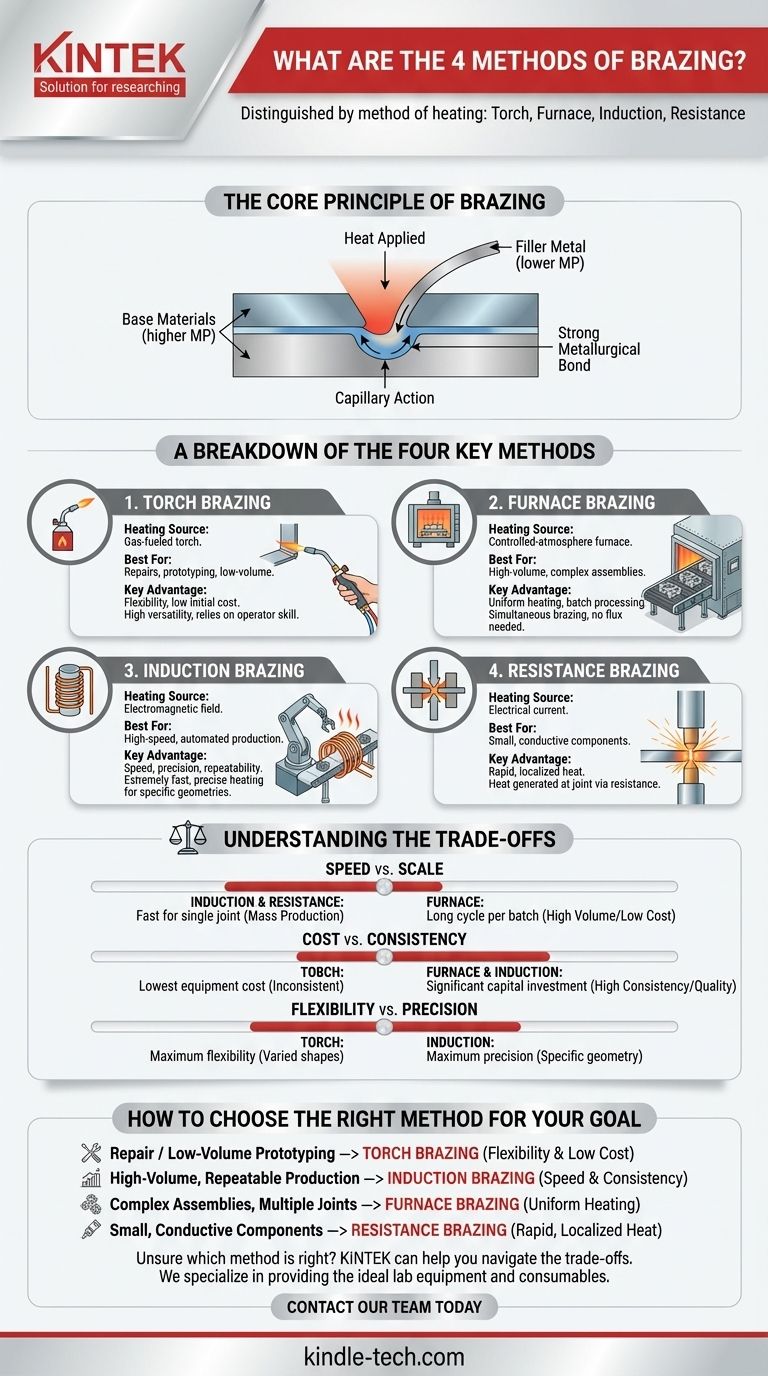
The four primary methods of brazing are distinguished by their method of heating: torch, furnace, induction, and resistance brazing. Each technique applies heat differently to melt a filler metal and join components without melting the base materials themselves. The choice of method depends entirely on the application's requirements for production volume, joint complexity, and precision.
While the user's question is about "what" the methods are, the more critical understanding is "why" you would choose one over another. The decision hinges on a single trade-off: localized, precise heating for individual parts versus uniform, mass heating for entire assemblies.
The Core Principle of Brazing
Brazing creates a strong, permanent bond between two or more metal parts by using a filler metal that has a lower melting point than the base materials. This process is distinct from welding, where the base metals are melted and fused together.
The Brazing Process
A filler metal is introduced to the joint between the parts. The entire assembly is then heated to a temperature above the filler metal's melting point but below the melting point of the base materials.
The Role of Capillary Action
Once molten, the filler metal is drawn into the tight-fitting space between the parts through capillary action. Upon cooling, it solidifies to form a strong metallurgical bond.
A Breakdown of the Four Key Methods
The fundamental difference between brazing methods is how heat is applied. This dictates the speed, scale, and suitability of the process for a given task.
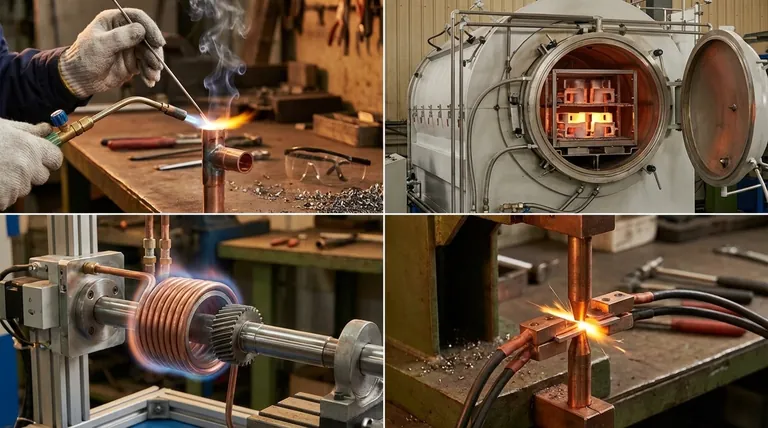
1. Torch Brazing
This is the most common manual method. Heat is applied using a gas-fueled torch directed at the joint area. It is highly versatile and requires relatively low initial investment.
Torch brazing is ideal for one-off repairs, prototyping, and low-volume production where automation is not practical. Operator skill is a critical factor in achieving a quality joint.
2. Furnace Brazing
In this method, the entire assembly (with filler metal pre-placed) is heated in a controlled-atmosphere or vacuum furnace. This allows for the simultaneous brazing of many assemblies or a single complex part with multiple joints.
Furnace brazing is suited for high-volume production and complex geometries. The controlled atmosphere prevents oxidation, often eliminating the need for flux and resulting in very clean joints.
3. Induction Brazing
Induction heating uses a high-frequency alternating current passed through a copper coil. This creates an electromagnetic field that heats the conductive metal parts placed within it, melting the filler metal.
This method is extremely fast, precise, and repeatable, making it perfect for high-speed, automated production lines where the same joint is made over and over.
4. Resistance Brazing
Heat is generated directly at the joint by passing a high electrical current through the parts. The resistance to the current flow at the interface of the components creates intense, localized heat.
Resistance brazing is typically used for joining small, electrically conductive components where heat must be applied very quickly and in a highly localized area.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right method requires balancing cost, speed, quality, and production volume. There is no single "best" method, only the most appropriate one for the job.
Speed vs. Scale
Induction and resistance brazing are extremely fast for a single joint but are best suited for mass production of identical parts.
Furnace brazing has a long cycle time per batch, but because it can process hundreds or thousands of parts at once, the cost per part can be very low in high-volume scenarios.
Cost vs. Consistency
Torch brazing has the lowest equipment cost but is highly dependent on operator skill, leading to potential inconsistencies between joints.
Furnace and induction systems require significant capital investment, but they deliver highly consistent and repeatable results, reducing human error and improving quality control in production environments.
Flexibility vs. Precision
The manual nature of torch brazing offers maximum flexibility for handling a wide variety of part shapes and sizes on the fly.
Induction brazing offers maximum precision, but the heating coil is often designed for a specific part geometry, making it less flexible for varied work without tooling changes.
How to Choose the Right Method for Your Goal
Your application's specific goals should guide your decision.
- If your primary focus is repair or low-volume prototyping: Torch brazing offers the best combination of flexibility and low initial cost.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, repeatable production of a single part: Induction brazing provides unmatched speed and consistency.
- If your primary focus is joining complex assemblies with multiple joints at once: Furnace brazing is the only method that provides the necessary uniform heating and atmospheric control.
- If your primary focus is joining small, conductive components with rapid, localized heat: Resistance brazing is the most effective and efficient choice.
Ultimately, understanding these core heating principles empowers you to select the most efficient and effective brazing method for any application.
Summary Table:
| Method | Heating Source | Best For | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Torch Brazing | Gas-fueled torch | Repairs, prototyping, low-volume | Flexibility, low initial cost |
| Furnace Brazing | Controlled-atmosphere furnace | High-volume, complex assemblies | Uniform heating, batch processing |
| Induction Brazing | Electromagnetic field | High-speed, automated production | Speed, precision, repeatability |
| Resistance Brazing | Electrical current | Small, conductive components | Rapid, localized heat |
Unsure which brazing method is right for your laboratory or production line? The experts at KINTEK can help you navigate the trade-offs between speed, cost, and precision. We specialize in providing the ideal lab equipment and consumables for your specific brazing applications, ensuring optimal results and efficiency.
Contact our team today for a personalized consultation to discuss your project requirements and find the perfect brazing solution.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is vacuum brazing? The Ultimate Guide to High-Purity, Flux-Free Metal Joining
- What are vacuum furnaces used for? Unlock Ultimate Material Purity and Performance
- What are the different types of brazing welding? A Guide to Choosing the Right Heat Source
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock Purity in High-Temperature Processing
- What is the difference between welding and vacuum brazing? Choose the Right Joining Method for Your Project



















