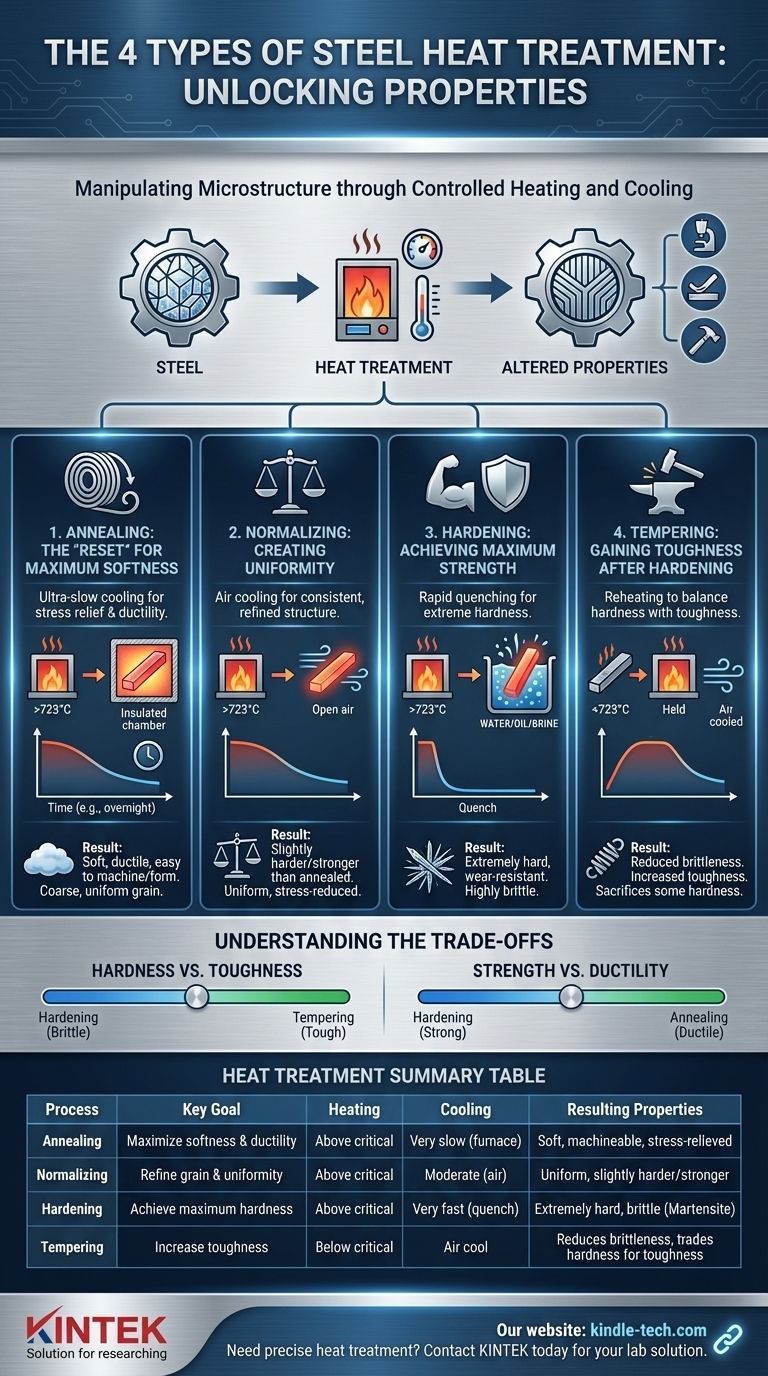
At its core, steel undergoes four primary types of heat treatment: annealing, normalizing, hardening, and tempering. These processes are not interchangeable; each involves a precise cycle of heating and cooling designed to manipulate the steel's internal structure and, as a result, fundamentally change its mechanical properties like hardness, toughness, and ductility.
Heat treatment is the controlled use of temperature to reorganize steel’s internal crystal structure, or "microstructure." By carefully managing the heating temperature, holding time, and cooling rate, you can deliberately trade one property for another—for instance, sacrificing some hardness to gain essential toughness.

Why Heat Treatment is Necessary
To understand the four methods, you must first understand the goal. Heat treating steel is about intentionally changing its internal structure to fit a specific purpose.
The Role of Microstructure
Steel, under a microscope, is a landscape of crystalline grains. The size, shape, and composition of these grains—its microstructure—dictate its physical behavior.
The key is that heat allows this structure to change. When heated above a critical temperature (typically over 723°C or 1333°F), the steel's carbon and iron form a new, malleable structure called austenite. What happens when it cools determines everything.
The Two Levers: Temperature & Cooling Rate
Every heat treatment process manipulates two fundamental variables: the peak temperature the steel is heated to and the speed at which it is cooled.
A slow cooling rate allows the crystals to form in an orderly, low-stress state, resulting in softer steel. A rapid cooling rate, or quenching, freezes the atomic structure in a chaotic, high-stress state, resulting in very hard steel.
The Four Core Heat Treatment Processes
Each of the four major processes uses these principles to achieve a different outcome.
1. Annealing: The "Reset" for Maximum Softness
Annealing is the process of heating steel above its critical temperature, holding it there, and then cooling it as slowly as possible, often by leaving it in the insulated furnace to cool overnight.
This ultra-slow cooling creates a coarse, uniform microstructure that makes the steel extremely soft, ductile, and easy to machine or form. It is the ultimate stress-relief process, effectively hitting the "reset button" on the material's internal structure.
2. Normalizing: Creating Uniformity
Normalizing also involves heating steel above its critical temperature. However, it is then removed from the furnace and cooled in still air.
This air cooling is faster than furnace cooling but much slower than quenching. The result is a steel that is slightly harder and stronger than an annealed steel, but not as soft. The primary goal of normalizing is to refine the grain structure and create a more uniform, consistent material before subsequent hardening.
3. Hardening: Achieving Maximum Strength
Hardening aims to make steel as hard as possible. The steel is heated above its critical temperature to form austenite, then rapidly cooled by plunging it into a liquid like water, oil, or brine.
This severe quench traps the steel's carbon atoms in a highly stressed, needle-like microstructure called martensite. Martensite is extremely hard and wear-resistant, but it is also very brittle, like glass, and can shatter under sharp impact.
4. Tempering: Gaining Toughness After Hardening
A hardened part is often too brittle to be useful. Tempering is a secondary process performed after hardening to reduce that brittleness.
The hardened steel is reheated to a much lower temperature (below the critical point), held for a specific time, and then allowed to cool. This process relieves internal stresses and allows the hard martensite to transform slightly, sacrificing some hardness to gain a significant amount of toughness—the ability to absorb energy and deform without fracturing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a heat treatment process is a deliberate act of balancing competing properties. You can rarely maximize everything at once.
The Hardness vs. Toughness Compromise
This is the most critical trade-off in heat treatment.
- Hardening creates maximum hardness but results in extreme brittleness.
- Tempering directly trades that hardness for toughness. The higher the tempering temperature, the more hardness you lose, but the tougher the part becomes.
Strength vs. Ductility
Strength (resistance to bending) and ductility (ability to be stretched or deformed without breaking) are also opposing properties.
- Annealing produces maximum ductility but minimum strength.
- Hardening produces maximum strength but minimum ductility.
The Critical Role of Carbon
These hardening processes are only effective on steels with sufficient carbon content (typically medium- to high-carbon steels). Low-carbon steels lack the necessary carbon to form the hard martensite structure, so they cannot be significantly hardened through this method.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The correct process depends entirely on the intended function of the final component.
- If your primary focus is maximum machinability or ease of forming: Choose annealing to make the steel as soft and ductile as possible.
- If your primary focus is to refine the grain structure for a consistent starting point: Use normalizing to create a uniform and stress-reduced material before further processing.
- If your primary focus is creating a wear-resistant tool or cutting edge: The two-step process of hardening followed by tempering is required to achieve high hardness with usable toughness.
- If your primary focus is a durable part that must withstand shock or impact: Use hardening followed by a higher-temperature tempering cycle to prioritize toughness over maximum hardness.
Understanding these four processes gives you the power to transform a single piece of steel into a material precisely engineered for its task.
Summary Table:
| Process | Key Goal | Heating | Cooling | Resulting Properties |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annealing | Maximize softness & ductility | Above critical temperature | Very slow (furnace cool) | Soft, easy to machine, stress-relieved |
| Normalizing | Refine grain structure & uniformity | Above critical temperature | Moderate (still air) | Slightly harder/stronger than annealed, uniform |
| Hardening | Achieve maximum hardness & wear resistance | Above critical temperature | Very fast (quench in water/oil) | Extremely hard but brittle (martensite) |
| Tempering | Increase toughness after hardening | Below critical temperature | Air cool | Reduces brittleness, trades hardness for toughness |
Need precise heat treatment for your components? The right process is critical for performance. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs for material testing and preparation. Our expertise ensures your steel achieves the exact hardness, toughness, or ductility required. Contact our experts today to discuss your project and discover the ideal heat treatment solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How to cool a muffle furnace? Ensure Safety and Maximize Equipment Lifespan
- What are the disadvantages of a muffle furnace? Understanding the Trade-offs for Your Lab
- Why is ceramic used in making furnace? Achieve Superior Heat Resistance and Efficiency
- What is the temperature of furnace exhaust? A Key Indicator of Efficiency and Safety
- What is the principle of muffle furnace in laboratory? Master Precise High-Temp Heating



















