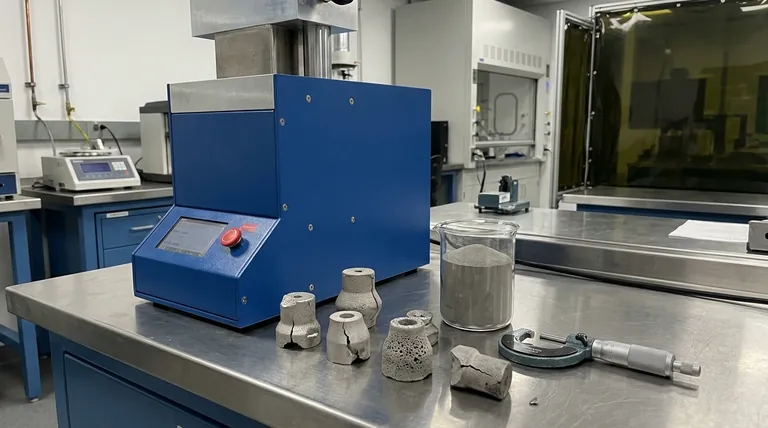
While highly efficient for specific applications, powder metallurgy (PM) is not a universal solution. Its primary disadvantages are significant limitations on part size, constraints on geometric complexity, and mechanical properties, such as strength and ductility, that are generally inferior to parts produced by forging or casting.
The core trade-off of powder metallurgy is accepting limitations in size and ultimate strength in exchange for exceptional precision, high production speeds, and minimal material waste on small, relatively simple components.

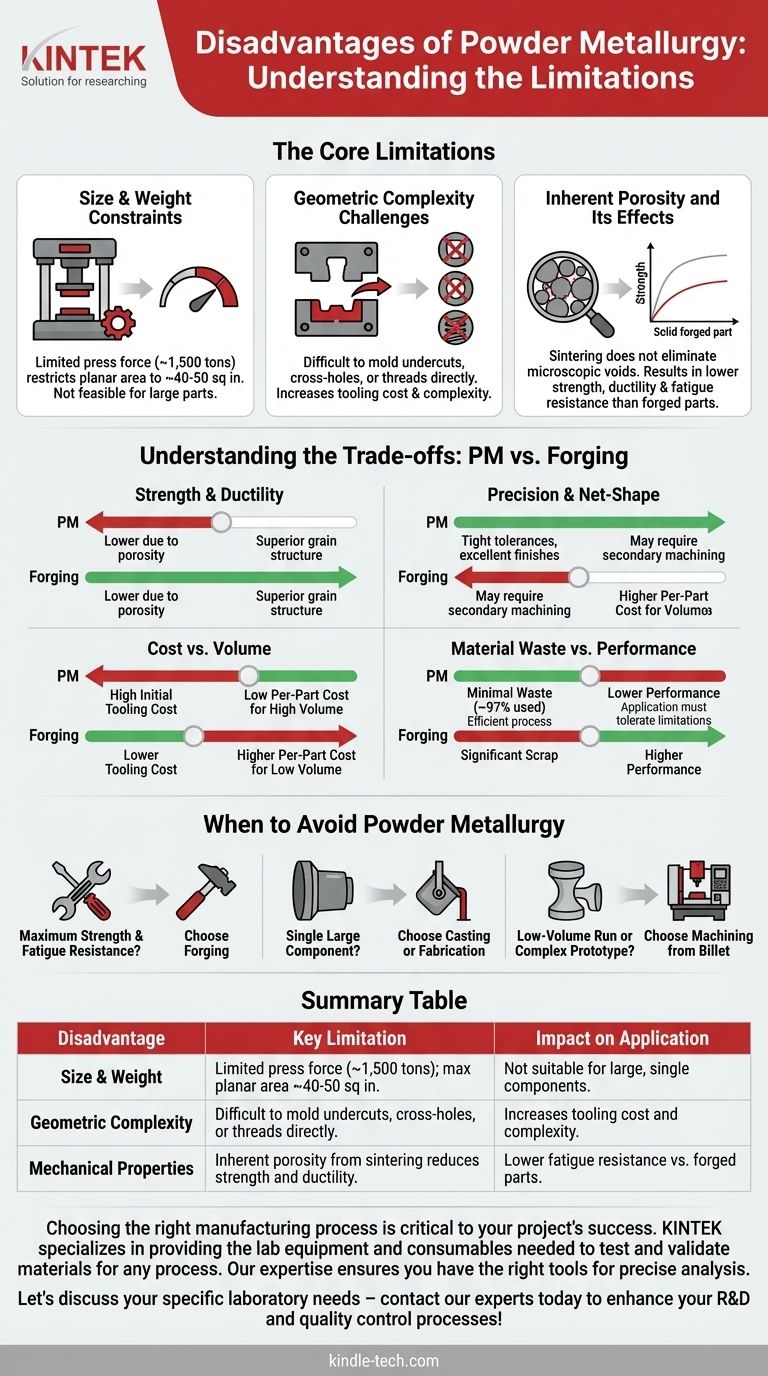
The Core Limitations of Powder Metallurgy
Understanding the disadvantages of PM requires looking at the fundamental steps of the process: compacting metal powder in a rigid die and then heating (sintering) it below its melting point. These steps are the source of both its strengths and its weaknesses.
Size and Weight Constraints
The PM process relies on massive presses to compact the metal powder into a "green" compact before sintering. The industry's largest presses are limited to around 1,500 tons of force.
This directly restricts the practical size of a component to a planar area of approximately 40-50 square inches. Attempting to produce larger parts would require forces that are not economically or technically feasible with current equipment.
Geometric Complexity Challenges
The need to fill a die cavity uniformly with powder and then eject the compacted part presents geometric hurdles.
Features like undercuts, cross-holes, or threads are difficult or impossible to mold directly. While skilled manufacturers can design complex, multi-part tooling to overcome some of these issues, it adds significant cost and complexity, undermining one of PM's key benefits.
Inherent Porosity and Its Effects
Sintering heats the part to fuse the powder particles together, but this occurs below the metal's full melting point. The process does not completely eliminate the microscopic voids between the original powder particles.
This residual porosity is the primary reason PM parts are typically not as strong or ductile as components made from solid metal. Forged parts, which benefit from heat and immense pressure that refines the metal's grain structure, will almost always have superior fatigue resistance and tensile strength.
Understanding the Trade-offs: PM vs. Forging
Choosing a manufacturing process involves weighing competing factors. The disadvantages of PM become clear when compared directly to a process like forging.
Strength vs. Precision
A forged part possesses superior strength and ductility due to its dense, non-porous, and aligned grain structure.
However, PM parts offer exceptional net-shape accuracy. They emerge from the die with tight tolerances and excellent surface finishes, often eliminating the need for costly secondary machining operations that are common with forged components.
Cost vs. Volume
The rigid steel dies required for PM are expensive to design and manufacture. This high initial tooling cost makes the process uneconomical for low-volume production or one-off prototypes.
Conversely, for high-volume production runs (tens of thousands to millions of parts), the cost of the die is amortized, making the per-part cost extremely low.
Material Waste vs. Performance
The PM process is remarkably efficient, using approximately 97% of the raw material in the final part. This contrasts sharply with subtractive manufacturing (machining), which can generate significant scrap.
This environmental and cost benefit, however, is balanced against the performance limitations caused by porosity. The application must be able to tolerate lower strength and ductility to gain the advantage of minimal waste.
When to Avoid Powder Metallurgy
Based on these trade-offs, you can make a clear decision about when another process is a better fit for your goals.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and fatigue resistance: Choose forging, as its process creates a superior grain structure free of the porosity inherent in PM.
- If your primary focus is producing a single large component: Choose casting or fabrication, as PM presses are physically incapable of producing parts beyond a certain size.
- If your primary focus is a low-volume run or a complex prototype: Choose machining from billet to avoid the high upfront tooling costs of powder metallurgy.
Ultimately, selecting the right manufacturing process requires a clear understanding of your component's non-negotiable performance requirements.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Key Limitation | Impact on Application |
|---|---|---|
| Size & Weight | Limited by press force (~1,500 tons); max planar area ~40-50 sq in. | Not suitable for large, single components. |
| Geometric Complexity | Difficult to mold undercuts, cross-holes, or threads directly. | Increases tooling cost and complexity. |
| Mechanical Properties | Inherent porosity from sintering reduces strength and ductility. | Lower fatigue resistance vs. forged parts. |
Choosing the right manufacturing process is critical to your project's success. While powder metallurgy has its limitations, KINTEK specializes in providing the lab equipment and consumables needed to test and validate materials for any process. Whether you're comparing PM to forging or casting, our expertise ensures you have the right tools for precise analysis. Let's discuss your specific laboratory needs – contact our experts today to enhance your R&D and quality control processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Automatic Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Electric Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine for Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Manual Cold Isostatic Pressing Machine CIP Pellet Press
People Also Ask
- What advantages does Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP) offer for nickel-alumina composites? Enhance Density & Strength
- What role does a Cold Isostatic Press (CIP) play in aluminum matrix composites? Achieve 90% Density for Better Hot Pressing
- What is cold isostatic pressing of metal powder? Achieve Uniform Density in Complex Metal Parts
- What are the advantages of using a Cold Isostatic Press for perovskite solar cells? Unlock High-Pressure Performance
- What is the process of cold isostatic pressing? Achieve Uniform Density in Complex Parts



















